1、参数传递
1.1 类名作为形参和返回值
- 类名——方法形参
方法的形参是类名,需要的是该类的对象;实际传递的是该对象的地址值
- 类名——返回值
方法的返回值是类名,返回的是该类的对象;实际传递的是该对象的地址值
- 示例代码
public class Cat {
public void eat(){
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
}
public class CatOperator {
//类名作为方法的形参
public void useCat(Cat c){ //Cat c = new Cat();
c.eat();
}
//类名作为方法的返回值
public Cat getCat(){
Cat c = new Cat();
return c;
}
}
public class CatDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建操作类对象,并调用方法
CatOperator co = new CatOperator();
Cat c = new Cat();
co.useCat(c);
Cat c2 = co.getCat();
c2.eat();
}
}1.2 抽象类作为形参和返回值(理解)
- 抽象类作为形参和返回值
- 方法的形参是抽象类,其实需要的是该抽象类的子类对象
- 方法的返回值是抽象类,其实返回的是该抽象类的子类对象
- 示例代码
public class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
}
public abstract class Animal {
public abstract void eat();
}
public class AnimalOperator {
public void userAnimal(Animal a){
a.eat();
}
public Animal getAnimal(){
Animal a = new Cat();
return a;
}
}
public class AnimalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnimalOperator ao = new AnimalOperator();
Animal a = new Cat();
ao.userAnimal(a);
Animal ao2 = ao.getAnimal();
ao2.eat();
}
}1.3 接口作为形参和返回值(理解)
- 接口作为形参和返回值
- 方法的形参是接口,其实需要的是该接口的实现类对象
- 方法的返回值是形参,其实返回的是该接口的实现类对象
- 示例代码
public interface Jumpping {
void jump();
}
public class Cat implements Jumpping{
@Override
public void jump() {
System.out.println("猫可以跳高");
}
}
public class JumppingOperator {
public void useJumpping(Jumpping j){//Jumpping j = new Cat();
j.jump();
}
public Jumpping getJumpping(){
Jumpping j = new Cat();
return j;
}
}
public class JumppingDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JumppingOperator jo = new JumppingOperator();
Jumpping j = new Cat();
jo.useJumpping(j);
Jumpping j2 = jo.getJumpping();
j2.jump();
}
}2、内部类
2.1 内部类的基本使用(理解)
- 内部类概念
- 在一个类中定义一个类。举例:在一个类A的内部定义一个类B,类B就被成为内部类
- 内部类定义格式
- 格式:
class 外部类名{
修饰符 class 内部类名{
}
}-
-
- 举例
-
public class Outer {
public class Inner{
}
}- 内部类的访问特点
- 内部类可以直接访问外部类的成员,包括私有
- 外部类要访问内部类的成员,必须创建对象
- 示例代码
public class Outer {
private int num = 10;
public class Inner{
public void show(){
System.out.println(num);
}
}
public void method(){
Inner i = new Inner();
i.show();
}
}2.2 成员内部类(理解)
- 成员内部类的定义位置
- 在类中方法外,跟成员变量是一个位置
- 外界拆功能键成员内部类格式
- 格式:外部类名.内部类名 对象名 = 外部类对象.内部类对象;
- 举例:Outer.Inner oi = new Outer().new Inner();
- 示例代码
public class Outer {
private int num =10;
private class Inner {
public void show(){
System.out.println(num);
}
}
public void method(){
Inner i = new Inner();
i.show();
}
}
public class OuterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer o = new Outer();
o.method();
}
}2.3 局部内部类(理解)
- 定义位置
- 定义在方法中
- 使用方式
- 局部内部类,外界是无法直接使用,需要在方法内部创建对象并使用
- 该类可以直接访问外部类的成员,也可以访问方法内的局部变量
public class Outer {
private int num = 10;
public void method(){
int num2 = 20;
class Inner{
public void show(){
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println(num2);
}
}
Inner i = new Inner();
i.show();
}
}
public class OuterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer o = new Outer();
o.method();
}
}2.4 匿名内部类(应用)
- 匿名内部类的前提
- 存在一个类或接口,这里的类可以是具体类也可以是抽象类
- 匿名内部类的格式
- 格式:new 类名(){重写方式} /new 接口名 () {重写方法}
- 举例
new Inter(){
@Override
public void method(){}
}- 匿名内部类的本质
- 本质:是一个继承了该类或者实现类该接口的子类匿名对象
- 匿名内部类的细节
- 匿名内部类可以通过多态的形式接受
Inter i = new Inter(){
@Override
public void method(){
}
}- 匿名内部类直接调用方法
public interface Inner {
public void method();
}
public class InnerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Inner(){
@Override
public void method(){
System.out.println("我是匿名内部类");
}
}.method();
}
}2.4 匿名内部类在开发中的使用(应用)
- 使用
- 当发现某个方法需要,接口或抽象类的子类对象,我们就可以传递一个匿名内部类过去,来简化传统代码
- 示例代码
public interface Jumpping {
void jump();
}
public class Cat implements Jumpping{
@Override
public void jump() {
System.out.println("猫可以跳高了");
}
}
public class Dog implements Jumpping{
@Override
public void jump() {
System.out.println("狗可以跳高了");
}
}
public class JumppingOperator {
public void method(Jumpping j){
j.jump();
}
}
public class JumppingDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建接口操作类对象调用method方法
JumppingOperator jo = new JumppingOperator();
//方式一:传统方式
//操作猫的行为
Jumpping j1 = new Cat();
jo.method(j1);
//操作狗的行为
Jumpping j2= new Dog();
jo.method(j2);
//方式二:匿名内部类的方式
//操作猫的行为
jo.method(new Jumpping() {
@Override
public void jump() {
System.out.println("猫可以跳高了");
}
});
//操作狗的行为
jo.method(new Jumpping() {
@Override
public void jump() {
System.out.println("狗可以跳高了");
}
});
}
}3、常用API
3.1 Math(应用)
- 概述:Math包含执行基本数字的方法
- 方法的调用方式:Math类中无构造方法,但内部的方法都静态的,则可以通过 类名进行调用
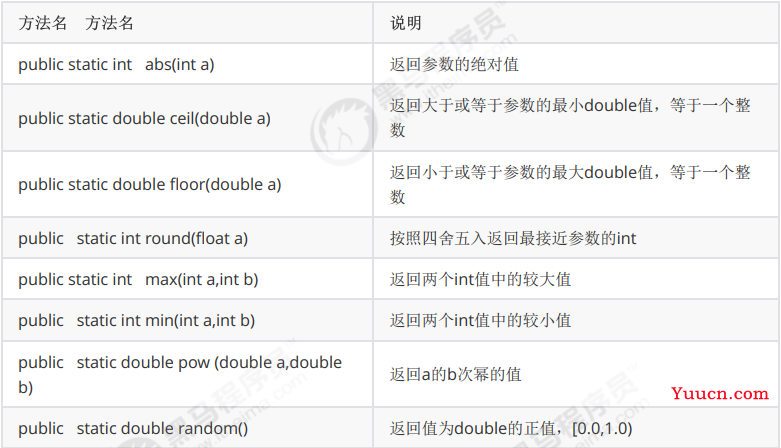
- 常用方法:
3.2 System(应用)
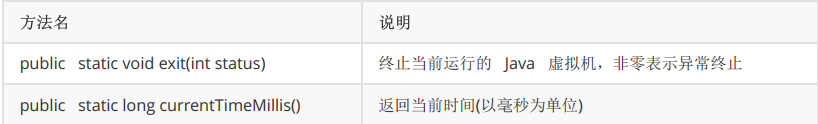
- 常用方法
- 示例代码
- 需求:在看控制台输出1-10000,计算这段代码执行了多少毫秒
public class SystemDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:在控制台输出1-10000,计算这段代码执行了多少毫秒
//获取开始的时间节点
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("这段代码执行耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
}3.3 Object类的toString方法(应用)
- 概述:
- Object是类层次结构的跟,所有类都直接或间接的继承自Object类。
- 重写toString()
- Alt+Insert选择toString()
- toString()的作用
- 以良好的格式,更方便的展示对象中的属性值
- 示例代码:
public class Student extends Object{
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(){
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public class ObjectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.setName("林青霞");
s.setAge(30);
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
}- 运行结果:
Student{name='林青霞', age=30}
Student{name='林青霞', age=30}3.4 Object类的equals方法(应用)
- equals方法的作用
- 用于对象之间的比较,返回true和false的结果
- 举例:s1.equals(s2); s1和s2是两个对象
- 重写equals方法的场景
- 不希望比较对象的地址值,想要结合对象属性进行比较的时候。
- 重写equals方法的方式
- 1.alt + insert选择equals()and hashCode(), InteliJ Default
- 示例代码
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Student)) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
if (getAge() != student.getAge()) return false;
return getName() != null ? getName().equals(student.getName()) : student.getName() == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = getName() != null ? getName().hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + getAge();
return result;
}
}
public class ObjectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("林青霞");
s1.setAge(30);
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.setName("林青霞");
s2.setAge(30);
//需求:比较两个对象的内容是否相同
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
}
}3.5 冒泡排序原理(理解)
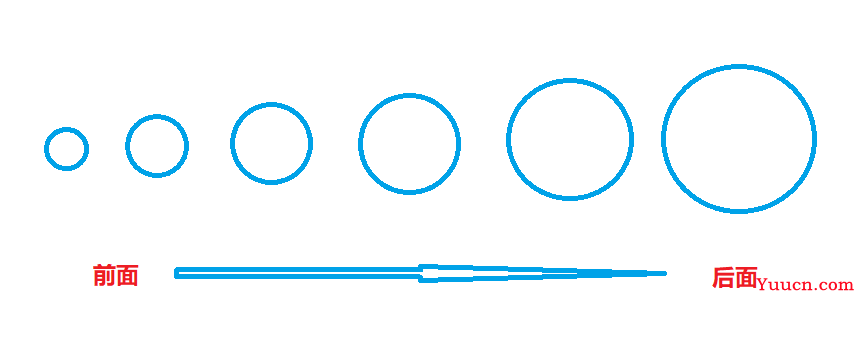
- 概述: 一种排序的方式,对要进行排序的数据中相邻的数据进行两两比较,将较大的数据放在后面,依次对所
有的数据进行操作,直至所有数据按要求完成排序 - 如果有n个数据进行排序,总共需要n-1轮排序
- 每一次比较完毕,下一次的比较就会少一个数据参与
3.6 冒泡排序的实现(理解)
- 代码实现
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个数组
int[] arr = {24, 69, 80, 57, 13};
System.out.println("排序前:"+ArrayDemo.arrayToString(arr));
//排序的轮数
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
//每轮排序次数
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length-1-i; j++) {
if (arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("排序后:"+ArrayDemo.arrayToString(arr));
}
public static String arrayToString(int[] arr){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (i == arr.length-1){
sb.append(arr[i]);
}else {
sb.append(arr[i]).append(",");
}
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}3.7 Array(应用)
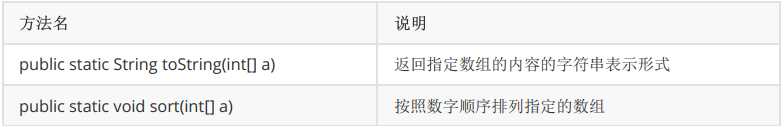
- Arrays的常用方法
- 工具类设计思想
1、构造方法用private修饰
2、成员用public static修饰
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个数组
int[] arr = {26,69,80,57,13};
System.out.println("排序前:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
//使用sort方法进行排序
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println("排序后:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}