一、前言
使用vuex可以实现数据的共享。
二、安装
vscode中新建终端安装vuex。由于vue2不能使用vuex4的版本,所以在安装时需要指定版本3
npm i vuex@3三、vuex工作流
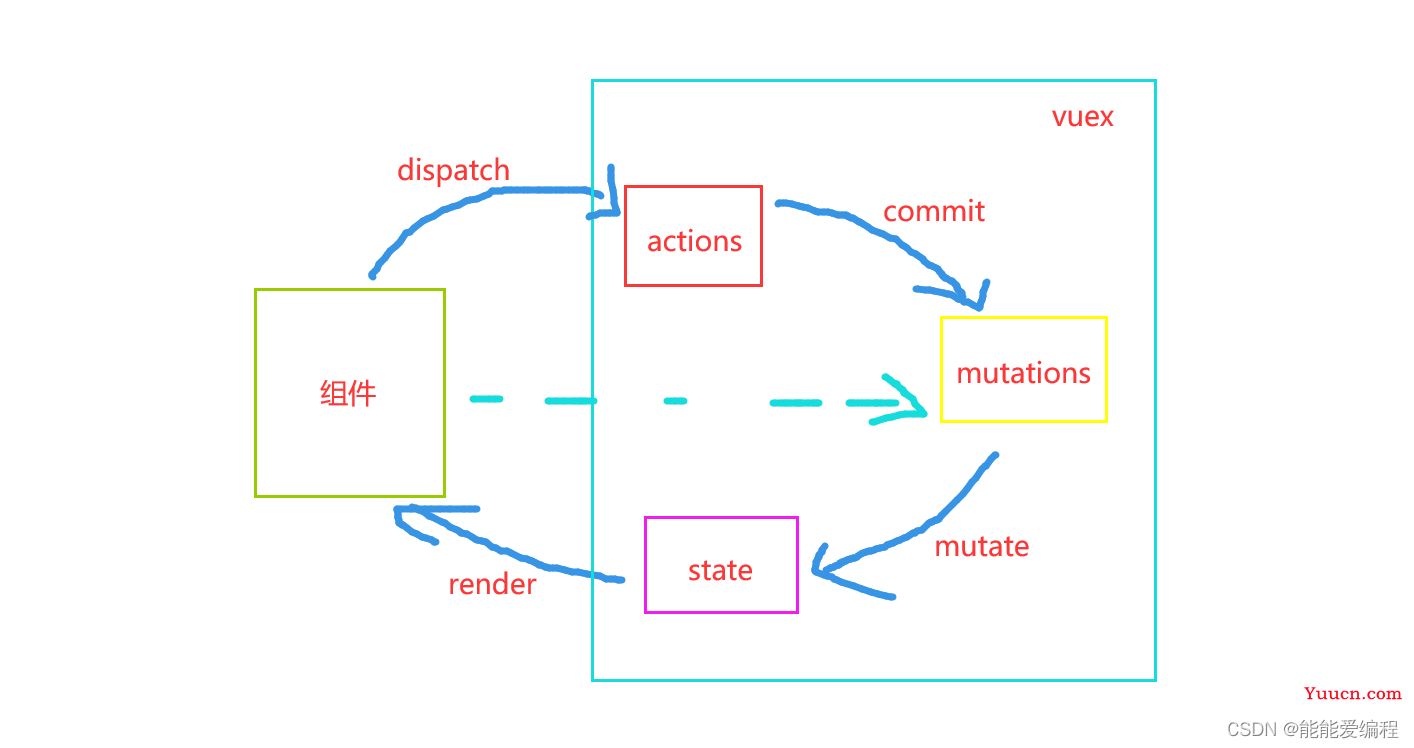
vuex核心包括actions、mutations、state。
①state用来存储数据;
②actions用来响应组件的事件,也可以对数据进行加工,或者进行后端请求,也就是说组件中调用dispatch方法,可以触发actions中的方法;
③mutations用来操作state,actions中调用commit方法来调用mutations。
④其他:当不需要对数据进行额外加工的时候,可以直接在组件中调用commit方法触发mutations中的方法
四、配置
步骤一:新建文件夹store,文件夹下新建index.js文件
步骤二:index.js中完成配置:还没有配置数据和事件
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 用来存储数据
const state = {
}
// 响应组件中的事件
const actions = {
}
// 操作数据
const mutations = {
}
// 用来将state数据进行加工
const getters = {
}
// 新建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
actions,
mutations,
getters
})
步骤三:main.js中引入
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store/index';
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')
五、使用
5.1、常规写法
1、state
组件中使用$store.state.xxx获取值,例如:
<li v-for="p in $store.state.person" :key="p.id">
姓名:{{ p.personName }} 年龄:{{ p.age }}
<button @click="deletePerson(p.id)">删除</button>
</li>
vuex的index.js:
const state = {
person: [
{ id: nanoid(), personName: "张三", age: 18 },
{ id: nanoid(), personName: "张4", age: 28 },
{ id: nanoid(), personName: "张5", age: 38 },
]
}2、getter
组件中使用$store.getters.xxx获取getters中的返回值
<span> 学生年龄总和:{{ $store.getters.getAllPersonAge }} </span>index.js:
// 用来将state数据进行加工:类似于computed
const getters = {
getAllPersonAge(state) {
var sumAge = 0;
state.person.forEach(element => {
sumAge += element.age
});
return sumAge
}
}3、actions
组件中使用this.$store.dispatch("aaa", xxx)触发actions中的aaa方法,参数为xxx
<input type="text" v-model="newPerson" />
<button @click="addPerson">添加</button>
addPerson() {
if (this.newPerson == "") {
alert("请输入姓名");
return;
}
this.$store.dispatch("addPerson", this.newPerson);
this.newPerson=""
},index.js
// 响应组件中的事件
const actions = {
//添加人员
addPerson(content, value) {
console.log(value)
const person = {
id: nanoid(),
personName: value,
age: 18//暂时写死
}
content.commit("addPerson", person)
}
}4、mutations
组件中:
<button @click="deletePerson(p.id)">删除</button>
deletePerson(id) {
this.$store.commit("deletePerson", id);
},index.js
const mutations = {
addPerson(_, value) {
this.state.person.unshift(value)
},
deletePerson(_, id) {
const newArr = this.state.person.filter(p => {
return p.id != id
})
this.state.person = newArr
}
}5.2 四个map写法
上述写法都需要手动写this.$store.xxx比较麻烦,可以在组件中引入vuex的四个map,简化操作
组件中引入:
import { mapState, mapActions, mapGetters, mapMutations } from "vuex";使用:
computed: {
...mapState(["person"]),
...mapGetters(["getAllPersonAge"]),
},
methods: {
...mapActions({
addPerson1: "addPerson", //第一个为本地方法名,第二个参数为actions中的方法名
}),
...mapMutations(["deletePerson"]),//当本地和index.js中的方法名一致时,可以简化成数组写法
},使用:直接使用上面中定义的参数名
<input type="text" v-model="newPerson" />
<button @click="addPerson1(newPerson)">添加</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="p in person" :key="p.id">
姓名:{{ p.personName }} 年龄:{{ p.age }}
<button @click="deletePerson(p.id)">删除</button>
</li>
</ul>
<span> 学生年龄总和:{{ getAllPersonAge }} </span>五、其他
以上就是vuex的所有介绍,我们一起进步。