如何查看所有的数据库:
Show databases;
如何进入某个数据库:
use xxx;
如何新进数据库:
Create database jx;
如何删除数据库:
Drop database jx;
如何查看所有的表格:
Show tables;
如何创建数据表:
create table teacher(id int,name
varchar(10),address varchar(100),score float,time date);
如何修改表(添加列):
alter table teacher add phone varchar(11);
如何修改表(删除列):
alter table teacher drop score;
如何修改表(修改列):
alter table teacher modify phone int;
如何删除表:
drop table student;
表的约束管理:
非空约束 not null
唯一约束 unique
主键约束 primary key
默认约束 default
示例:
create table student
(id int primary key, name varchar(10) not null, phone varchar(11) default "18502348498",address
varchar(100) unique)
对于数据库中表的操作有4种操作:
增删改查
增加操作:
INSERT INTO employees_cn
(employee_name, employee_address, employee_price) VALUES ("李兰","长沙",14500),("李兰妈妈","株洲",9000);
删除操作:
DELETE FROM employees_cn WHERE employee_name="诸葛亮";
DELETE FROM employees_cn WHERE employee_name="周杰" AND employee_address = "深圳";
修改操作:
UPDATE employees_cn set employee_address = "佛山" , employee_price = 51000 WHERE employee_name = "马超";
查询操作:
SELECT * from employees_cn WHERE employee_price >= 20000;
SELECT 1+2*8+5/2 as result;
去重:
SELECT DISTINCT employees_price FROM employees_cn;
分页:
SELECT * FROM city LIMIT 3,15;
解释:3:是从4开始,不包括3
15:往后数15行。
使用完全限定表名:
SELECT city.population FROM city;
排序:
SELECT*from employees_us ORDER BY employees_price;
升序:asc,可以不写,因为默认升序。
降序:desc
以多个序列排序:
当第一个序列起作用时,那么后面的列不起作用,反之,后面的列才起作用。
SELECT * from employees_us ORDER BY employees_price,employees_name;
Where的使用:
SELECT * from employees_cn where employees_price BETWEEN 10000 and 20000;
SELECT * from employees_cn where
employees_price>=10000and employees_price<=20000;
SELECT * from employees_cn where
employees_price >= 10000 and employees_price <= 20000
ORDER BY employees_price;
SELECT * from employees_cn where
Employees_name is null;
组合where使用:
And:
Select * form employees_cn where employees_name=”周杰” and employees_address=”抚州”;
Or:
Select * form employees_cn where employees_name=”周杰” or employees_address=”抚州”;
In:
Select * form employees_cn where employees_id=18 or employees_id=21 or employees_id=23;
等于
Select * form employees_cn where employees_id in(18,21,23);
Not in:
Select * form employees_cn where employees_address not in(“抚州”,”株洲”,”上海”);
Like的使用
当like单独使用的时候,它相当于=。
Select * from employees_us where employee_name like “jerry”;
通配符:
%:表示任意多个字符
Select * from employees_us where employee_name like “%jerry%”;
_:表示任意一个字符
Select * from employees_cn where employee_name like “张_”;
转义字符:
Select * from employees_cn where employee_name like “jerry/_%”escape”/”;
拼接字段
SELECT concat(employee_name,"---",employee_address) as "结果" FROM `employees_cn`;
计算字段
SELECT sid*score FROM `score`;
函数的使用
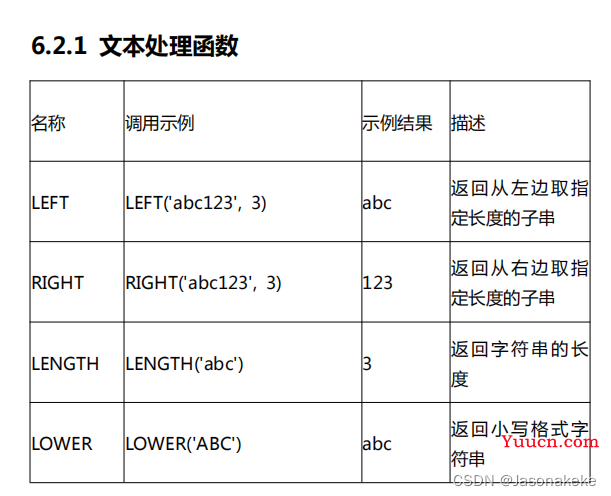
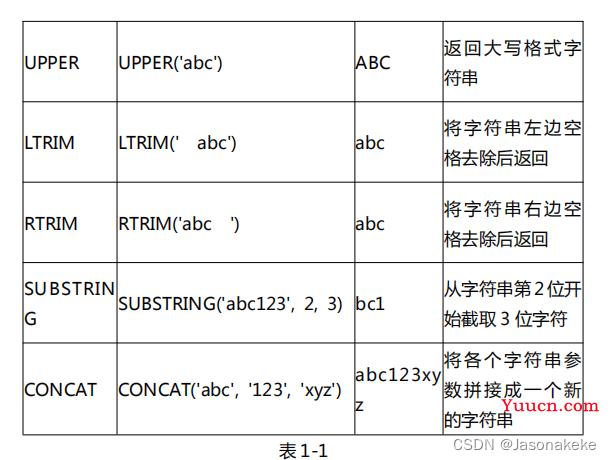
SELECT concat(employee_name,"---",employee_address) as "结果" FROM `employees_cn`
SELECT sid*score from score;
select LEFT("你好,你吃饭了吗?",4)
select RIGHT("你好,你吃饭了吗?",4)
select left(employee_name,2) from employees_cn where employee_id = 21
select LENGTH("你好")
select length(employee_name) from employees_cn where employee_id = 21
select SUBSTRING("你好,你吃饭了吗???",2)
select SUBSTRING("你好,你吃饭了吗???",2,4)
select SUBSTRING(employee_name,2) from employees_cn where employee_id = 21
日期处理函数
获取当前日期
SELECT NOW();
SELECT SYSDATE();
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP();
SELECT CURRENT_DATE;
SELECT CURRENT_TIME;
日期格式化:
select DATE_FORMAT('2008-08-09 22:23:01','%y-%m-%d %h:%i:%s');
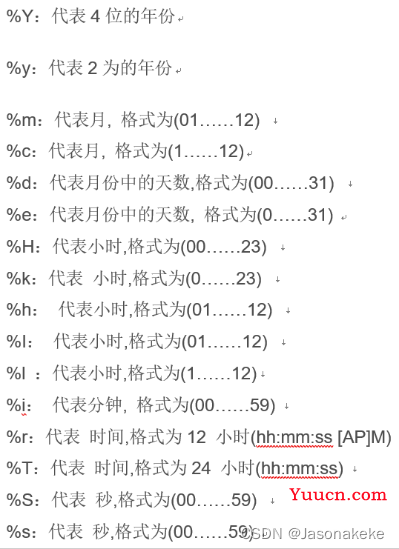
字符串变日期:
select STR_TO_DATE('08/09/2008','%m/%d/%y');
时间变秒
select TIME_TO_SEC('01:00:05');
天数变日期
SELECT MAKEDATE(2019,300);
SELECT DAYOFYEAR("2019-10-23");
数值函数:
四舍五入
select ROUND(48.3847)
select ROUND(48.3847,1)
select MOD(CEIL(ROUND(employee_price)), 10) from employees_cn
向上取整
select CEIL(48.2)
向下取整
select FLOOR(48.9)
取余
SELECT MOD(18,3)
开方
SELECT SQRT(9)
指数
select POW(2,10)
绝对值
select ABS(-9)
平均值
Select avg(score) from score
计数
Select count(*) from score
Select count(distinct name) from score
最值
Select max(score), name from score
Select min(score), name from score
求和
Select sum(score) from score
分组查询
SELECT round(avg(score)),class from score GROUP BY class;
过滤分组
SELECT avg(score) as a,class from score GROUP BY class HAVING a < 80;
SELECT score from score where score < 80
where作用于表之后,having作用于组之后
select子句顺序
from, on, join, where, group by, having, select, distinct, order by, limit
select round(avg(score),1) as a, class from score where score > 70 GROUP BY class HAVING a >= 85 ORDER BY a LIMIT 0,2;
子查询:
select * from score where score = (select min(score) from score)
也就等于下面两个语句之和
select min(score) from score;
select * from score where score = 60;
连接查询
适用于多表操作
外连接:包括左连接、右连接
SELECT a.*, b.* from student_info a left join student_score b on a.student_id = b.student_id
SELECT a.*, b.* from student_info a right join student_score b on a.student_id = b.student_id
笛卡尔积连接:包括内连接、自然连接、交叉连接、自连接(原理: 笛卡尔积)
select a.*, b.* from student_info a inner join student_score b
select a.*, b.* from student_info a inner join student_score b on a.student_id = b.student_id
SELECT A.*, B.* from student_info A cross join student_score B
SELECT A.*, B.* from student_info A cross join student_score B on A.student_id = B.student_id
SELECT A.*, B.* from student_info A natural join student_score B
select B.* from score as A join score as B on A.score < B.score and A.name = "王兰"
组合查询
select vend_id, prod_id, prod_price from products where prod_price < 5 union select vend_id, prod_id, prod_price from products where vend_id in (1001,1002)
select vend_id, prod_id, prod_price from products where prod_price < 5 union all select vend_id, prod_id, prod_price from products where vend_id in (1001,1002)
select vend_id, prod_id, prod_price from products where prod_price < 5 union all select vend_id, prod_id, prod_price from products where vend_id in (1001,1002) order by prod_price
union的结果去重,而union all的结果不去重
视图
如何创建视图 create view abc as select * from employees_cn where employee_id BETWEEN 14 and 20
视图的操作和表的操作相同
索引
作用:提高检索速度
如何创建索引 create index aaa on employees_cn(employee_name, employee_price)
如何使用索引
事务
- 概念
- 特征 原子性 一致性 隔离性 持续性
start TRANSACTION;
INSERT into score (name, class, score, sex, phone) VALUES ("智慧化", "软件1" ,'43', "女", '1213');
SAVEPOINT p;
INSERT into score (class, score, sex, phone) VALUES ("张晓霞", "软件1", "23", "女", '12133');
ROLLBACK to SAVEPOINT p;
commit;
常量
变量
用户变量 @后为变量
set @name = "李兰";
select * from employees_cn where employee_name = @name;
select @xxx := (@xxx := 8) + 2;
局部变量
作用于存储过程
DECLARE abc int DEFAULT 0;
系统变量
Select CURRENT_TIME
Select CURRENT_USER
If控制语句
Case控制语句
循环控制语句
自定义函数
存储过程
触发器