本文已收录至Github,推荐阅读 ? Java随想录
微信公众号:Java随想录
CSDN: 码农BookSea
烈火试真金,逆境试强者。——塞内加
- 什么是ThreadLocal
-
ThreadLocal 原理
- set()方法
- get()方法
- remove()方法
- ThreadLocal 的Hash算法
- ThreadLocal 1.7和1.8的区别
-
ThreadLocal 的问题
-
ThreadLocal 内存泄露问题
- 为什么使用弱引用而不是强引用?
- ThreadLocal 父子线程继承
-
ThreadLocal 内存泄露问题
什么是ThreadLocal
首先看下ThreadLocal的使用示例:
public class ThreadLocalTest {
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
threadLocal.set("本地变量1");
print("thread1");
System.out.println("线程1的本地变量的值为:"+threadLocal.get());
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
threadLocal.set("本地变量2");
print("thread2");
System.out.println("线程2的本地变量的值为:"+threadLocal.get());
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
public static void print(String s){
System.out.println(s+":"+threadLocal.get());
}
执行结果如下

我们从 Thread 类讲起,在 Thread 类中有维护两个 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap 对象,分别是:threadLocals 和inheritableThreadLocals。
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
/*
* InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is
* maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class.
*/
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
初始它们都为 null,只有在调用 ThreadLocal 类的 set 或 get 时才创建它们。ThreadLocalMap可以理解为线程私有的HashMap。
ThreadLoalMap是ThreadLocal中的一个静态内部类,类似HashMap的数据结构,但并没有实现Map接口。
ThreadLoalMap中初始化了一个大小16的Entry数组,Entry对象用来保存每一个key-value键值对。key是ThreadLocal对象。
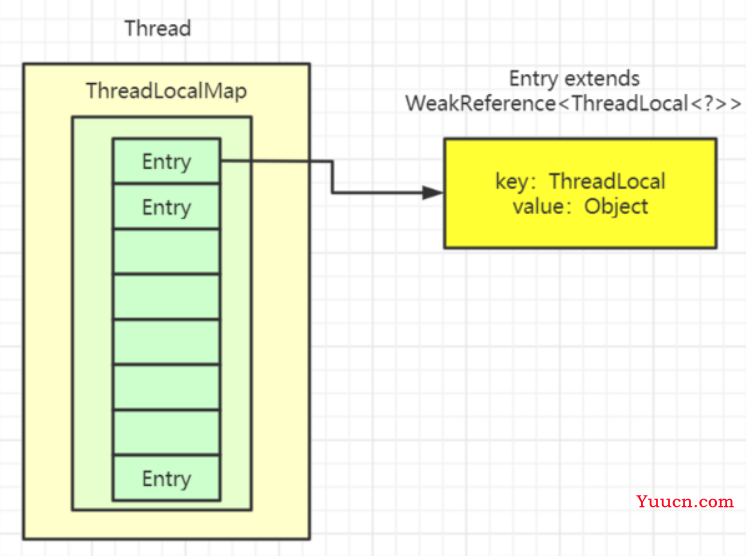
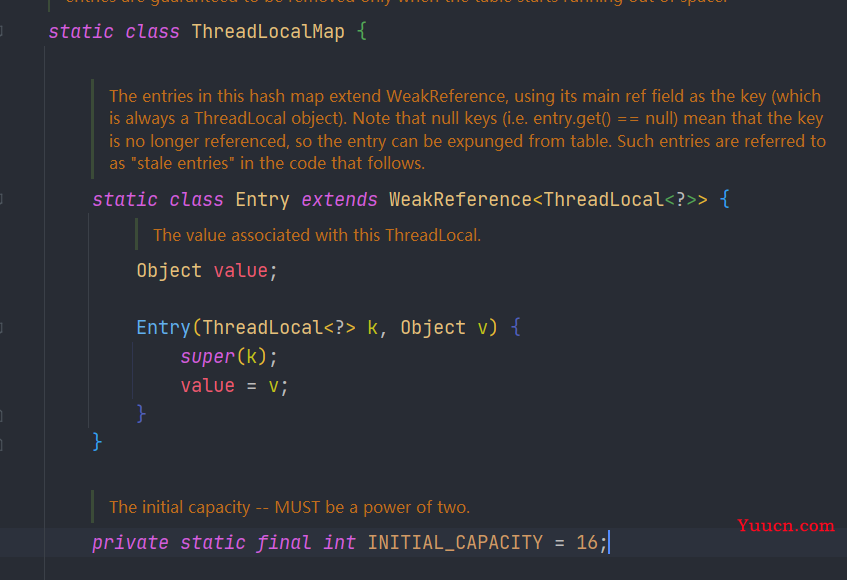
Entry用来保存数据 ,而且还是继承的弱引用。在Entry内部使用ThreadLocal作为key,使用我们设置的value作为value。
ThreadLocal 原理
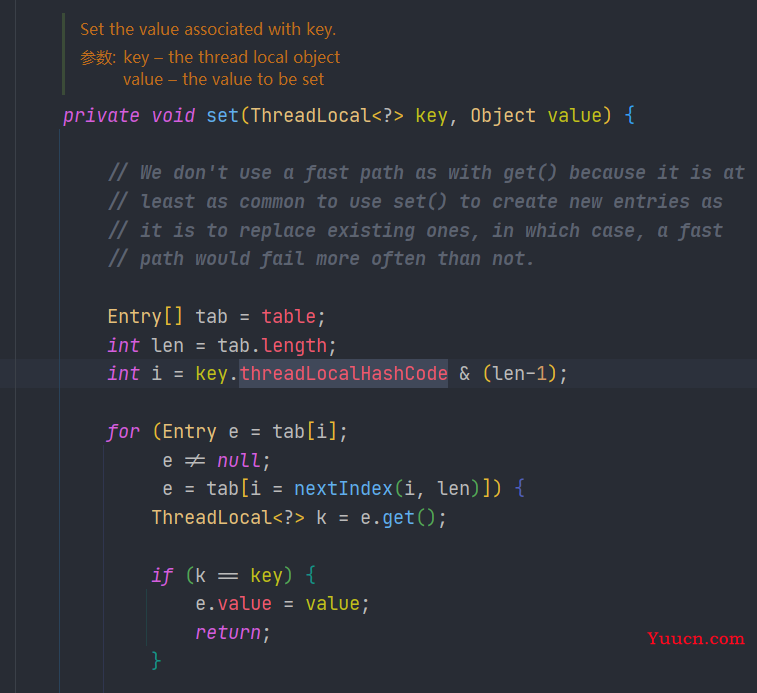
set()方法
当我们调用 ThreadLocal 的 set() 方法时实际是调用了当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap 的 set() 方法。ThreadLocal 的 set() 方法中,会进一步调用Thread.currentThread() 获得当前线程对象 ,然后获取到当前线程对象的ThreadLocal,判断是不是为空,为空就先调用creadMap()创建再set(value)创建 ThreadLocalMap 对象并添加变量。不为空就直接set(value) 。
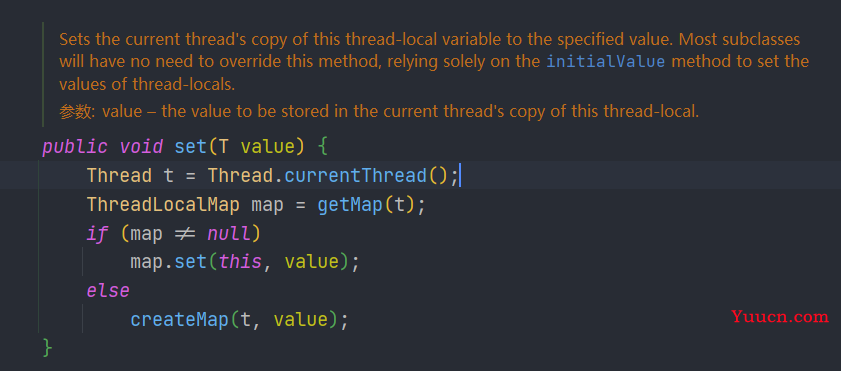

这种保证线程安全的方式称为线程封闭。线程只能看到自己的ThreadLocal变量。线程之间是互相隔离的。
get()方法
其中get()方法用来获取与当前线程关联的ThreadLocal的值,如果当前线程没有该ThreadLocal的值,则调用initialValue函数获取初始值返回,所以一般我们使用时需要继承该函数,给出初始值(不重写的话默认返回Null)。
主要有以下几步:
- 获取当前的Thread对象,通过getMap获取Thread内的ThreadLocalMap
- 如果map已经存在,以当前的ThreadLocal为键,获取Entry对象,并从从Entry中取出值
- 否则,调用setInitialValue进行初始化。
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
我们可以重写initialValue(),设置初始值。
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Integer>(){
@Override
protected Integer initialValue() {
return Integer.valueOf(0);
}
}
remove()方法
最后一个需要探究的就是remove方法,它用于在map中移除一个不用的Entry。也是先计算出hash值,若是第一次没有命中,就循环直到null,在此过程中也会调用expungeStaleEntry清除空key节点。代码如下:
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
/**
* Remove the entry for key.
*/
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
实际上 ThreadLocalMap 中使用的 key 为 ThreadLocal 的弱引用,弱引用的特点是,如果这个对象只存在弱引用,那么在下一次垃圾回收的时候必然会被清理掉。
所以如果 ThreadLocal 没有被外部强引用的情况下,在垃圾回收的时候会被清理掉的,这样一来 ThreadLocalMap中使用这个 ThreadLocal 的 key 也会被清理掉。但是,value 是强引用,不会被清理,这样一来就会出现 key 为 null 的 value。出现内存泄漏的问题。
在执行 ThreadLocal 的 set、remove、rehash 等方法时,它都会扫描 key 为 null 的 Entry,如果发现某个 Entry 的 key 为 null,则代表它所对应的 value 也没有作用了,所以它就会把对应的 value 置为 null,这样,value 对象就可以被正常回收了。但是假设 ThreadLocal 已经不被使用了,那么实际上 set、remove、rehash 方法也不会被调用,与此同时,如果这个线程又一直存活、不终止的话,那么刚才的那个调用链就一直存在,也就导致了 value 的内存泄漏。
ThreadLocal 的Hash算法
ThreadLocalMap类似HashMap,它有自己的Hash算法。
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
public final int getAndAdd(int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta);
}
HASH_INCREMENT这个数字被称为斐波那契数 也叫 黄金分割数,带来的好处就是 hash 分布非常均匀。
每当创建一个ThreadLocal对象,这个ThreadLocal.nextHashCode 这个值就会增长 0x61c88647 。
讲到Hash就会涉及到Hash冲突,跟HashMap通过链地址法不同的是,ThreadLocal是通过线性探测法/开放地址法来解决hash冲突。
ThreadLocal 1.7和1.8的区别
ThreadLocal 1.7版本的时候,entry对象的key是Thread。
1.8版本entry的key是ThreadLocal。
1.8版本的好处 :当Thread销毁的时候,ThreadLocalMap也会随之销毁,减少内存的使用。因为ThreadLocalMap是在Thread里面的,所以只要Thread消失了,那ThreadLocalMap就不复存在了。
ThreadLocal 的问题
ThreadLocal 内存泄露问题
在 ThreadLocalMap 中的 Entry 的 key 是对 ThreadLocal 的 WeakReference 弱引用,而 value 是强引用。当 ThreadLocalMap 的某 ThreadLocal 对象只被弱引用,GC 发生时该对象会被清理,此时 key 为 null,但 value 为强引用不会被清理。此时 value 将访问不到也不被清理掉就可能会导致内存泄漏。
注意构造函数里的第一行代码super(k),这意味着ThreadLocal对象是一个弱引用
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
因此我们使用完 ThreadLocal 后最好手动调用 remove() 方法。但其实在 ThreadLocalMap 的实现中以及考虑到这种情况,因此在调用 set()、get()、remove() 方法时,会清理 key 为 null 的记录。
为什么使用弱引用而不是强引用?
为什么采用了弱引用的实现而不是强引用呢?

注释上有这么一段话:为了协助处理数据比较大并且生命周期比较长的场景,hash table的条目使用了WeakReference作为key。
所以,弱引用反而是为了解决内存存储问题而专门使用的。
实际上,采用弱引用反而多了一层保障,ThreadLocal被清理后key为null,对应的value在下一次ThreadLocalMap调用set、get,就算忘记调用 remove 方法,弱引用比强引用可以多一层保障。
所以,内存泄露的根本原因是是否手动清除操作,而不是弱引用。
ThreadLocal 父子线程继承
异步场景下无法给子线程共享父线程的线程副本数据,可以通过 InheritableThreadLocal 类解决这个问题。
它的原理就是子线程是通过在父线程中调用 new Thread() 创建的,在 Thread 的构造方法中调用了 Thread的init 方法,在 init 方法中父线程数据会复制到子线程(ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);)。
代码示例:
public class InheritableThreadLocalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
ThreadLocal<String> inheritableThreadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set("父类数据:threadLocal");
inheritableThreadLocal.set("父类数据:inheritableThreadLocal");
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("子线程获取父类threadLocal数据:" + threadLocal.get());
System.out.println("子线程获取父类inheritableThreadLocal数据:" +inheritableThreadLocal.get());
}
}).start();
}
}
但是我们做异步处理都是使用线程池,线程池会复用线程会导致问题出现。我们可以使用阿里巴巴的TTL解决这个问题。
https://github.com/alibaba/transmittable-thread-local
如果本篇博客有任何错误和建议,欢迎给我留言指正。文章持续更新,可以关注公众号第一时间阅读。
