Java集合 Map 集合 与 操作集合的工具类: Collections 的详细说明

每博一文案
别把人生,输给心情
师父说:心情不是人生的全部,却能左右人生的全部。
你有没有体会到,当你心情好的时候,生活仿佛阳光灿烂,顺风顺水,
当你心情不好的时候,似乎周围的一切都糟糕透了。
有时候,我们不是输给了别人,而是败给了坏心情的自己。
人活着就像一个陀螺,为了生活不停的转动,永远都有忙不完的事。
有时候又像沙漠中的骆驼,背负着重担努力地前行,却不知道哪里才是终点。
先现在情绪低落,只是因为陷进了自我纠缠的陷阱,等到熬过了这段苦难,
你会发现你所纠结的东西,真的只是无关痛痒的小事。
生活就像天气,不会总是晴天,也不会一直阴雨,喜欢和讨厌是次要的,关键是你要学会调整自己。
心静了,才能听见自己的心声,心清了,才能照见万物的本性。
假如任由坏情绪累积和蔓延,很多事只会变得越来越糟糕,
既然做不到让所有人都满意,为何不努力让自己开心?
生活是你自己的,喜怒悲欢都由你自己决定,记得别被坏情绪束缚住,
不要让你的人生,输给了心情。
—————— 一禅心灵庙语
-
Java集合 Map 集合 与 操作集合的工具类: Collections 的详细说明
- 每博一文案
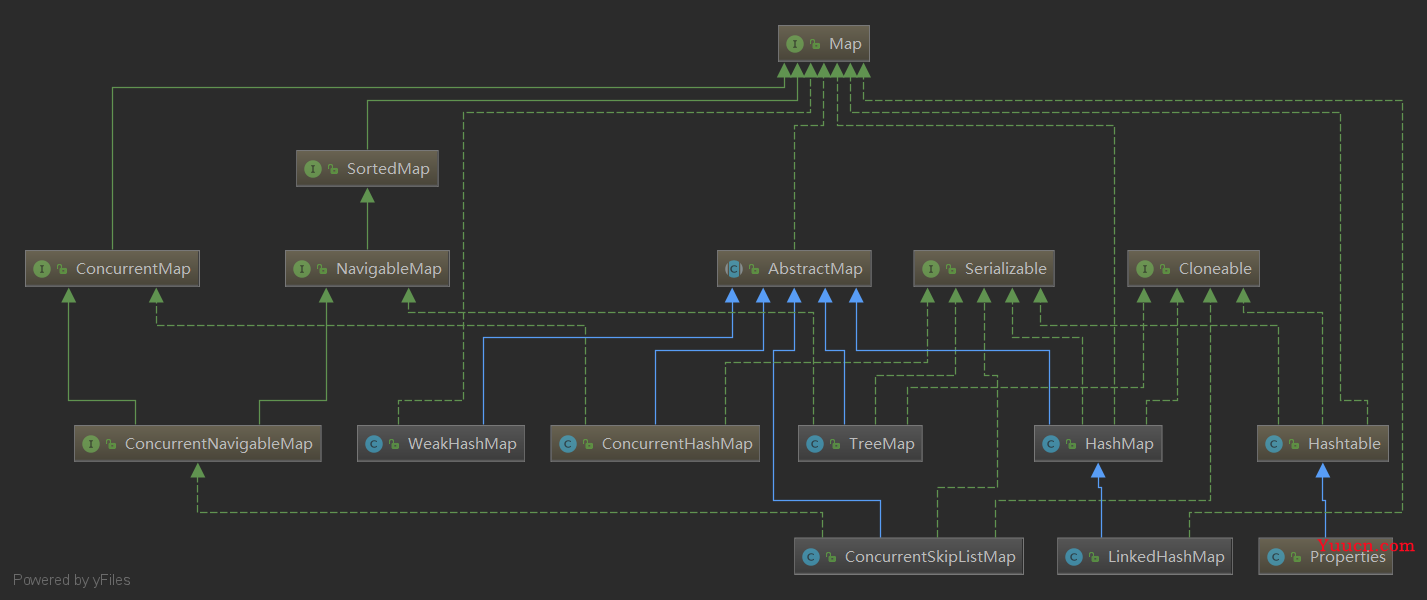
- 1. Map接口概述
- 2. Map接口:常用方法
-
3. Map实现类之一:HashMap
- 3.1 HashMap的存储结构
- 3.2 HashMap源码中的重要常量
-
3.3 HashMap的存储结构:JDK 1.8之前 / JDK 1.8之后
- 3.3.1 JDk 1.8 之前
- 3.3.2 JDk 1.8 及之后
- 3.3.3 JDK8 HashMap 集合添加元素的过程
- 3.3.4 JDK8 HashMap 进行 "扩容"和 "树形化"
- 3.3.5 总结:JDK1.8 相较于之前的变化:
- 4. Map实现类之二:LinkedHashMap
- 5. Map实现类之三:TreeMap
- 6. Map实现类之四:Hashtable
- 7. Map实现类之五:Properties
- 8. Map 接口下的集合遍历方式
-
9. Collections工具类
- 9.1 Collections常用方法
- 10. 总结:
- 11. 最后:
1. Map接口概述
-
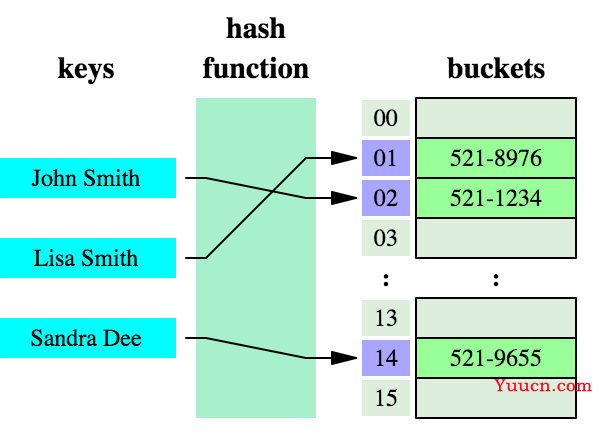
Map 接口与 Collection 并列存在的,用于保存具有映射关系的数据:key-value 被称为 键值对 。
-
Java集合可分为 Collection 和 Map 两种体系。
-
Collection 接口:单例数据,定义了存取一组对象的方法的集合。
- List : 元素有序,可重复的集合。
- Set :元素无序,不可重复的集合。
- Map 接口:双列数据,保存具有映射关系”key-value对“ 的集合。
-
Collection 接口:单例数据,定义了存取一组对象的方法的集合。
-
Map 中的 key 和 value 都可以是任何引用类型的数据。
- key 和 value 都是引用数据类型,都是存储对象的内存地址的。不是基本数据类型。
- 其中 key 起到主导地位,value 是 key 的一个附属品。
-
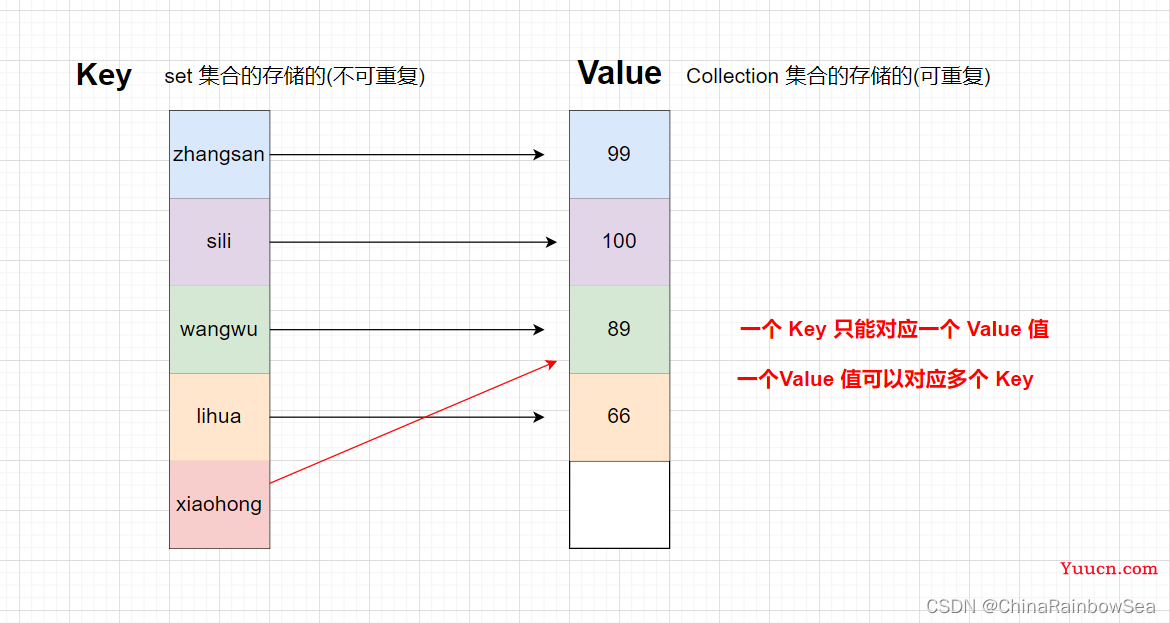
Map 中的 key 用 Set 集合存储的,不允许重复。即同一个 Map 对象所对应的类,必须重写hashCode() 和 equals() 方法。但是其中的 value 值是可以存储重复的数据的。而 value 值则是被 Collection 接口集合存储的。
-
常用 String 类作为 Map 的 ”键“。
-
key 和 value 之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的 key 总能找到唯一的,确定的 value 。
-
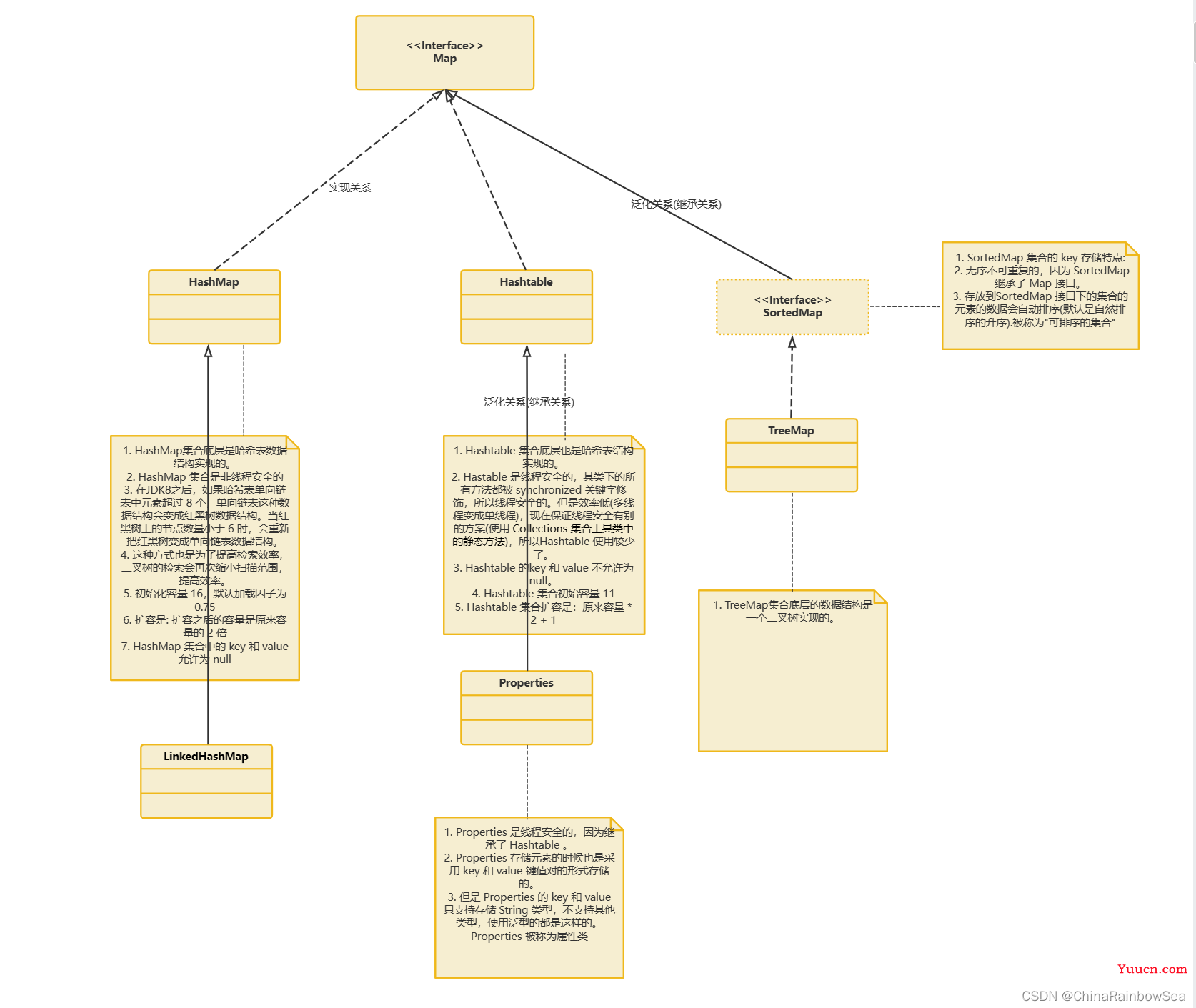
Map 接口的常用实现类:
- HashMap 作为Map的主要实现类,线程不安全的,效率高,可以存储 null 的key 和 value。HashMap是 Map 接口使用频率最高的实现类
- LinkedHashMap 保证再遍历Map元素时,可以按照添加的顺序实现遍历,原因: 在原有的HashMap底层结构基础上,添加了一对指针,指向前一个和后一个元素。对于频繁的遍历操作,此类执行效率高于HashMap
- TreeMap 保证按照添加的 key-value键值对进行排序,实现排序遍历.此时考虑key的自然排序或定制排序,底层使用红黑树:
- Hashtalbe 作为古老的实现类,线程安全的,效率低,不可以存储 null
- Properties 主要用于配置文件的读取。
-
键值对的示图:
2. Map接口:常用方法
添加、删除、修改操作:
- put(K key, V value) : 将指定的 key 和 value 值添加/修改到该集合当中。
V put(K key,V value); // 将指定的 key 和 value 值添加/修改到该集合当中。
- putAll(Map m) : 将 m 中所有的key-value 值存放到当前 对象集合当中。
void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m); // 将m中的所有key-value对存放到当前map集合当中
- remove(Object key) : 移除指定key的key-value对,并返回value。
V remove(Object key); // 移除指定key的key-value对,并返回value
- clear() : 清空当前map中的所有数据。
void clear(); // 清空当前map中的所有数据
- size() : 返回此集合中存储的元素数据(键值对)的数量。
int size(); // 返回此集合中存储的元素数据(键值对)的数量。
举例:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map 接口 , HashMap实现类,多态,<String,Integer> 泛型
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
// 添加元素数据:
map.put("zhangsan",66);
map.put("lisi",89);
map.put("wangwu",97);
map.put("lihua",99);
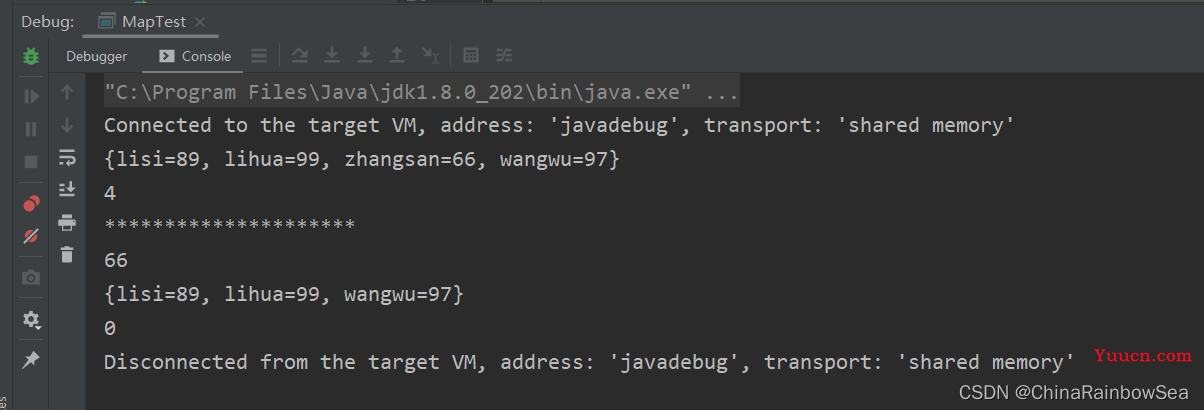
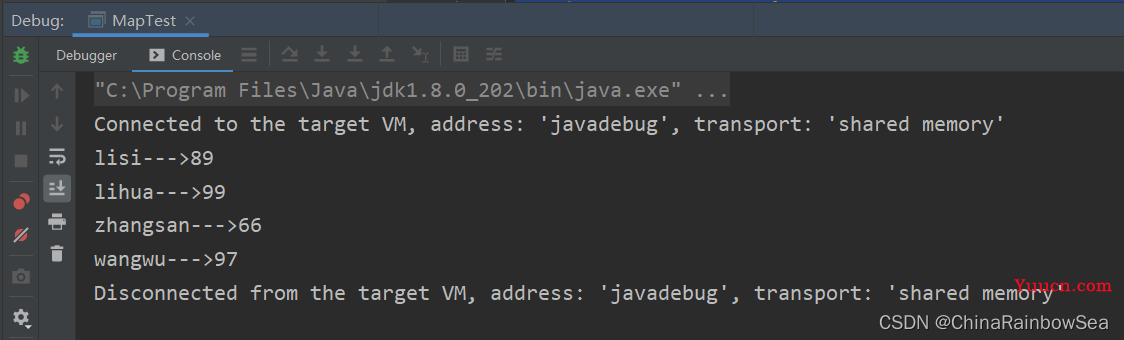
System.out.println(map);
int size = map.size(); // 返回该集合中存储的键值对的数量。
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println("*********************");
Integer zhangsan = map.remove("zhangsan"); // 移除key = zhangsan的元素数据,并返回该移除的value值。
System.out.println(zhangsan);
System.out.println(map);
map.clear(); // 清空该Map 集合当中的存储的元素数据
System.out.println(map.size());
}
}
举例
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map 接口 , HashMap实现类,多态,<String,Integer> 泛型
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
// 添加元素数据:
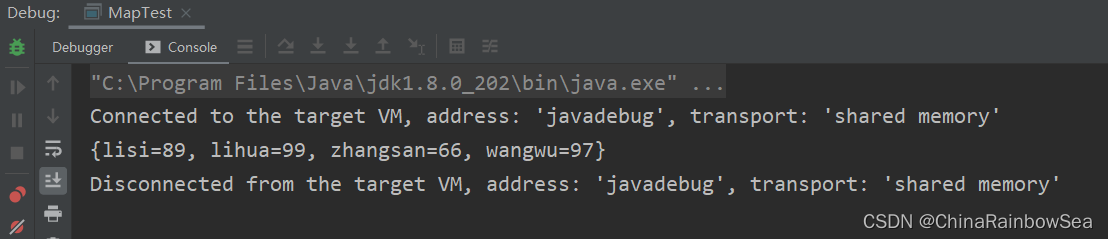
map.put("zhangsan",66);
map.put("lisi",89);
Map<String,Integer> map2 = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map2.put("wangwu",97);
map2.put("lihua",99);
map.putAll(map2); // 将 map2 集合中所有的key-value键值对添加到此 map集合当中去
// 注意:两者集合存储的元素数据类型必须是一致的才可以添加成功。
System.out.println(map);
}
}
元素查询的操作:
- get(Object key) : 获取指定key对应的value。
V get(Object key); // 获取指定key对应的value
- containsKey(Object key) : 判断该集合当中是否包含指定的 key值。
boolean containsKey(Object key); // 判断该集合当中是否包含指定的 key 值。
- containsValue(Object key) : 判断该集合当中是否包含指定的 value 值。
boolean containsValue(Object value); // 判断判断该集合当中是否包含指定的 value 值。
- isEmpty() : 判断此集合是否为 空,是返回 true,不是返回 false。
boolean isEmpty(); // 判断此集合是否为 空,是返回 true,不是返回 false;
- equals(Object o) : 判断当前map和参数对象 o 是否相等。
boolean equals(Object o); // 判断当前map和参数对象 o 是否相等
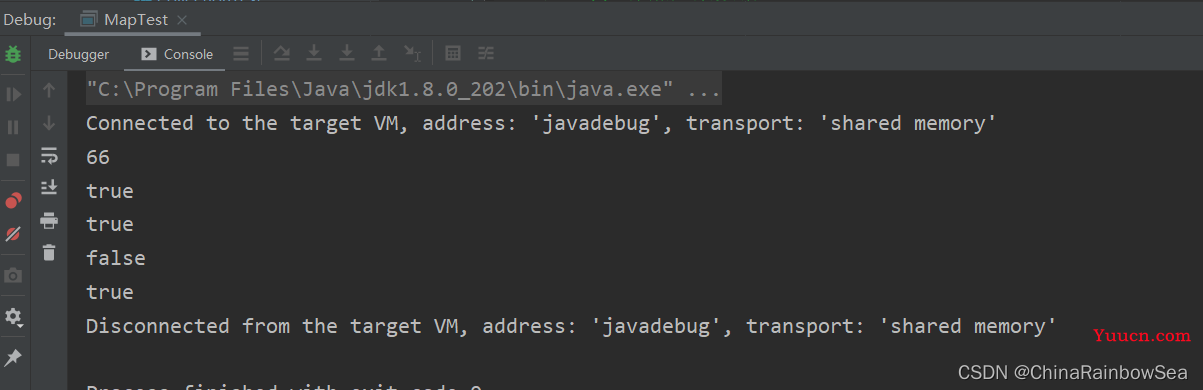
举例:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map 接口 , HashMap实现类,多态,<String,Integer> 泛型
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
// 添加元素数据:
map.put("zhangsan",66);
map.put("lisi",89);
map.put("wangwu",97);
map.put("lihua",99);
System.out.println(map.get("zhangsan")); // 获取到对应 key上的 value值
System.out.println(map.containsKey("zhangsan")); // 判断该集合当中是否存在 key = zhangsan的键值对
System.out.println(map.containsValue(99)); // 判断该集合当中是否存在 value = 99的键值对
System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); // 判断该集合是否为空
System.out.println(map.equals(map)); // 判断当前map和参数对象 o 是否相等
}
}
元视图操作的方法:
- keySet() : 返回所有key构成的Set集合。从该方法中可以看出 Map 接口下的集合中的 key 值是存储在 Set 接口集合当中的。
Set<K> keySet(); // 返回所有key构成的Set集合
- values() : 返回所有value构成的Collection集合。从该方法中可以看出 Map 接口下的集合中的 value 值是存储在 Collection 接口集合当中的。
Collection<V> values(); // 返回所有value构成的Collection集合
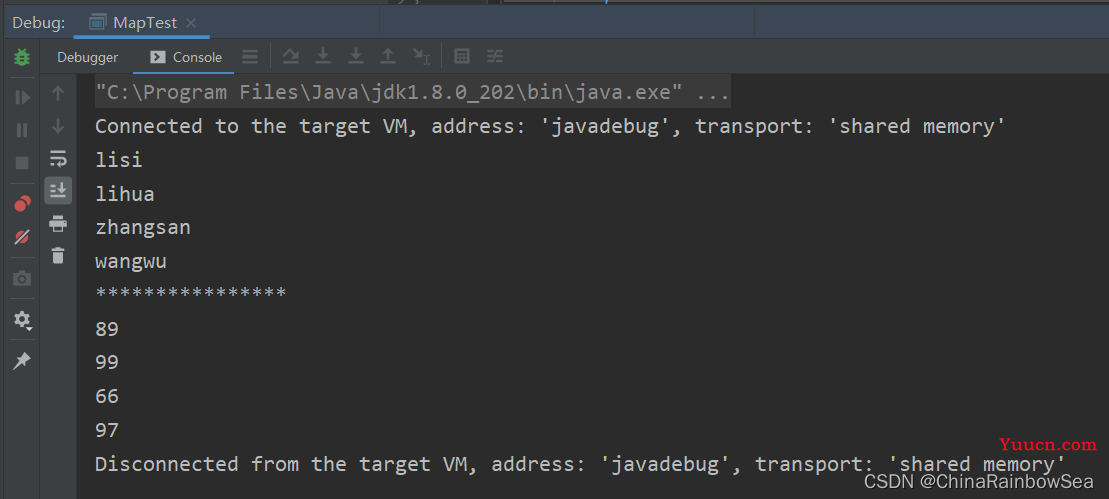
举例:
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map 接口 , HashMap实现类,多态,<String,Integer> 泛型
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
// 添加元素数据:
map.put("zhangsan",66);
map.put("lisi",89);
map.put("wangwu",97);
map.put("lihua",99);
Set<String> keys = map.keySet(); // 返回此集合当中所有的 key 值存储到 Set 集合当中
for (String s : keys) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("****************");
Collection<Integer> values = map.values(); // 返回此集合当中所有的 value 值存储到 Collection 集合当中
// Collection 接口集合可以使用迭代器
Iterator<Integer> iterator = values.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
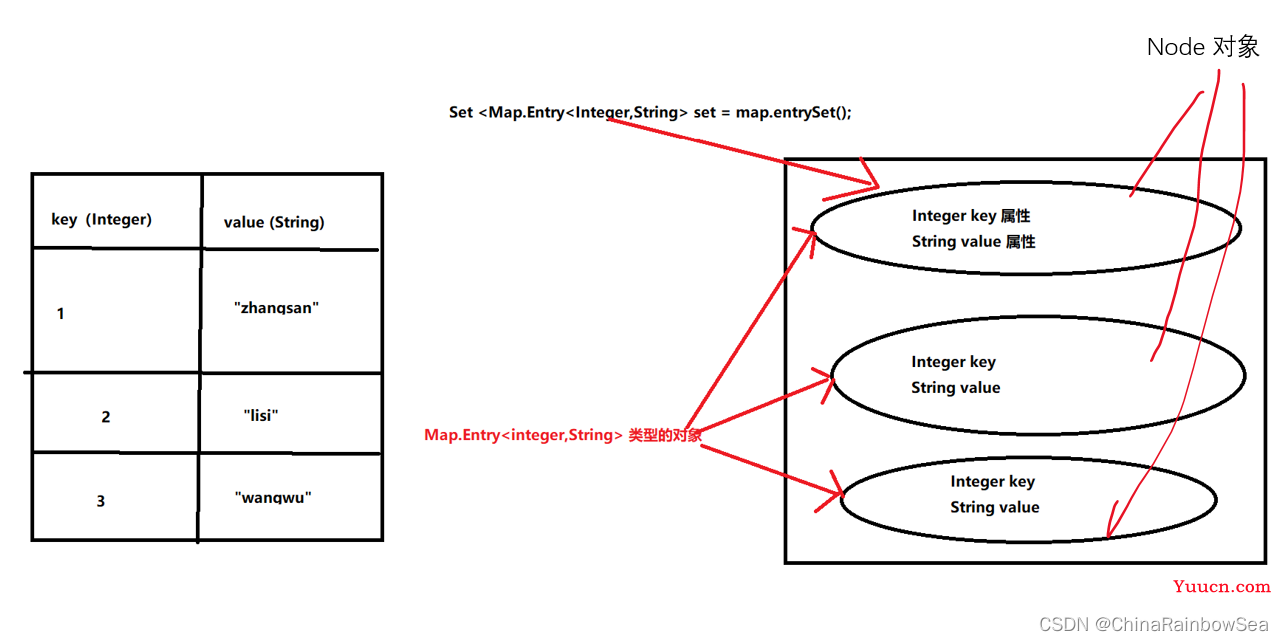
- entrySet() : 返回该集合当中的所有 key-value键值对,并存储到 Set 集合当中后,再返回一个 Set 集合对象(该集合存储了所有的key-value) 值。
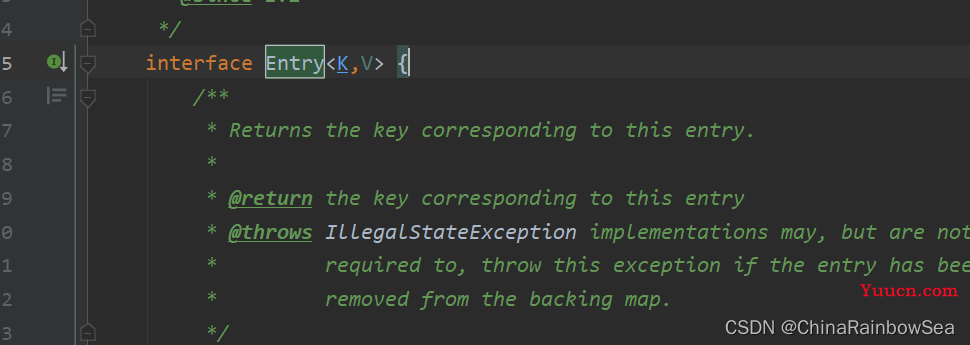
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet(); // 返回所有key-value对构成的Set集合
其中的 Map.Entry 表示的是一个接口,也可以理解为是一个类。
* Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 将 Map集合转换成 Set集合
* 假设现在有一个 Map集合 ,如下所示:
* map1 集合对象
* key value
* 1 zhangsan
* 2 lisi
* 3 wangwu
* 4 zhaoliu
*
* Set set = mop1.entrySet();
* set 集合对象
* 1=zhangsan
* 2=lisi
* 3=wangwu
* 4=zhaoliu
Map.Entry<K,V> 的图示:
举例:
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map 接口 , HashMap实现类,多态,<String,Integer> 泛型
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
// 添加元素数据:
map.put("zhangsan",66);
map.put("lisi",89);
map.put("wangwu",97);
map.put("lihua",99);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = entries.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
// getKey()获取 key 值,getValue()获取value值
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--->" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
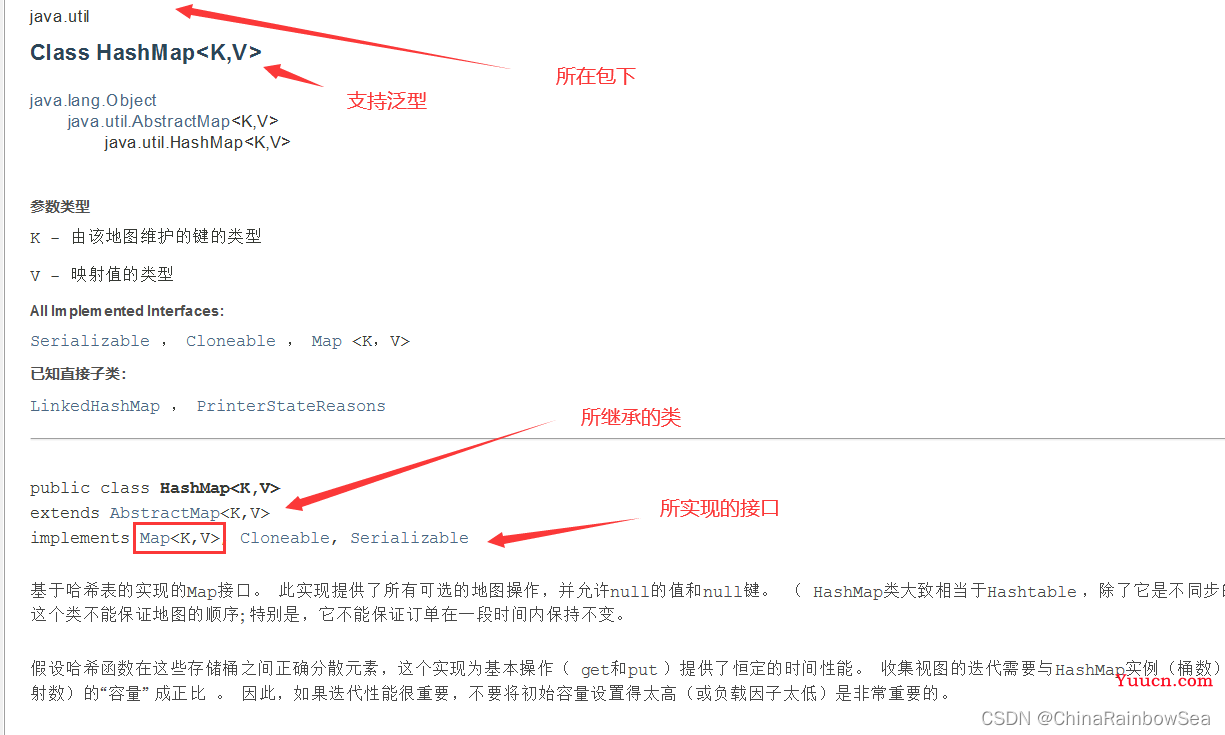
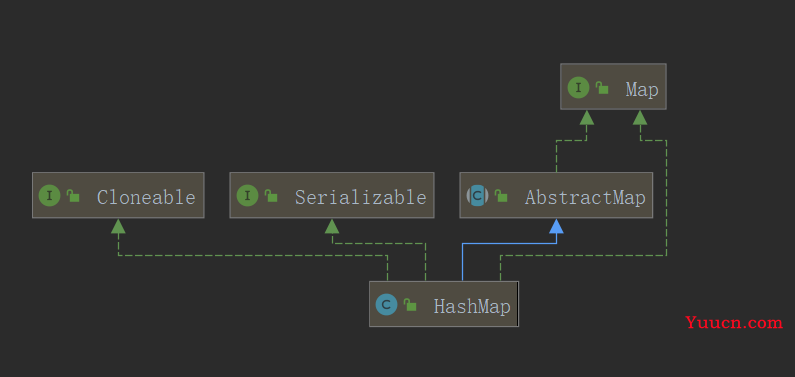
3. Map实现类之一:HashMap
-
HashMap 是 Map 接口使用频率最高的实现类。
-
HashMap 允许存储 null 值,key 可以为 null ,但仅仅只能有一个,因为不可重复,value 可以为 null 。无序
-
HashMap 中所有的 key 构成的集合是存储在 Set 当中的,无序的,不可重复的,所以:key 所在类和 Set 集合是一样的必须重写 euqlas() 和 hashCode() 方法。其中 Java当中的包装类和String 类都重写了 equals() 和 hashCode()方法。基本上只有我们自定的类需要重写。
-
一个key-value 构成一个
Map.Entry。 -
所有的 Map.Entry 构成的集合是 Set 无序的,不可重复的。
-
HashMap
判断两个 key 相等的标准是: 两个key 通过 equals() 方法返回 true , hashCode 值也相等。 -
HashMap
判断两个 value 相等的标准是: 两个 value 通过 equals() 方法返回 true。 -
HashMap 集合底层是哈希表的数据结构
- 哈希表是一个数组 + 单向链表 的结合体。
- 数组:在查询方面效率很高,随机增删方面很低。
- 链表:在随机增删方面效率较高,在查询方面效率低。
- 而哈希表:将以上两种数据结构融合在一起,充分发挥它们各自的优点。
-
对于 HashMap 中的方法基本上都是继承了对应的 Map 接口的方法,上面已经说明了,这里就不多介绍了。
举例:
如下是 Set 中的 Key 存储自定义类 Person5 ,其中并没有重写Object 中的 equals() 方法和 hashCode()方法。会出现 Key 存储到重复的数据。
package blogs.blogs7;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Person5,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<Person5, Integer>();
hashMap.put(new Person5("Tom",19),1);
hashMap.put(new Person5("Tom",19),1);
hashMap.put(new Person5("Tom",19),1);
hashMap.put(new Person5("zhangsan",23),4);
hashMap.put(new Person5("lihua",20),5);
// 遍历HashMap 集合
Set<Map.Entry<Person5,Integer>> entries = hashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Person5,Integer> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry);
}
}
}
class Person5 {
String name;
int age;
public Person5() {
}
public Person5(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person5{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
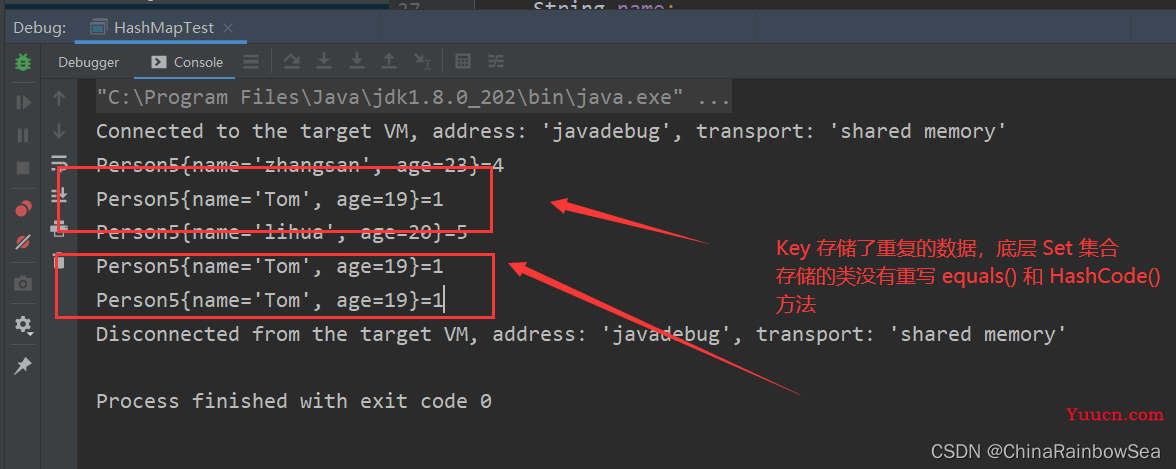
修改: 重写其中的 Key 值的 Set 集合中存储的 类中的 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法。
package blogs.blogs7;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Person5,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<Person5, Integer>();
hashMap.put(new Person5("Tom",19),1);
hashMap.put(new Person5("Tom",19),1);
hashMap.put(new Person5("Tom",19),1);
hashMap.put(new Person5("zhangsan",23),4);
hashMap.put(new Person5("lihua",20),5);
// 遍历HashMap 集合
Set<Map.Entry<Person5,Integer>> entries = hashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Person5,Integer> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry);
}
}
}
class Person5 {
String name;
int age;
public Person5() {
}
public Person5(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Person5)) return false;
Person5 person5 = (Person5) o;
return age == person5.age &&
Objects.equals(name, person5.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person5{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
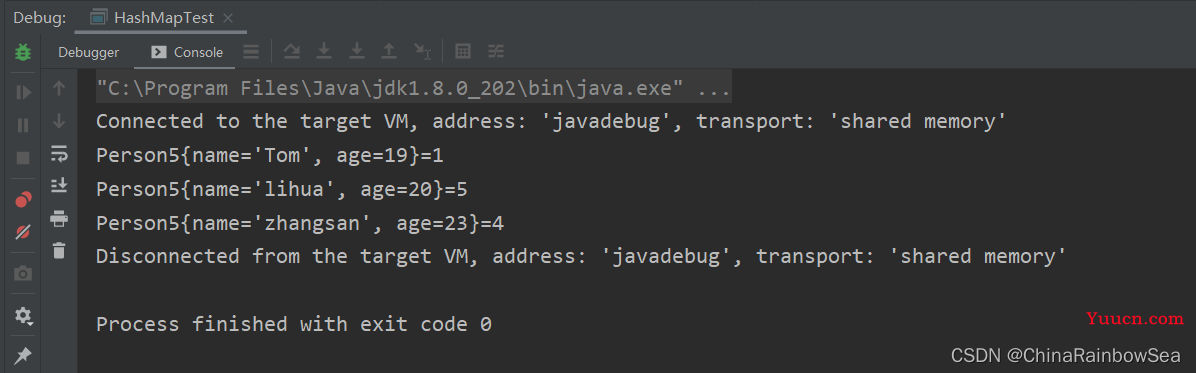
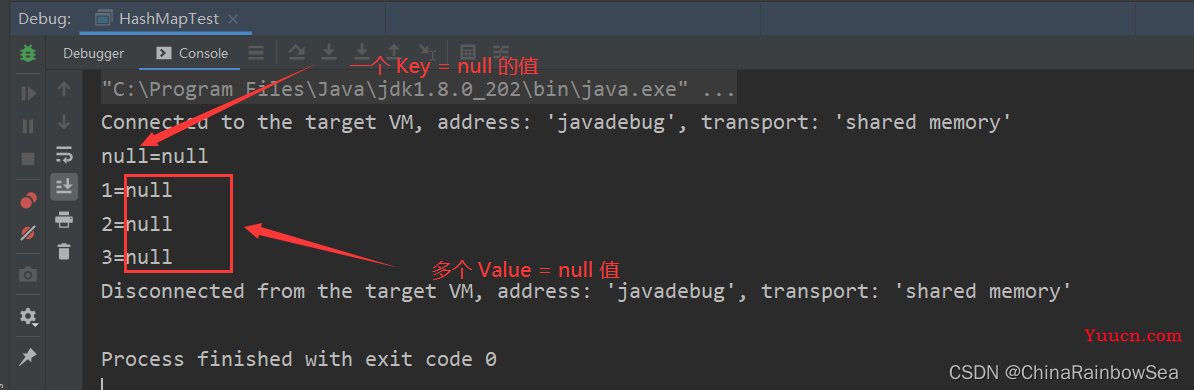
HashMap中的 Key值可以存储添加 null 值,但是仅仅只能添加一个 null ,因为 Key 中的数据存储在 Set集合当中的,不可重复,而 Value 值也可以存储 null值,而且可以存储多个 null 值,因为 Value 值数据底层是存储在Collection集合当中的。
举例:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
hashMap.put(null,null);
hashMap.put(null,null);
hashMap.put(null,null);
hashMap.put("1",null);
hashMap.put("2",null);
hashMap.put("3",null);
// 遍历HashMap 集合
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entries = hashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry);
}
}
}
常用方法总结:
- 添加: put(Object key,Object value)
- 删除: remove(object key)
- **修改: **put(Object key,Object value)
- 查询: get(Object key)
- 长度: size();
- 遍历: keySet()/values()/entrySet()
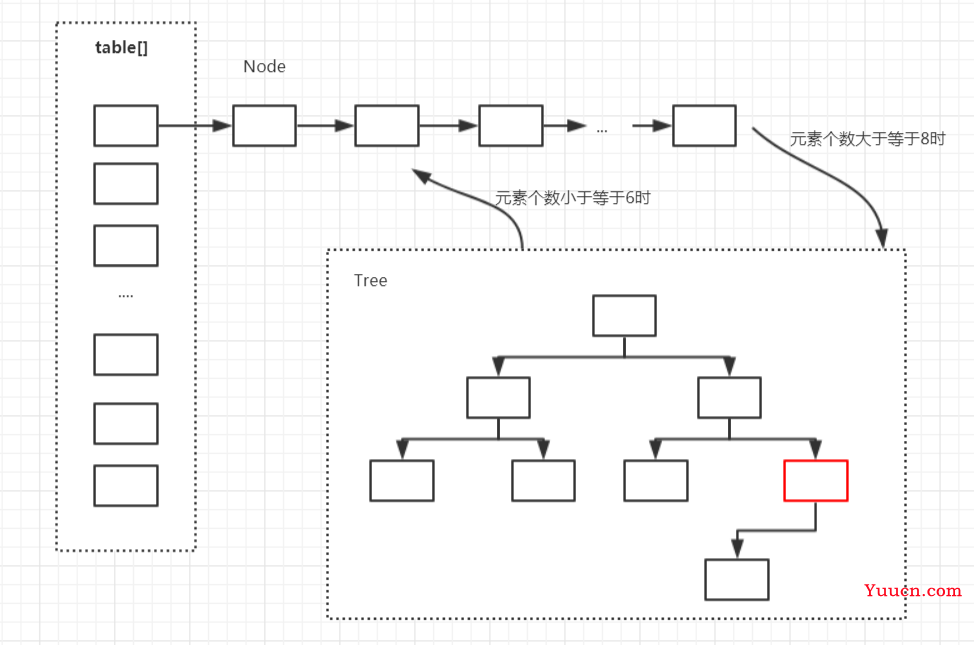
3.1 HashMap的存储结构
JDK 7及以前版本:HashMap是数组+链表结构(即为链地址法)
JDK 8版本发布以后:HashMap是数组+链表+红黑树实现
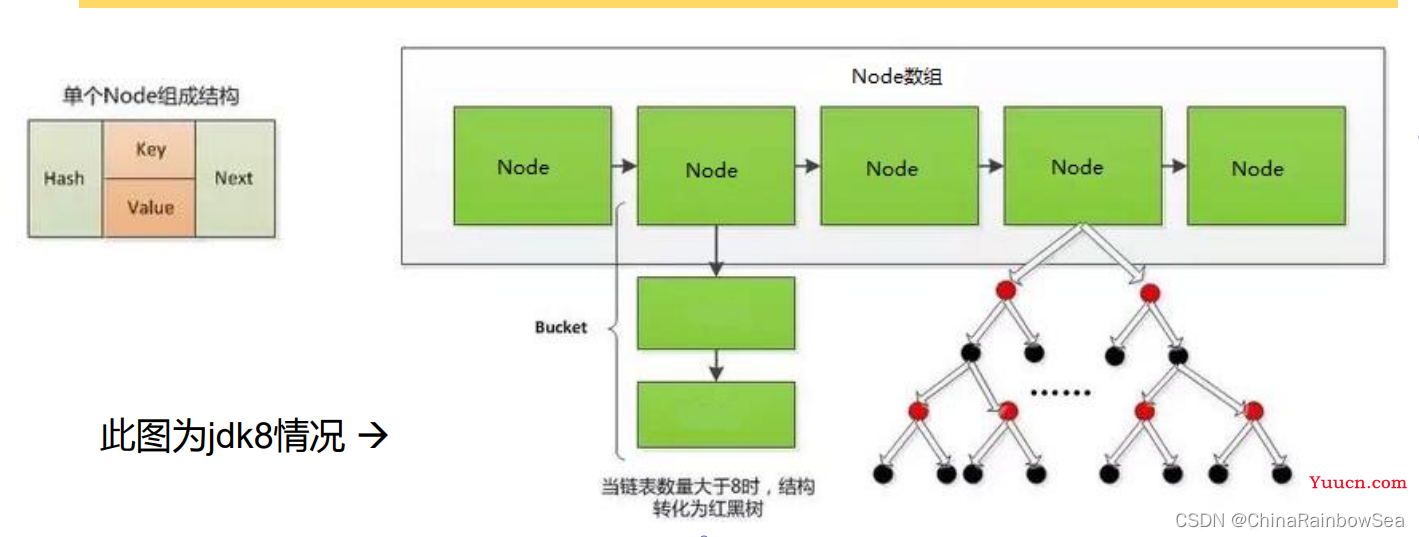
如下是 JDK8 的HashMap 结构图
3.2 HashMap源码中的重要常量
/**
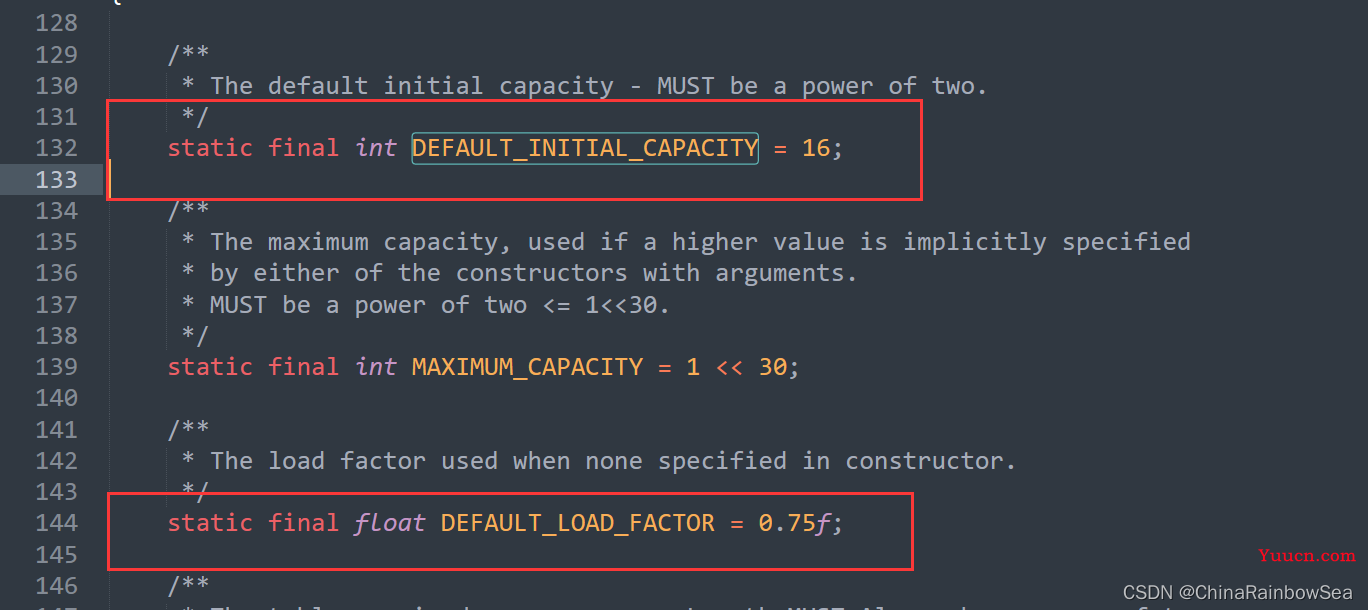
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 HashMap的默认容量是 16
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // HashMap的最大支持容量,2^30
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
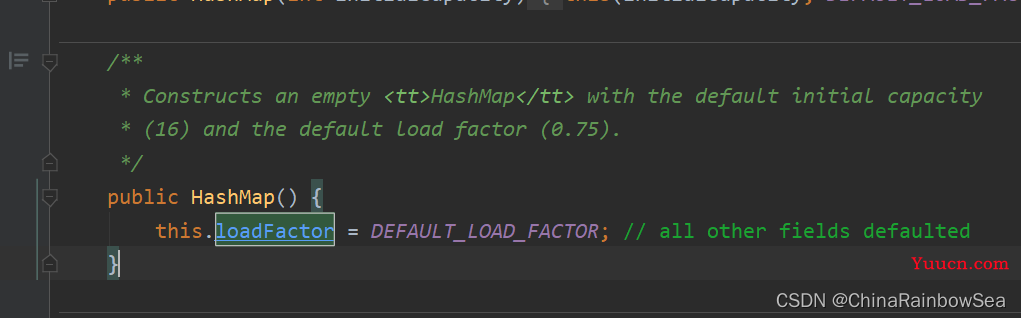
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // HashMap的默认加载因子
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; // Bucket中链表长度大于该默认值,转化为红黑树
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; // Bucket中红黑树存储的Node小于该默认值,转化为链表
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts
* between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; // 桶中的Node被树化时最小的hash表容量。(当桶中Node的数量大到需要变红黑树时,若hash表容量小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY时,此时应执行resize扩容操作这个MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY的值至少是TREEIFY_THRESHOLD的4倍。)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
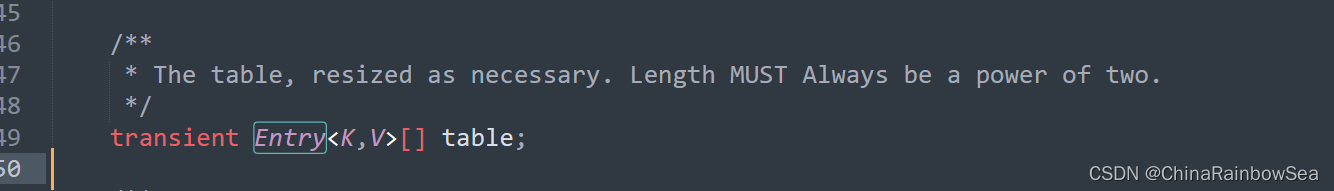
/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table; // 存储元素的数组,总是2的n次幂
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used
* for keySet() and values().
*/
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; // 存储具体元素的集合
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size; // HashMap中实际存储的键值对的数量
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
transient int modCount; // HashMap扩容和结构改变的次数。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
*
* @serial
*/
// (The javadoc description is true upon serialization.
// Additionally, if the table array has not been allocated, this
// field holds the initial array capacity, or zero signifying
// DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY.)
int threshold; // 扩容的临界值,=容量 * 填充因子
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
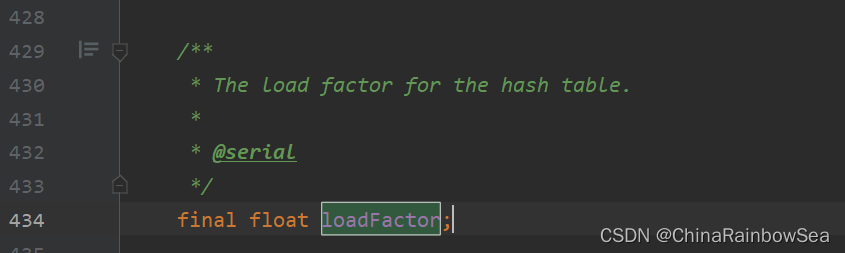
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor; // 填充因子
3.3 HashMap的存储结构:JDK 1.8之前 / JDK 1.8之后
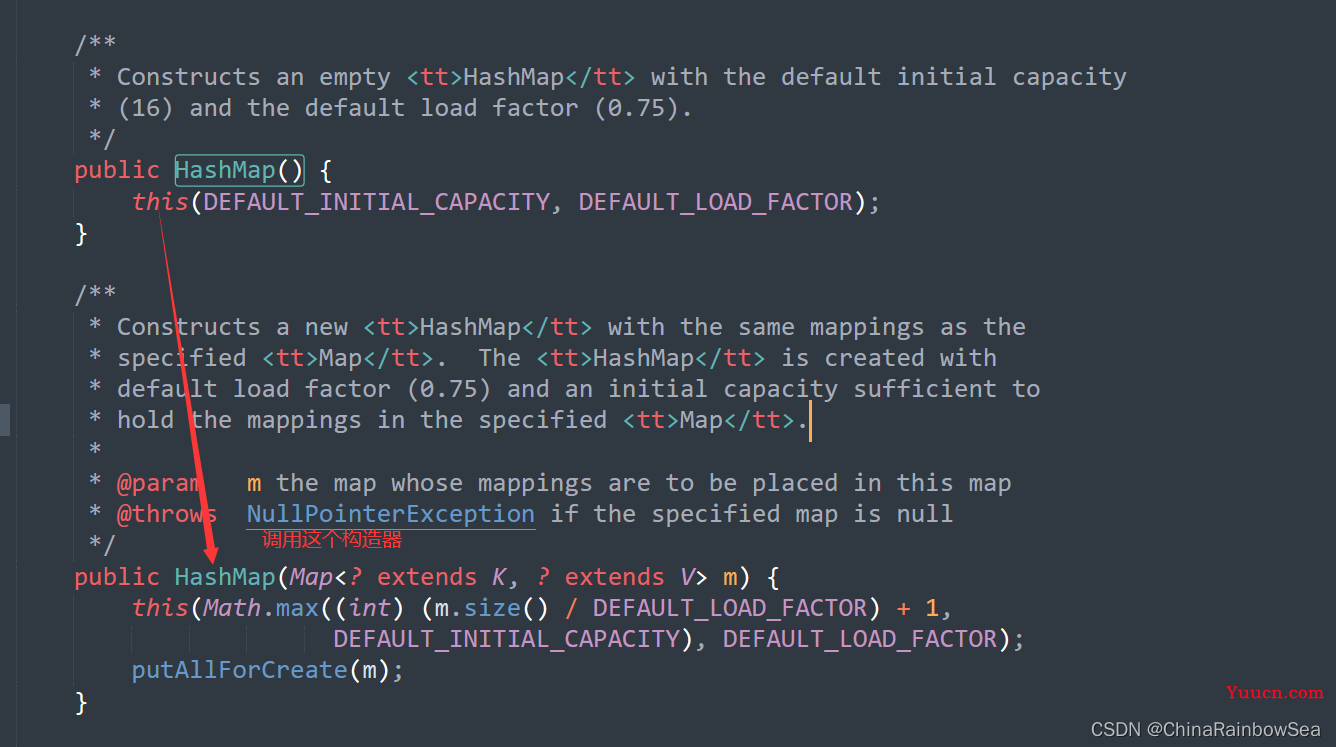
3.3.1 JDk 1.8 之前
-
HashMap 内部存储结构其实是
数组 + 链表的结合。当实例化一个 new HashMap() 时,实际上会创建一个长度为 Capacity 的 Entry 数组。这个长度在 哈希表中称为 容量(Capacity) ,在这个数组中可以存放元素的位置,我们称之为 ”桶“ (bucket) ,每个 bucket 都有自己的索引,系统可以根据索引快速的查找 bucket 中的元素。 -
每个bucket 中存储一个元素,即 一个 Entry 对象内部类 ,但每一个 Entry 对象可以带 一个引用变量,用于指向下一个元素,因此,在一个桶 (bucket) 中,就有可能生成一个 Entry 链。而且新添加的元素作为链表的 head 。
-
JDK7 源码分析如下:
3.3.2 JDk 1.8 及之后
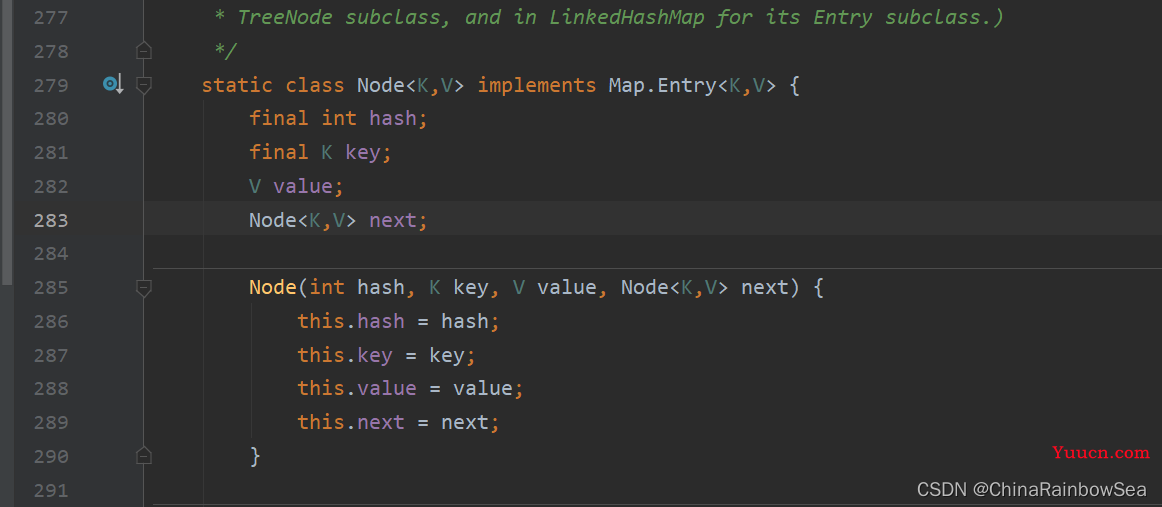
JDK8: HashMap 的内部存储结构其实是:数组+链表+树 的结合。当实例化一个 new HashMap 时,会初始化 initilCapacity 和 loadFactor ,在 put() 第一对映射关系(键值对)添加时,系统会创建一个长度为 initilCapacity 的 Node 数组 ,这个长度在哈希表中被称为 ”容量" (Capacity),在这个数组中可以存放元素的位置,我们称之为 “桶”(bucket) ,每个 bucket 都有自己的索引,系统可以根据索引快速的查找 bucket 中的元素。
每个bucket 中存储一个元素数据,既 一个 Node 对象,但每一个 Node 对象可以带一个引用变量 next ,用于指向下一个元素,因此,在一个桶中,就有可能生成一个 Node 链表。也可能是一个一个TreeNode 对象,每一个TreeNode 对象可以有两个叶子节点 left 和 right ,因此,在一个桶中,就有可能生成一个 TreeNode 树。而新添加的元素作为链表的 last ,或树的叶子节点。
JDK1.8 源码分析:

3.3.3 JDK8 HashMap 集合添加元素的过程
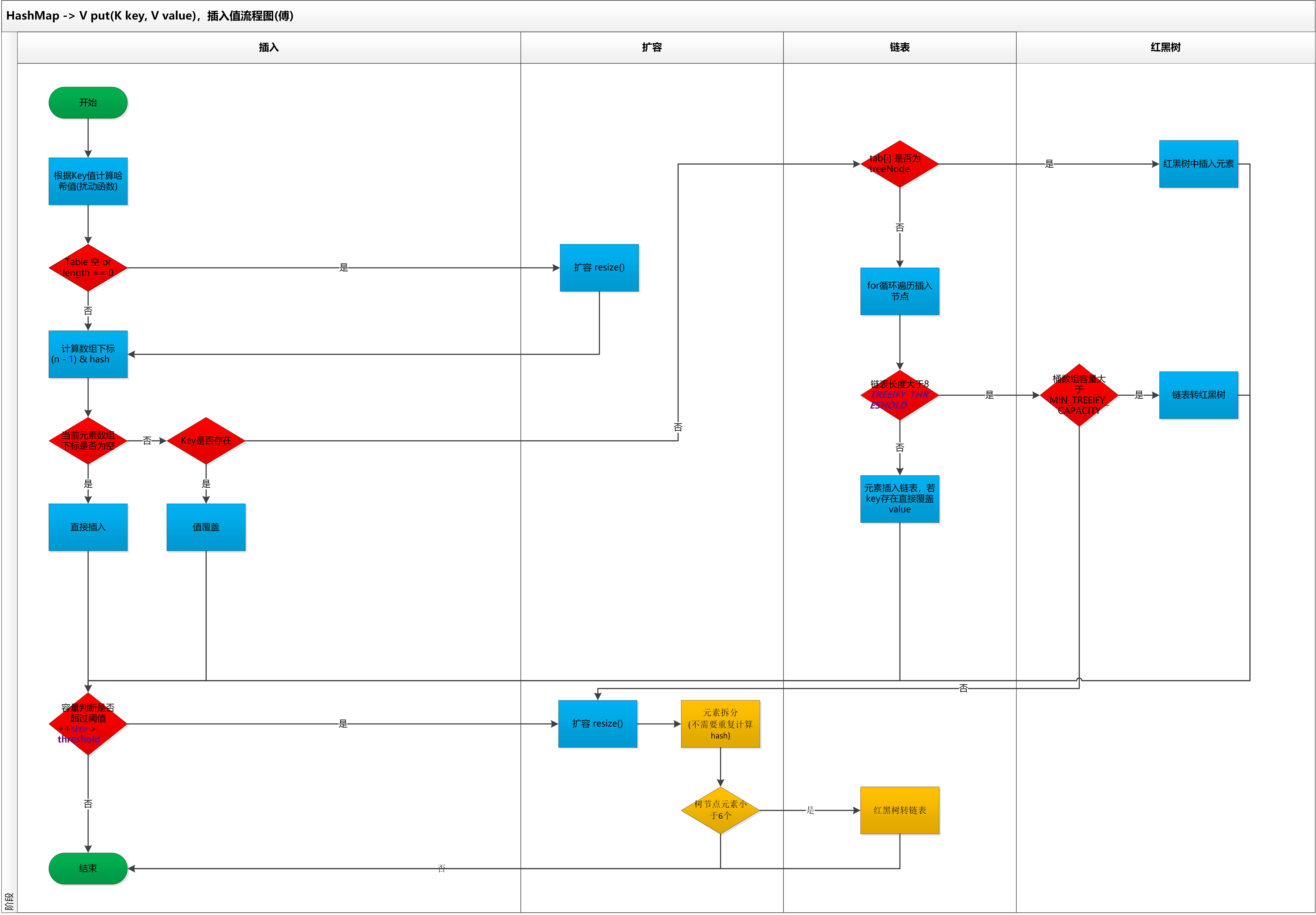
向 HashMap 集合中添加 put(key1,value1) 键值对, 首先调用 元素 key1 所在类的 hashCode() 方法,来得到该 key1对象的 hashCode(哈希) 值。
然后再根据得到的 hashCode (哈希)值,通过某种散列函数 计算除该对象在 HashSet 集合中底层Node[] 数组的存储位置(即为:索引下标位置),(这个散列函数会与底层数组的长度相计算得到在数组中的下标,并且这种散列函数计算还尽可能保证能均匀存储元素,越是散列分布,该散列函数设计的越好)。
-
判断此计算处理得到的数组下标位置上是否已经有元素存储了 :
- 如果没有其他元素数据存储,则 元素 key1-value1添加到该位置上。 —— 情况1
- 如果有其它元素数据存储(或以链表形式存储的多个元素) : 则比较key1和已经存在的一个或多个数据的哈希值):
-
如果 key1的hashCode() 哈希值与已经存在的数据的哈希值都 不相等, 则元素 key1-value1添加到该数组链表上。—— 情况2
-
如果 key1 的hashCode() 哈希值 与 已经存在的数据的哈希值都 相等, 则调用 key1 元素所在类的 equals() 方法,, 判断比较所存储的内容是否和集合中存储的相等。
- 如果 不相等 也就是 equals() 方法,返回 false ,则此时 key1-value1添加成功。—— 情况3
- 如果 相等 也就是 equals()方法,返回 true,不添加,替换掉其中存放的 value 值为 value1 ,因为 key1 是唯一的不可重复的,但是其 对应的 value 值是可以重复的。
-
-
对应上述 添加成功的 情况2 和 情况3 而言,关于情况2和情况3:此时key1-value1和原来的数据以链表的方式存储
-
如下是 添加键值对的过程的图示:
如下是查找图示:
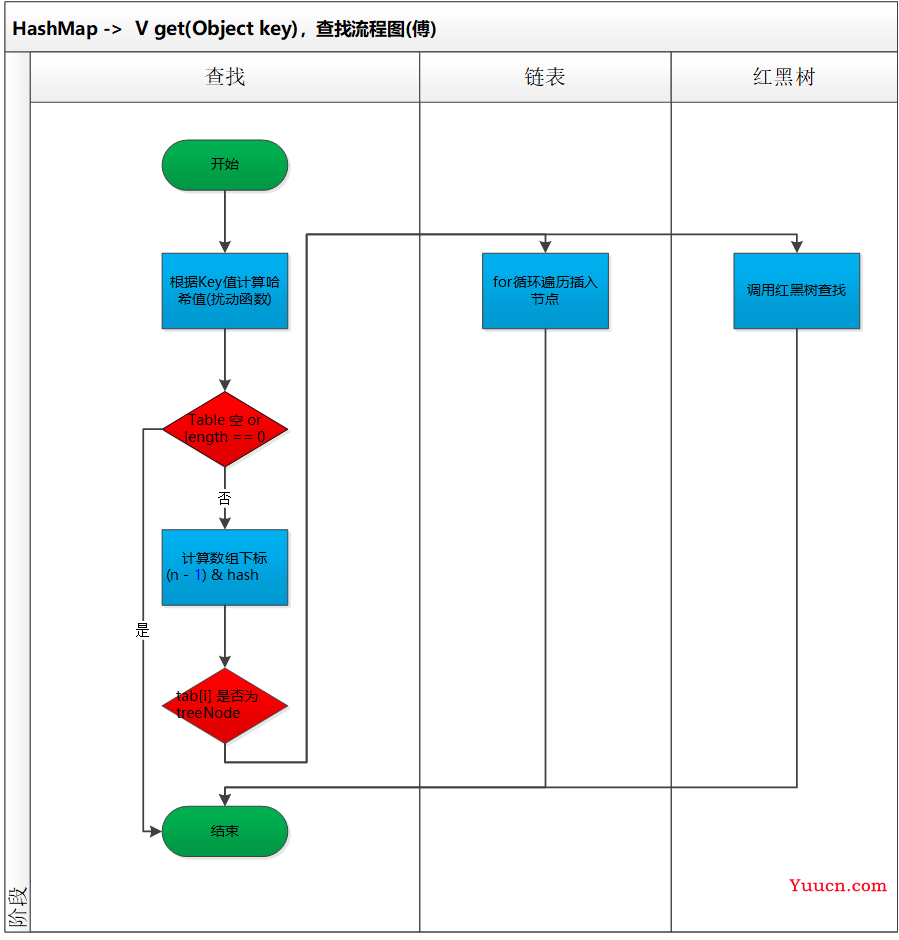
假设将所有的hashCode()方法返回设定为不一样的值,可以吗?,有什么问题:
不行,因为这样的话,就导致 HashMap 集合底层的哈希表就成为了一维数组了,没有链表的概念了,更没有哈希表的概念了。
假设将所有的hashCode()方法返回设返回值固定为某个值,可以吗?,有什么问题:
答:不可以,设将所有的hashCode()方法,返回值固定为某个值,那么会导致底层哈希表变成了纯单向链表。这种情况下我们称为:散列分别不均匀。
什么时散列分布不均匀
假设我们有 100 个元素,10个单向链表,那么每个单向链表上有10个节点,这是最好的,是散列分布均匀的
3.3.4 JDK8 HashMap 进行 "扩容"和 "树形化"
扩容
当 put(Key1,value1) 添加键值对个数超过 数组大小(数组总大小 length ,不是数组中实际存放的键值对个数 size),时,就会进行数组扩容。loadFactor 的默认值:DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR)为0.75,这是一个折中的取值,也就是说,默认情况下,数组大小(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)为16 ,那么当 HashMap 中元素个数超过 16 * 0.75 = 12 (这个值就是代码中的 threshold值,也叫临界值)的时候,就把数组的大小扩展为 2 * 16 = 32 ,即扩大 1倍 ,然后重新计算每个元素在数组中的位置,而这是一个非常消耗性能的操作。所以在开发中如果我们可以预估计其存储的数据量,也就是 HashMap中存储元素的个数,那么就调用其HashMap(int num) 设定存储容量的大小,减少扩容次数,提高 HashMap的性能 。
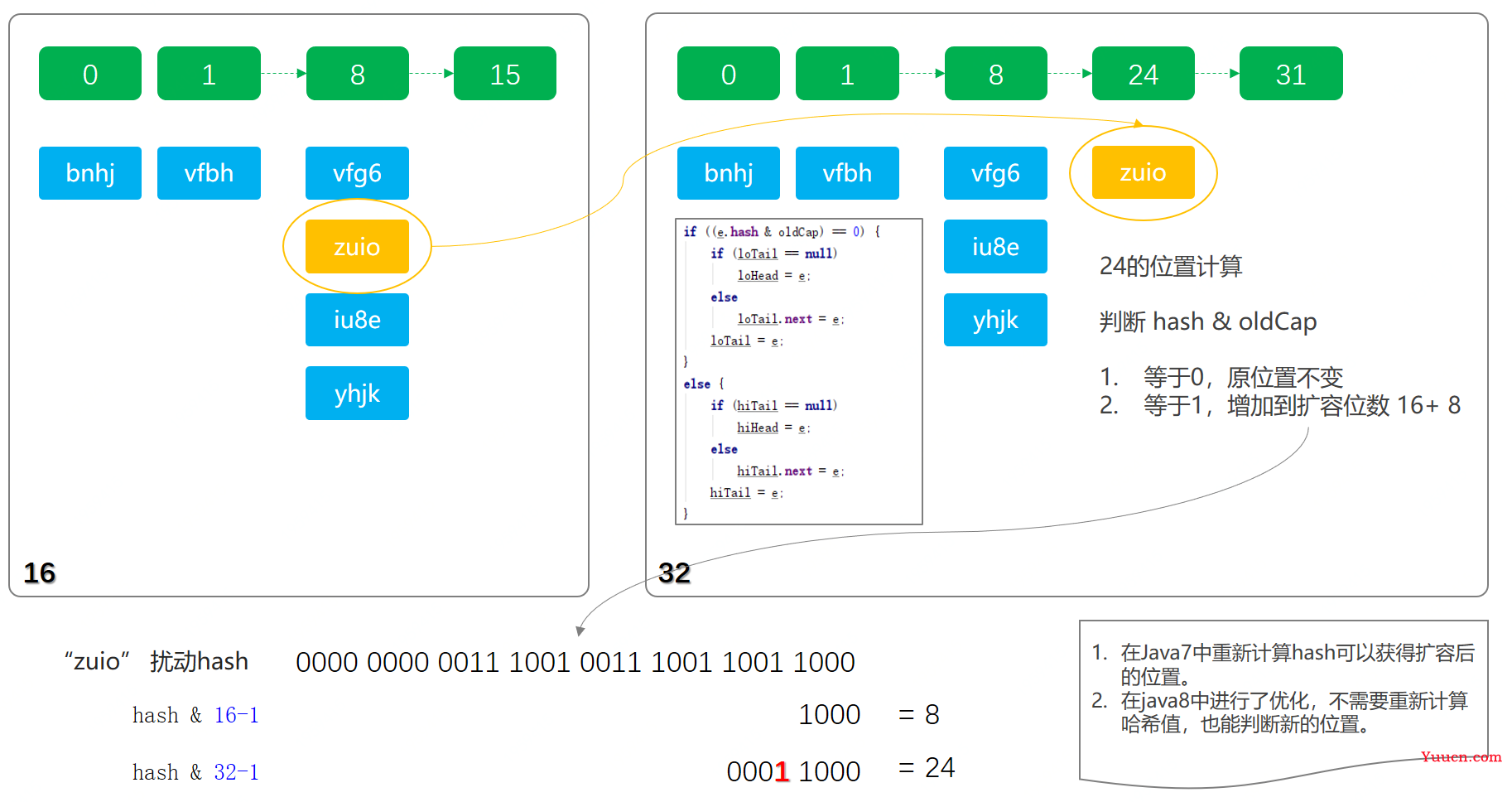
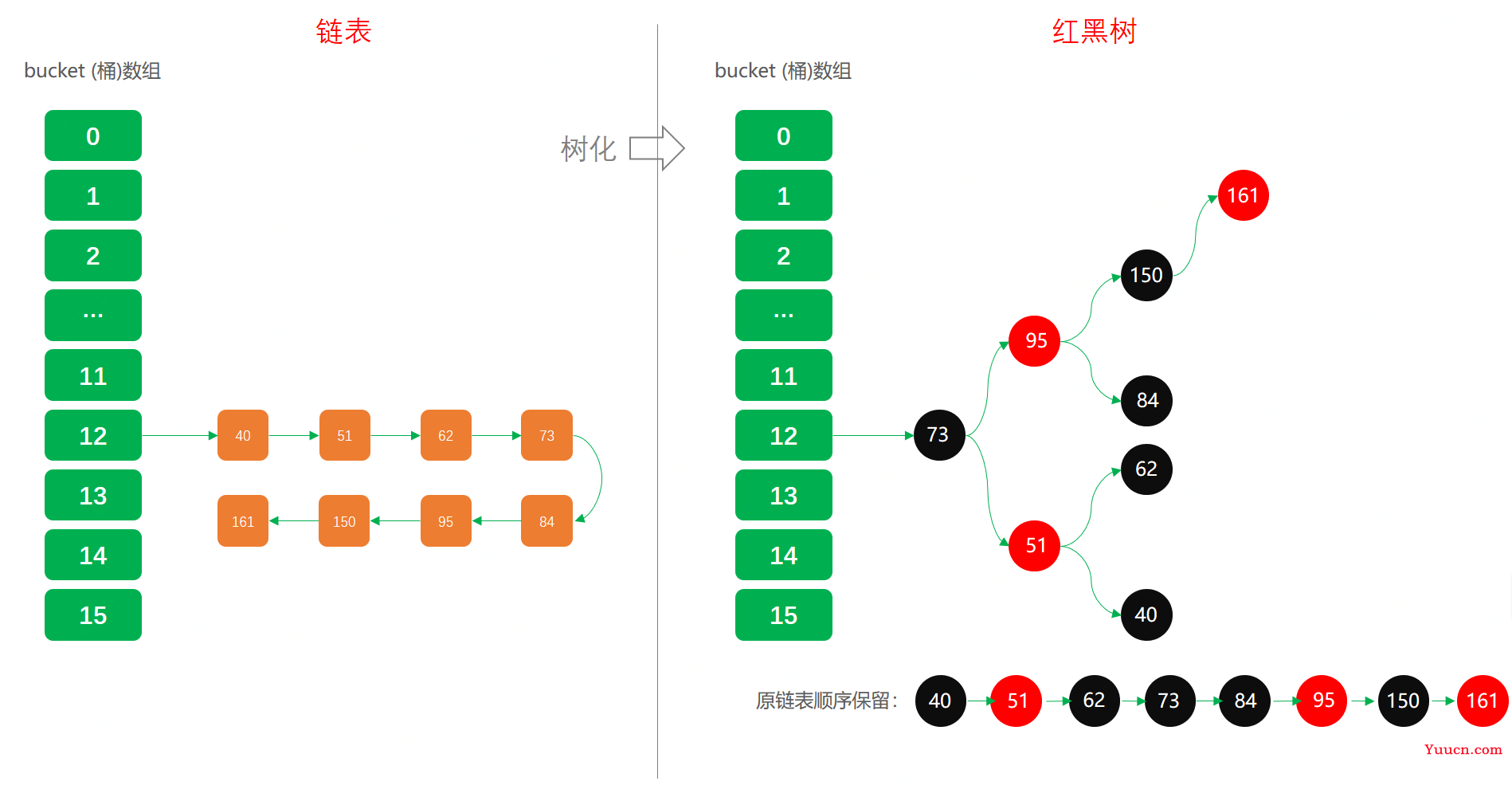
树形化
当HashMap中的其中一个链的对象个数如果达到了8个,此时如果capacity没有达到64,那么HashMap会先扩容解决,如果已经达到了64,那么这个链会变成树,结点类型由Node变成TreeNode类型。当然,如果当映射关系被移除后,下次resize方法时判断树的结点个数低于6个,也会把树再转为链表。
补充:
关于映射关系的key是否可以修改 ???
answer:不要修改,映射关系存储到 HashMap 中会存储 key 的 哈希值 ,这样就不用每次查找时,重新计算每一个 Entry 或 Node (TreeNode)的 哈希值了,因此如果已经 put 到 Map 中的映射关系,再修改 key 的属性,而这个属性有参与 hashCode值的计算,那么会导致匹配不上。
为什么HashMap扩容时,不是数组满了的时候扩容而是达到一个的 0.75 的额度才扩容 ???
因为HashMap 集合的底层时由 链表 + 数组 + 树 构成的。由于链表的存在,HashMap 当中的数组不一定会存储满了。
以及涉及到 HashMap 集合性能最优的效果,散列均匀分布,所以是到达一定额度 0.75 是最好的情况了.
负载因子值的大小,对HashMap有什么影响 ???
/** * The load factor used when none specified in constructor. */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // HashMap的默认加载因子负载因子的大小决定了HashMap的数据密度。
负载因子越大密度越大,发生碰撞的几率越高,数组中的链表越容易长,
造成查询或插入时的比较次数增多,性能会下降。
负载因子越小,就越容易触发扩容,数据密度也越小,意味着发生碰撞的
几率越小,数组中的链表也就越短,查询和插入时比较的次数也越小,性能会更高。但是会浪费一定的内容空间。而且经常扩容也会影响性能,建议初始化预设大一点的空间。
按照其他语言的参考及研究经验,会考虑将负载因子设置为0.7~0.75,此时平均检索长度接近于常数。
3.3.5 总结:JDK1.8 相较于之前的变化:
-
JDK8 :HashMap map = new HashMap() ,默认情况下,是不会先创建长度为 16 的 数组的,而是首先调用 map.put() 添加键值对的时候创建 长度为 16的数组(类比:单例模式中的饿汉式)。 JDK7 则是默认先创建了一个长度为 16的数组(类比:单例模式中的懒汉式)。
-
JDK8 底层的数组是 Node[ ] ,JDK7 底层的数组是 Entry[ ] 。
-
put(Key1,Value1) 添加键值对时,JDK7 是添加到链表上的头部(数组上),JDK8 是添加到链表的尾部(不在数组上),简称:七上八下。
-
jdk7 底层结构只有:数组 + 链表,jdk8 中底层结构: 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树
当数组的某一个索引位置上的元素以链表形式存在的数据个数 > 8 且当前数组的长度 > 64时,此时此索引位置上的所有数据改为使用“红黑树”存储。当小于 8 时,有会变成链表的形式存储。
4. Map实现类之二:LinkedHashMap

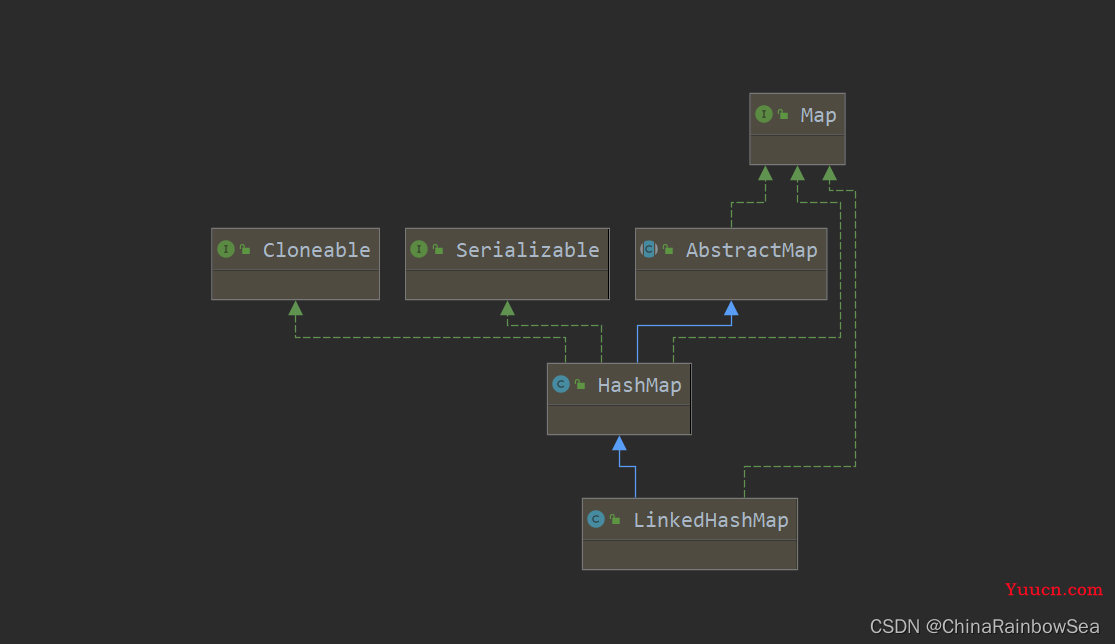
- LinkedHashMap 是 HashMap 的子类,所以 LinkedHashMap 继承了 HashMap 的特点:其中的 key 是无序,不可重复的,其 Key 存储的元素类必须重写 eqauls() 和 hashCode() 方法。同样的 Key 值是存储在 Set 集合当中的,而Value 则是存储在 Collection 集合当中的。
- LinkedHashMap 是在 HashMap 存储结构的基础上,使用了一对双向链表来记录添加元素的顺序的,所以你添加元素数据的顺序是怎样的,取元素数据的顺序就是怎样的。
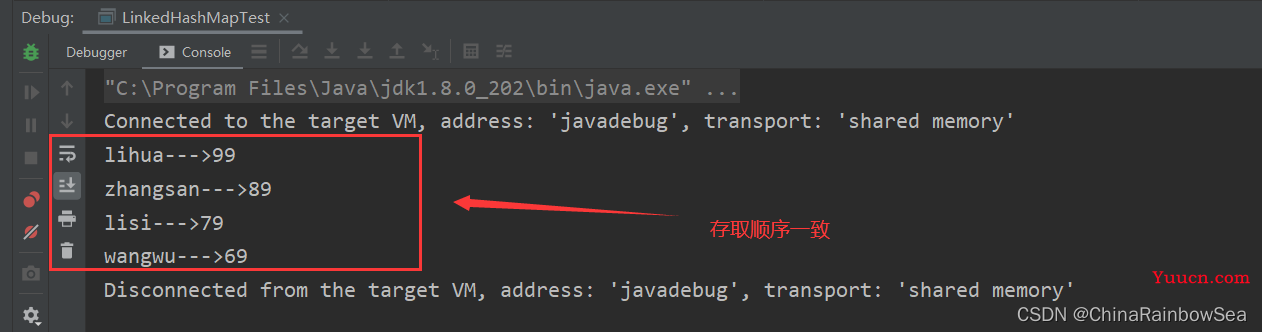
- 与 LinkedHashSet 类似, LinkedHashMap 可以维护 Map 的迭代顺序:迭代顺序与 Key-Value 键值对的插入顺序一致,简单的说就是:存取顺序一样。
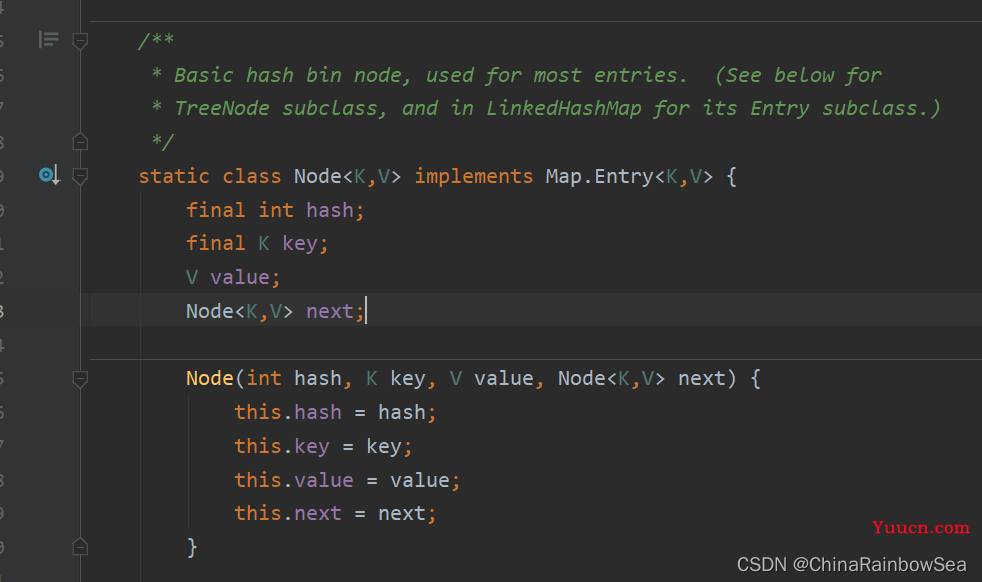
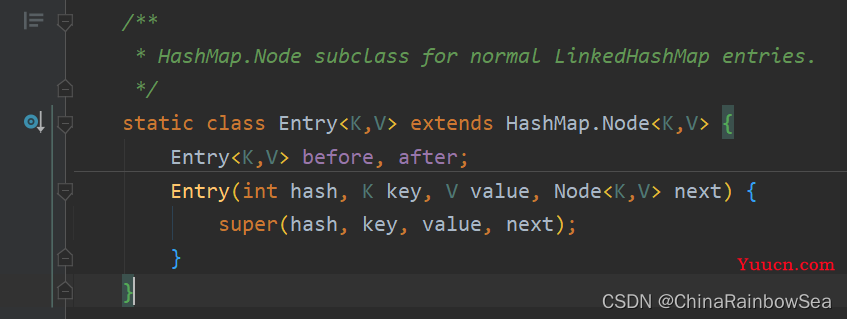
- LinkedHashMap 是继承了 HashMap 其常用的方法是一样的,这里就不多说明了。不同的是HashMap 底层的内部类是 Node ,而LinkedHashMap 底层的内部类是Entry ,该内部类继承了 HashMap.Node<K,V>
HashMap中的内部类:Node
LinkedHashMap中的内部类:Entry
举例:
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class LinkedHashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 LinkedHashMap 集合对象
LinkedHashMap<String,Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>();
// 添加元素数据(键值对)
linkedHashMap.put("lihua",99);
linkedHashMap.put("zhangsan",89);
linkedHashMap.put("lisi",79);
linkedHashMap.put("wangwu",69);
// 遍历 LinkedHashMap 集合
// 获取到key-value 存储的 Set Entry 内部类集合对象
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = linkedHashMap.entrySet();
// 获取到该 Set Entry 内部类集合的迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = entries.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--->" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
5. Map实现类之三:TreeMap
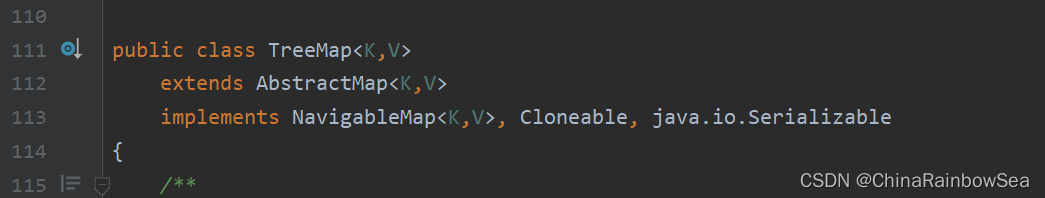
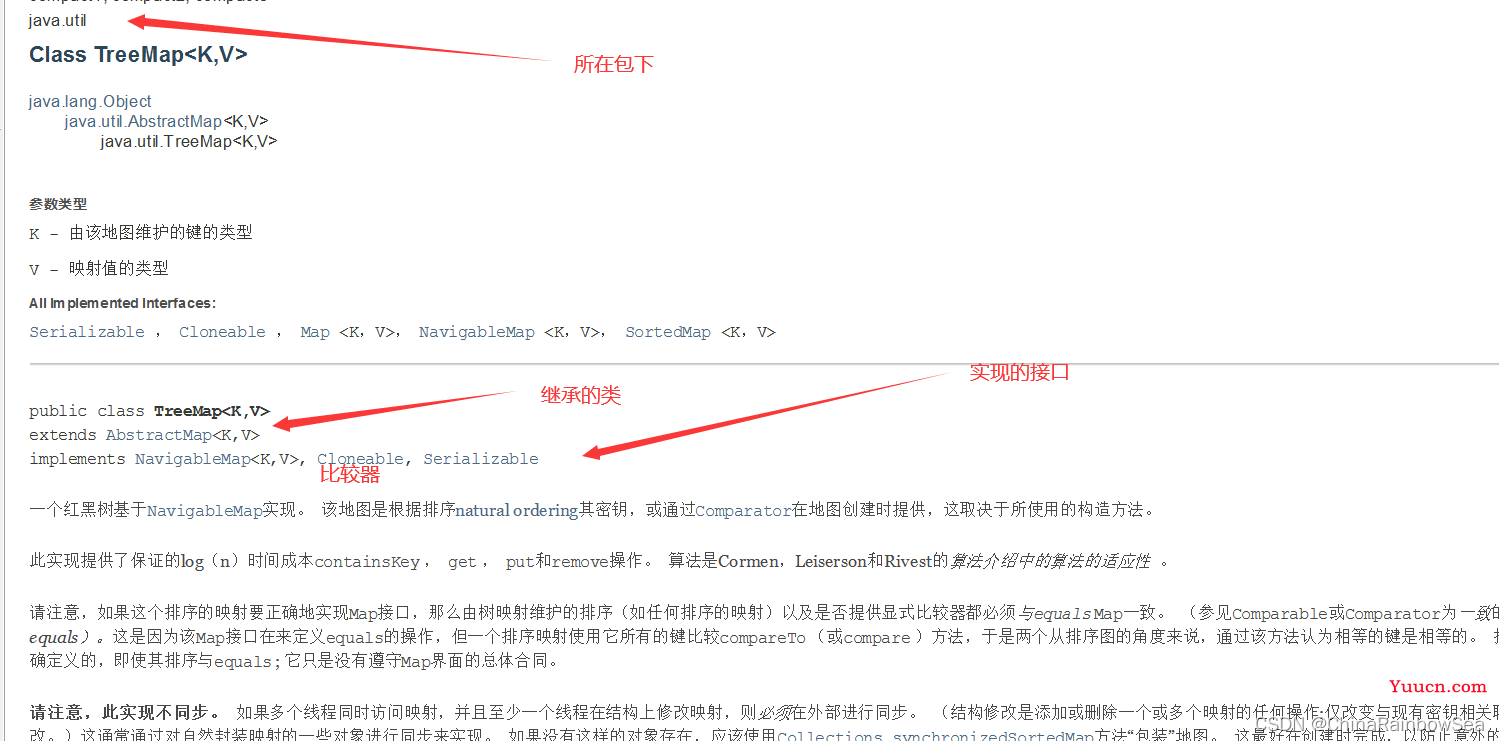
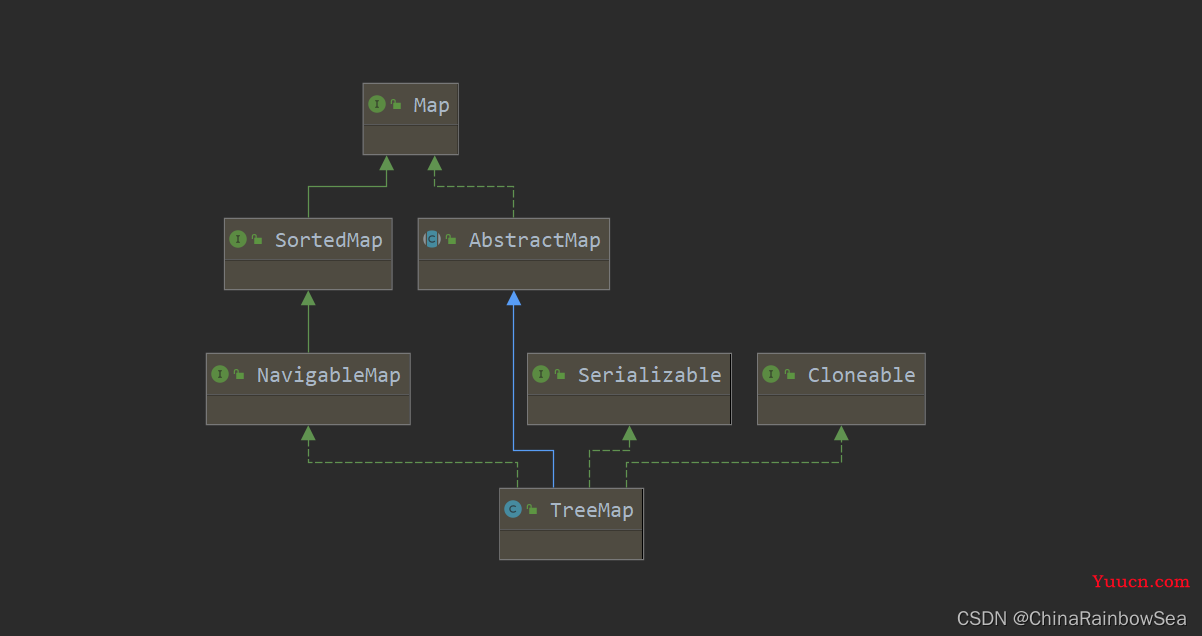
-
TreeMap 存储 Key-Value 键值对时,需要根据 key-value 键值对进行排序,TreeMap 可以保证所有的 key-value 键值对处于有序状态。
-
TreeSet 底层 就是由 TreeMap 构成的,new TreeSet 底层实际上说就是 new TreeMap 集合存储数据,向 TreeSet 中添加数据就是向 TreeMap 集合中添加数据。
-
TreeMap 中的 key 存储的数据类型必须是一致的,不然无法比较判断,从而排序。
-
TreeMap 的 排序是对 Key 的内容进行排序的,其中的 Key 值内部是由 Set 集合存储的,无序,不可重复性,所存储类必须重写 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法。因为会自动排序,所以还需要实现排序:两种方式一种是:
-
自然排序: TreeMap 的所有的 Key 必须实现(实现
java.lang.Comparable的接口,而且所有 的 Key 应该是同一个类的对象(因为不是同一类型无法比较判断),否则将会抛出ClasssCastException自然排序,重写其中的compareTo()抽象方法) 。在Java当中所有的包装类和String都实现了该java.lang.Comparable接口。所以一般要实现该接口的都是自定的类。 - 定制排序: 创建 TreeMap 时,传入一个 Comparator 对象,该对象负责对 TreeMap 中的所有 key 进行排序。此时不需要 Map 的 Key 实现 Comparable 接口
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator)v // 构造一个新的,空的树图,按照给定的比较器排序。- 关于自然排序与 定制排序 的详解内容大家可以移步至:??? 比较器: Comparable 与 Comparator 区别_ChinaRainbowSea的博客-CSDN博客
-
自然排序: TreeMap 的所有的 Key 必须实现(实现
-
TreeMap 判断两个 Key 相等的标准:两个 key 通过 重写的 compareTo()方法或 compare()方法,返回0 表示相等。
举例:
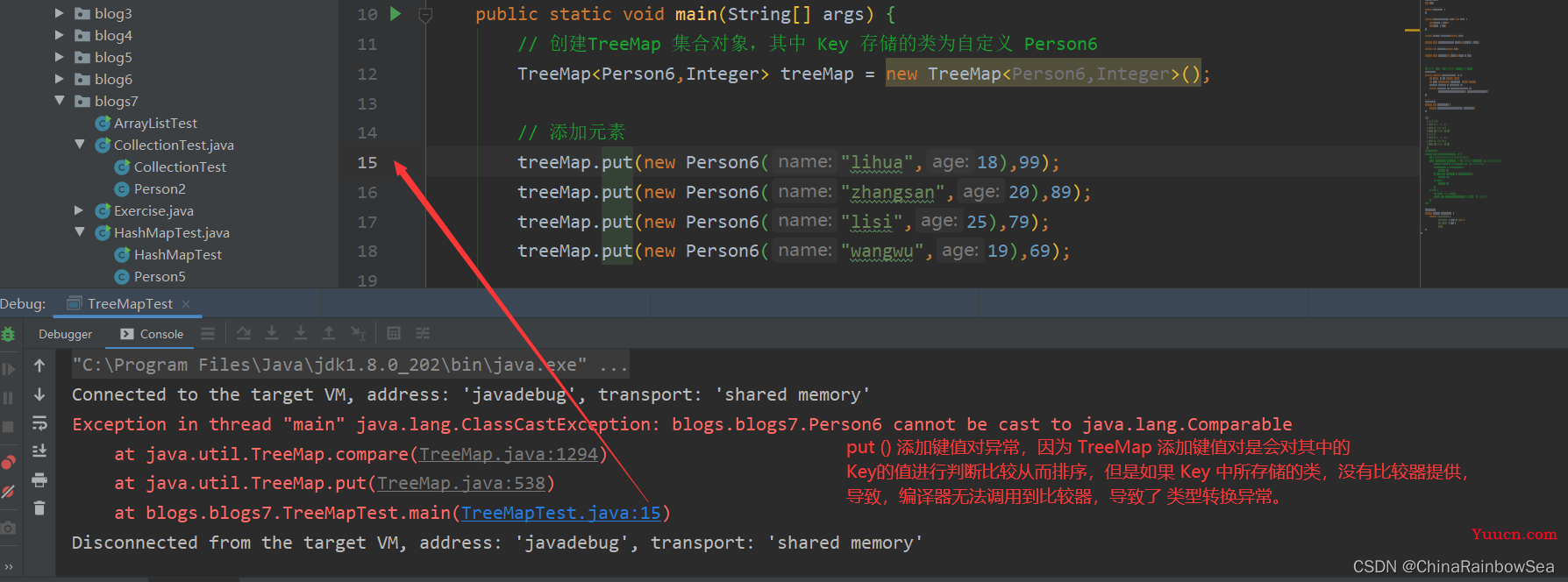
TreeMap 集合中存储自定义类 Person6 对象,其中的 Key 存储的类为自定义 Person6 对象,该对象重写了 equals() 和 hashCode()方法,但是没有重写比较器的情况,报异常:java.lang.ClassCastException 类型转换异常。
将其中的Person6 中 age 年龄,升序排列
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建TreeMap 集合对象,其中 Key 存储的类为自定义 Person6
TreeMap<Person6,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<Person6,Integer>();
// 添加元素
treeMap.put(new Person6("lihua",18),99);
treeMap.put(new Person6("zhangsan",20),89);
treeMap.put(new Person6("lisi",25),79);
treeMap.put(new Person6("wangwu",19),69);
// 遍历集合
// 遍历 TreeMap 集合
// 获取到key-value 存储的 Set Entry 内部类集合对象
Set<Map.Entry<Person6, Integer>> entries = treeMap.entrySet();
// 获取到该 Set Entry 内部类集合的迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<Person6, Integer>> iterator = entries.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Person6, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--->" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
class Person6 {
String name;
int age;
public Person6() {
}
public Person6(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
// 当对象中的 name 和 age 属性值相同返回 true,否则返回 fasle
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Person6)) return false;
Person6 person6 = (Person6) o;
return getAge() == person6.getAge() &&
Objects.equals(getName(), person6.getName());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getName(), getAge());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person6{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
修正: 对 Key 中所存储的类,提供比较器,方式一:自然排序,该存储类实现 java.lang.Comparable接口,并重写其中的 CompareTo()重写方法。
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建TreeMap 集合对象,其中 Key 存储的类为自定义 Person6
TreeMap<Person6,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<Person6,Integer>();
// 添加元素
treeMap.put(new Person6("lihua",18),99);
treeMap.put(new Person6("zhangsan",20),89);
treeMap.put(new Person6("lisi",25),79);
treeMap.put(new Person6("wangwu",19),69);
// 遍历集合
// 遍历 TreeMap 集合
// 获取到key-value 存储的 Set Entry 内部类集合对象
Set<Map.Entry<Person6, Integer>> entries = treeMap.entrySet();
// 获取到该 Set Entry 内部类集合的迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<Person6, Integer>> iterator = entries.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Person6, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--->" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
class Person6 implements Comparable<Person6>{
String name;
int age;
public Person6() {
}
public Person6(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
// 当对象中的 name 和 age 属性值相同返回 true,否则返回 fasle
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Person6)) return false;
Person6 person6 = (Person6) o;
return getAge() == person6.getAge() &&
Objects.equals(getName(), person6.getName());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getName(), getAge());
}
/**
* 升序的比较规则:
* this > 参数 ,返回 > 0
* this < 参数,返回 < 0
* this == 参数,返回 == 0;
* 降序反过来:
* this > 参数 ,返回 < 0
* this < 参数,返回 > 0
* this == 参数,返回 == 0;
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Person6 o) {
// 首先判断该需要比较的参数是否是同一个实例,同一个实例的对象才能比较
if(o instanceof Person6) { // 其实这里我们使用了<Person3 o> 泛型限定了,就不需要判断了
Person6 person6 = (Person6) o; // 是对应的实例向下转型。
if(this.age > person6.age) {
return 1;
} else if( this.age < person6.age) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
} else {
// throw 可以替代 return
throw new RuntimeException("类型不一致"); // 抛出运行时异常
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person6{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
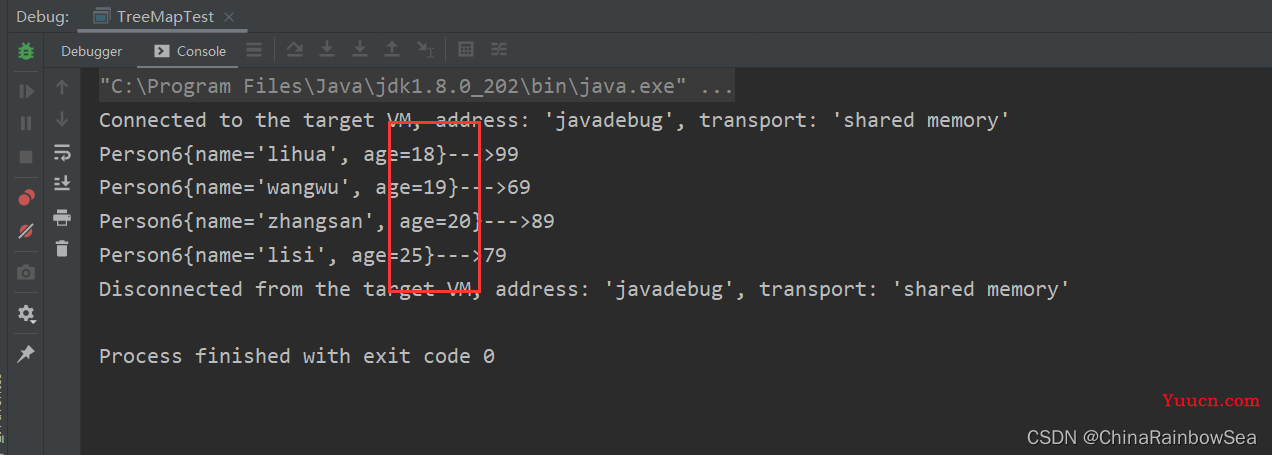
修改方式二:定制排序 创建 TreeMap 集合对象时,将一个匿名实现Com 的类,作为参数,传递给构造器。该匿名实现类定制排序按照你 Perso6 中的 age 年龄降序排列
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator); // 构造一个新的,空的树图,按照给定的比较器排序。
package blogs.blogs7;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 TreeMap 集合对象,将匿名实现的比较器(定制排序),作为参数,传递给构造器
TreeMap<Person6,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<Person6,Integer>(new Comparator<Person6>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person6 o1, Person6 o2) {
// 判断是否是对应比较的实例,其实这里我们可以不用判断的,因为使用的泛型限定
if(o1 instanceof Person6 && o2 instanceof Person6) {
Person6 p1 = (Person6)o1;
Person6 p2 = (Person6)o2; // 向下转型为对应的实例对象,从而获取比较属性
if(p1.age > p2.age) {
return -1;
} else if(p1.age < p2.age) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
// throw 可以代替 return
throw new RuntimeException("类型不一致"); // 抛出运行时异常
}
});
// 添加元素
treeMap.put(new Person6("lihua",18),99);
treeMap.put(new Person6("zhangsan",20),89);
treeMap.put(new Person6("lisi",25),79);
treeMap.put(new Person6("wangwu",19),69);
// 遍历集合
// 遍历 TreeMap 集合
// 获取到key-value 存储的 Set Entry 内部类集合对象
Set<Map.Entry<Person6, Integer>> entries = treeMap.entrySet();
// 获取到该 Set Entry 内部类集合的迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<Person6, Integer>> iterator = entries.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Person6, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--->" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
class Person6 implements Comparable<Person6>{
String name;
int age;
public Person6() {
}
public Person6(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
// 当对象中的 name 和 age 属性值相同返回 true,否则返回 fasle
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Person6)) return false;
Person6 person6 = (Person6) o;
return getAge() == person6.getAge() &&
Objects.equals(getName(), person6.getName());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getName(), getAge());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person6{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
6. Map实现类之四:Hashtable

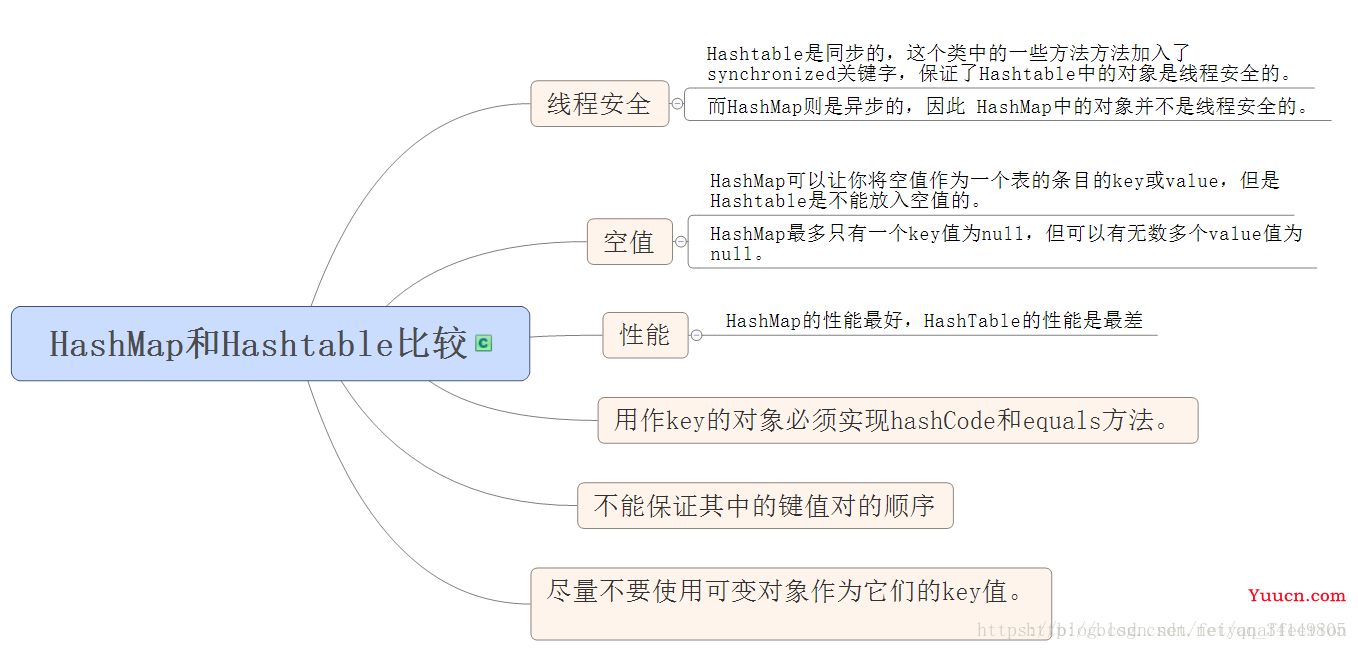
-
Hashtable 是个古老的 Map 实现类,JDK1.0 就提供了。不同于 HashMap ,Hashtable 是线程安全的,其中的方法基本上都不被
synchronized。 - Hashtable 实现原理和 HashMap 相同,功能相同。底层都使用哈希结构,速度快,很多情况下可以互用。
-
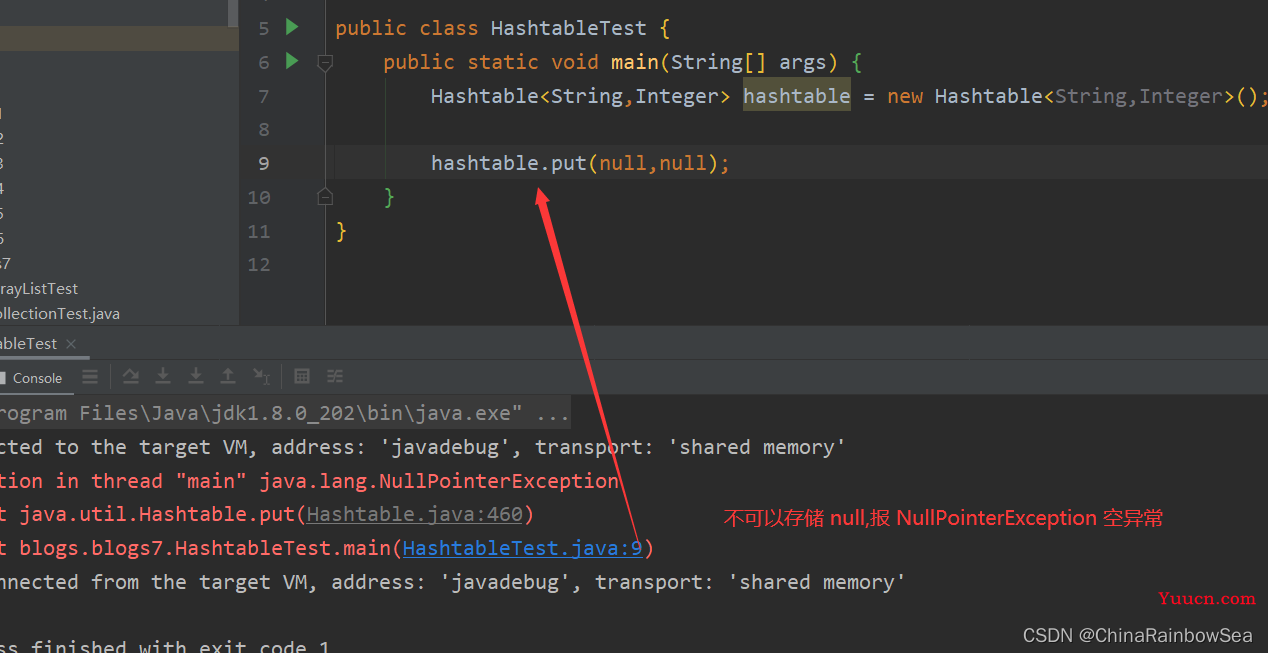
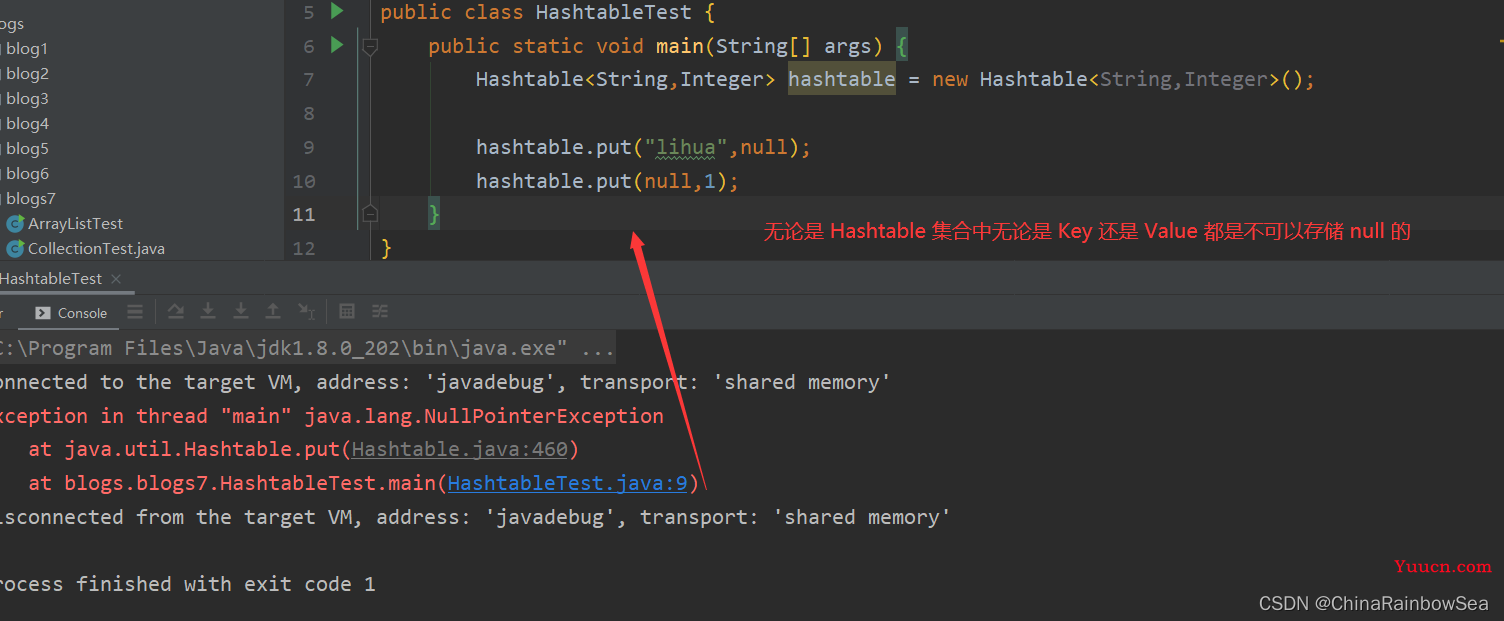
Hashteble 与 HashMap 不同,Hashtable 不允许使用 null 作为 Key 和 Value 的值。不然报,
java.lang.NullPointerException空指针异常。 - Hashtable 与 HashMap 一样,Hashtable 也不能保证其中 Key-Value 键值对的顺序。
- 同样的 其中的 Key 值内部是由 Set 集合存储的,无序,不可重复性,所存储类必须重写 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法。
-
Hashtable 判断两个 key 相等,两个 value 相等的标准,与 HashMap 是一样的。Hashtable和HashMap 一样,底层都是哈希表的数据结构,Hashtable 的初始容量为 11,默认加载因子是 : 0.75,Hashtable 的扩容:
原容量 * 2 + 1;
HashMap和HashTable的比较:
举例 :
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashtableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable<String,Integer> hashtable = new Hashtable<String,Integer>();
hashtable.put("lihua",1);
hashtable.put("zhangsan",2);
hashtable.put("lisi",3);
hashtable.put("wangwu",4);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = hashtable.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = entries.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
7. Map实现类之五:Properties
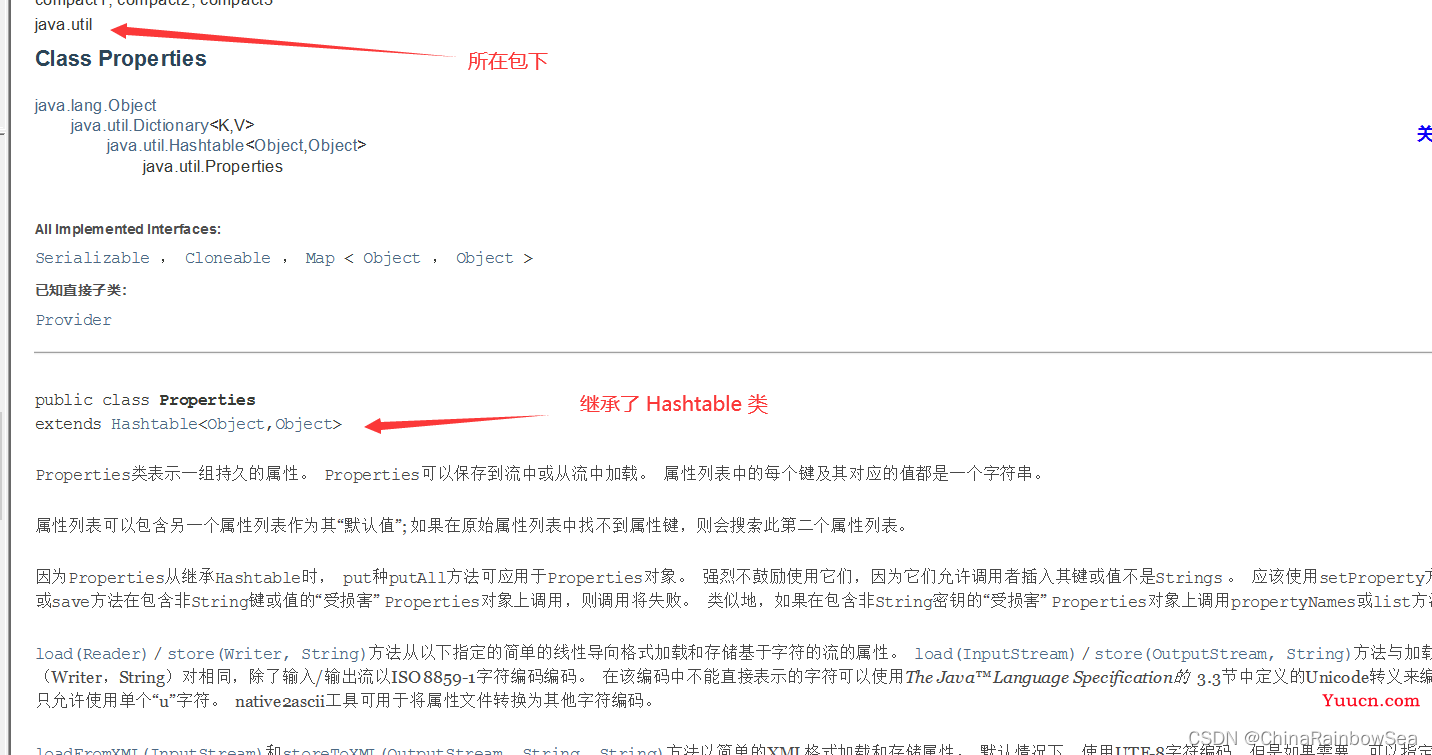
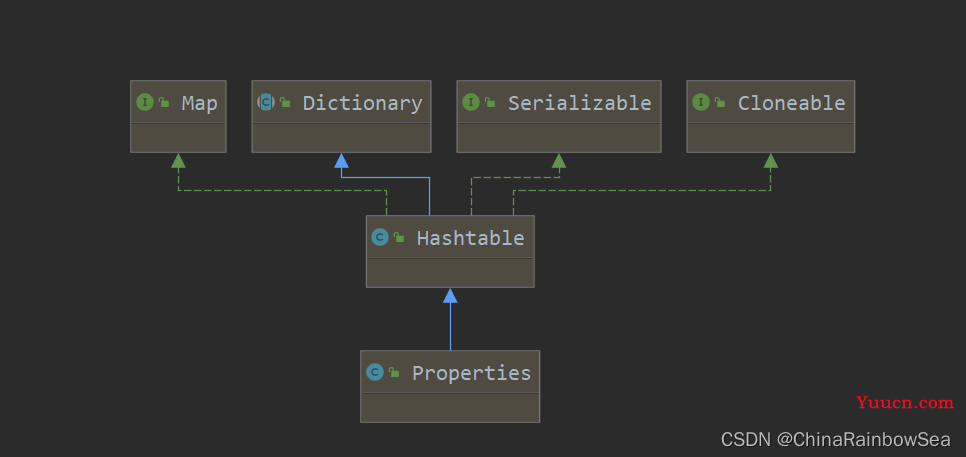
- Properties 类是 Hashtable 的子类,该对象用于处理读取属性文件。
- 由于属性文件里的 key,value都是字符串类型的,所以 Properties 里的 key 和 value 都是字符串类型 。
- 存取数据时,建议使用 setProperty(String key,String value) 方法 和 getProperty(String key) 方法。
public Object setProperty(String key,String value); // 致电Hashtable方法put 。 提供与getProperty方法的并行性 。 强制使用字符串的属性键和值。 返回的值是Hashtable调用put的结果。简单的说:就是向Property 集合中添加键值对元素。
public String getProperty(String key); // 通过 key 找到对应的 value值,如果没有找到返回 null
举例:
首先我们先在项目中(注意添加到顶级项目中也就是如下的Test 项目下,不是Test2,或者 day模块下 ,不然无法读取到)添加一个属性文件(以.properties后缀的配置文件)用于Properties 集合读取,内容如下:
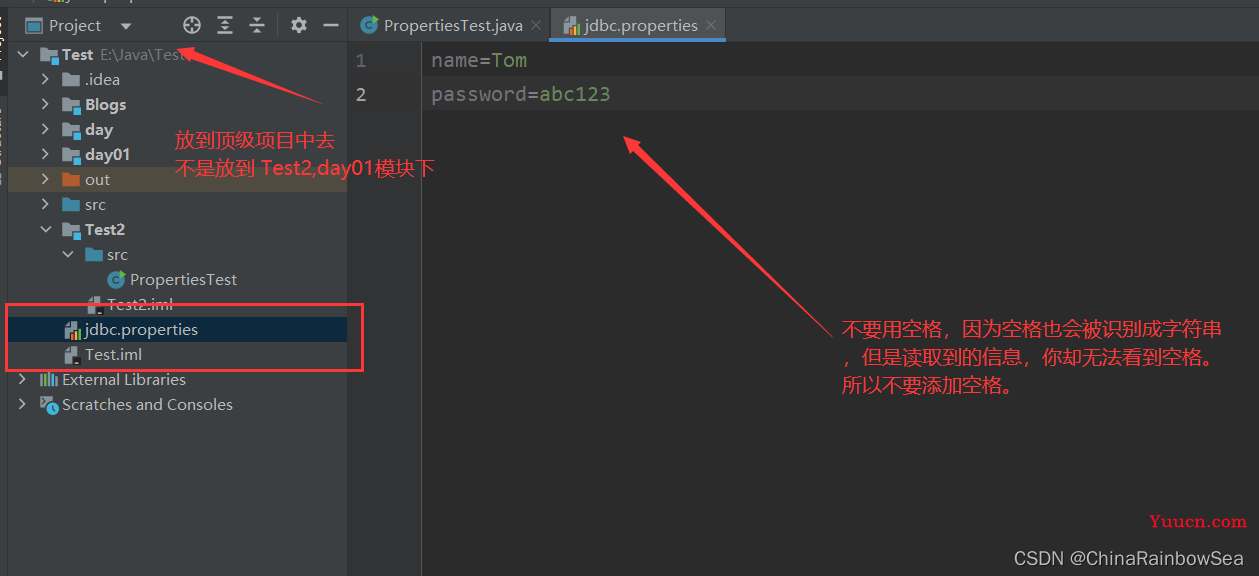
name=Tom
password=abc123
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class PropertiesTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Properties 集合常用来处理配置文件:key 和 value 都是String类型
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
// IO流读取文件信息,需要异常处理
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"); // 文件名
properties.load(fileInputStream); // 加载流对应的文件,同样需要异常处理
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
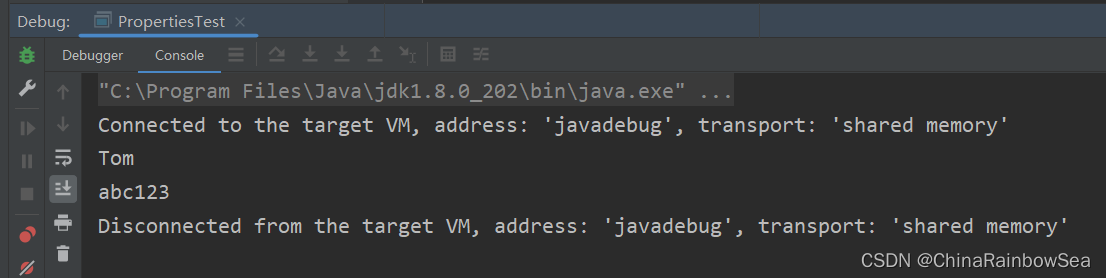
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
String password = properties.getProperty("password"); // 根据对应文件中的 key 值获取到对应的value值
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(password);
}
}
8. Map 接口下的集合遍历方式
Map 接口下的集合的遍历方式:注意:Map 集合中没有下标可以访问的。也没有迭代器可以使用的。
方式一: 普遍使用,二次取值。通过获取 keySet() 方法获取到 Map 集合中所有的 key 值,返回一个 Set 集合。再通过遍历 Set 集合中存储的所有的 key ,使用 get(key) 方法获取到对应的 value值。
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Traverse {
// Map 集合遍历方式一:
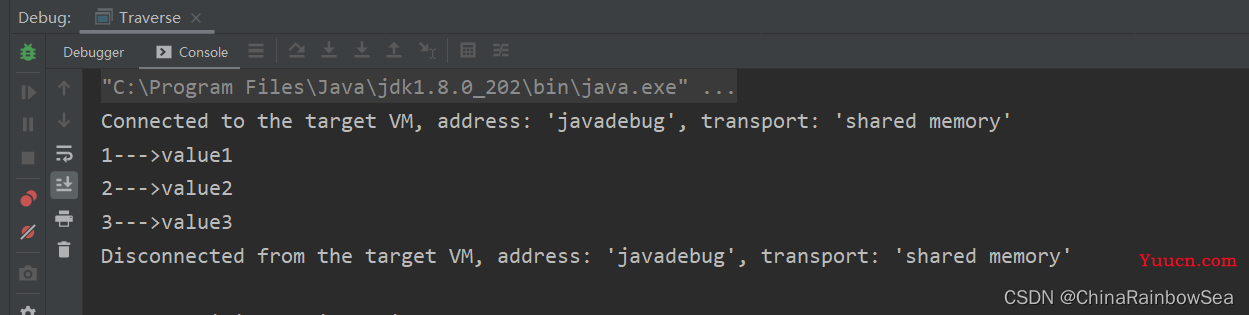
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("1", "value1");
map.put("2", "value2");
map.put("3", "value3");
// 1.获取到该 Map 集合当中的所有 Key 值
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
// 2.遍历所有的 key 值
for (String key : keys) {
// 3. 通过 key 获取到对应的 value 值
System.out.println(key + "--->" + map.get(key));
}
}
}
方式二: 通过使用 entrySet() 方法,返回一个:Set< Map.Entry<K, V> > 集合对象, 再通过获取到该 Set<Map.Entry> 集合 的迭代器,通过迭代器遍历,获取到Map.Entry中存储的 key(getKey()), value(getVale()) 方法
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Traverse {
// Map 集合遍历方式二:
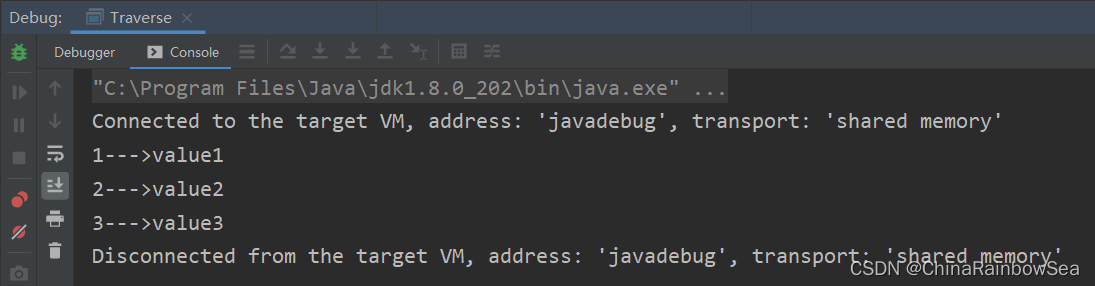
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("1", "value1");
map.put("2", "value2");
map.put("3", "value3");
// 1. 获取到 Set<Map.Entry> 集合对象
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
// 2. 获取到该 Set<Map.Entry> 集合 的迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = entries.iterator();
// 3. 通过迭代器遍历,获取到Map.Entry中存储的 key,value值
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--->" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
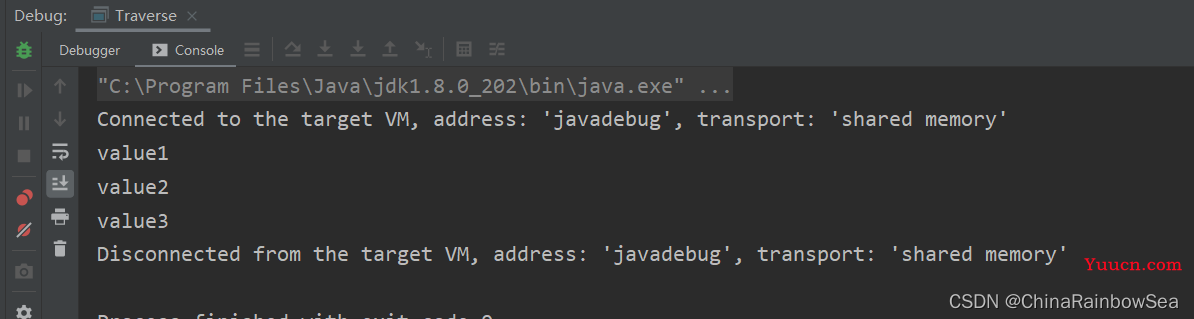
方式三: 推荐,尤其是容量大时。因为这是一次性获取到 Map 中所有的key-value 值后,再取出的,效率高
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Traverse {
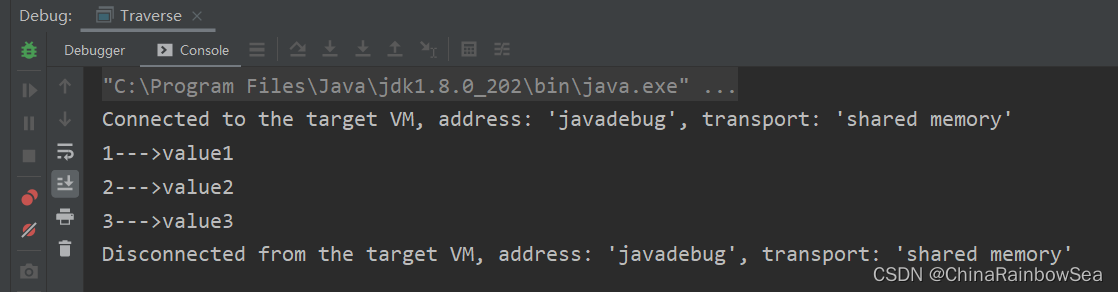
// Map 集合遍历方式三:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("1", "value1");
map.put("2", "value2");
map.put("3", "value3");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--->" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
方式四: 通过Map.values() 返回一个Collection 集合遍历所有的value,但不能遍历key
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Traverse {
// Map集合遍历方式四:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("1", "value1");
map.put("2", "value2");
map.put("3", "value3");
// 获取到集合当中所有的 value值
Collection<String> values = map.values();
for (String value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
9. Collections工具类
一个独立的集合 工具类
- Collections 是一个操作 Set,List 和 Map 等集合的工具类。
- 注意区别:Collection 是一个接口集合,而 Collection
s多了个 s 的是 集合工具类,都是在java.util.包下的。 - Collections 中提供了一系列静态的方法(工具方法麻,一般都是静态方法)对集合元素进行排序,查询和修改等操作,还提供了对集合对象设置不可变,对集合对象实现同步控制(解决线程安全问题)等方法。
9.1 Collections常用方法
排序:
- reverse(List lsit) : 反转 List 中元素的顺序
public static void reverse(List<?> list); // 反转 List 中元素的顺序
- shuffle(List list): 对 List 集合元素进行随机排序
public static void shuffle(List<?> list); // 对 List 集合元素进行随机排序
-
sort(List list) : 根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序,注意的是: 排序需要存储的类有比较器调用 自然排序(实现
java.lang.Comparable的接口 / 定制排序 Comparator接口)
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list); // 根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序
- sort(List list, Comparator c) : 根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list,Comparator<? super T> c); // 根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
- swap(List list , int i , int j ) : 将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换。注意是左闭右开的。
public static void swap(List<?> list,int i,int j); // 将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换
查找,替换 :
- max(Collection c) : 根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素。
public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll); // 根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- max(Collection coll, Comarator comp) : 根据Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素。
public static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll,Comparator<? super T> comp); // 根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- min(Collection c) : 根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素。
public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T min(Collection<? extends T> coll); // 根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素。
- min(Collection coll, Comarator comp) : 根据Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素。
public static <T> T min(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp); // 根据Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素。
- replaceAll(List list,T oldVal,T newVal) : 用新值替换List 对象的所有旧值。注意存储的类需要重写 equals()方法,才能比较判断找到对应替换的值。
public static <T> boolean replaceAll(List<T> list,T oldVal,T newVal); // 用新值替换List 对象的所有旧值.
- frequency(Collection c , Object o) : 返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数,注意 :存储的类需要重写 equals()方法才能比较判断查找对应的值的个数。
public static int frequency(Collection<?> c,Object o); // 返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
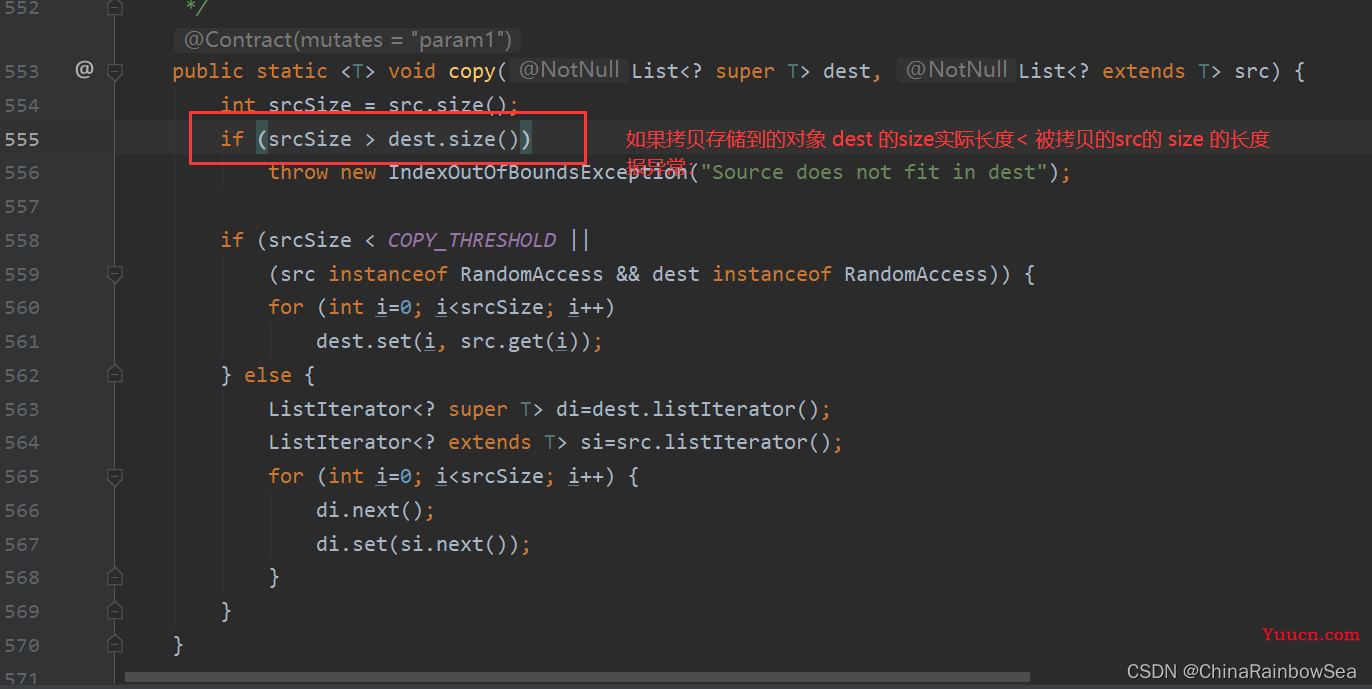
- copy(List dest,List src) : 将 src 集合中的内容复制到 dest 集合当中。
public static <T> void copy(List<? super T> dest,List<? extends T> src); // 将 src 集合中的内容复制到 dest 集合当中
注意该 copy(List dest,List src) 方法,两个集合对象存储的数据类型是必须是一样的,不然无法拷贝添加到 dest 集合当中的。
还有拷贝存储到的对象 dest 的 size()长度 < 被拷贝的 src 的 size()长度 就会拷贝失败,报异常: IndexOutOfBoundsException
所以拷贝存储到的对象 dest 的 size()长度 必须 >= 被拷贝的 src 的 size()长度 。注意是 size()实际存储元素数据的长度,不是length()集合的长度 。
如下源码:
举例 : 解决思路如下:
package blogs.blogs7;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
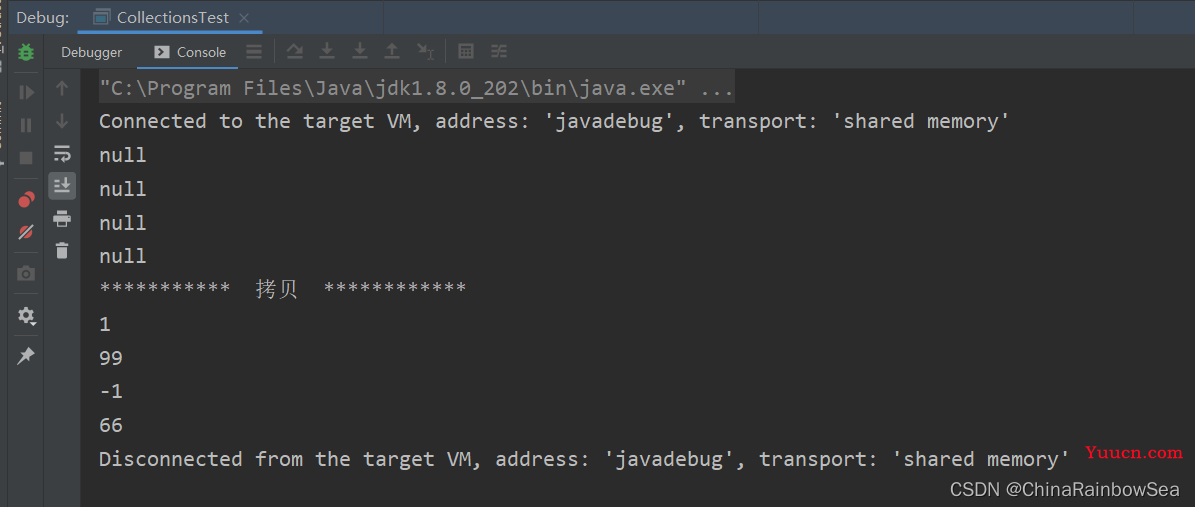
public class CollectionsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> src = new ArrayList<Integer>();
src.add(1);
src.add(99);
src.add(-1);
src.add(66);
// 创建一个 和 src 集合存储类型一样的 Arrays.asList(new Integer[src.size()])数组,并设置该数组的大小长度为 src.size()
// 再使用这个数组创建拷贝存储的 desc 集合对象,默认数组没有添加数据(这里的是 null)
// 这样就 desc 就拥有了一个和 sec集合一样大小的 size()长度了。
List<Integer> desc = new ArrayList<Integer>();
desc = Arrays.asList(new Integer[src.size()]);
for (Integer integer : desc) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
// copy()拷贝
Collections.copy(desc, src);
System.out.println("*********** 拷贝 ************");
for (Integer num : desc) {
System.out.println(num);
}
}
}
10. 总结:
补充 :各个集合的转换,可以使用对应的方法,或构造器
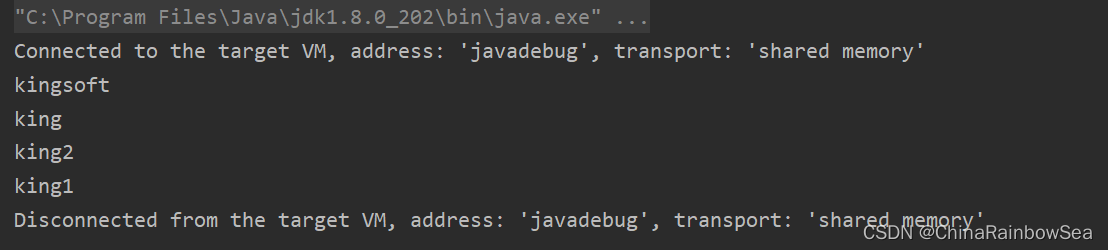
@Test
public void test2() {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("king");
set.add("kingsoft");
set.add("king2");
set.add("king1");
// 将Set集合转换成List集合
List<String> myList = new ArrayList<>(set);
for(String s : myList) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
-
Map 接口下的集合的特点:集合的key 就是一个 Set 集合存储的。而 value 值则是被 Collectio接口集合存储的。
在Set 集合中放数据,实际上放到了Map集合的key 部分中去了。 -
注意:Map集合中的 Key 都是存储在 Set 集合当中的(该集合无序,不可重复),所以Map集合当中的 key 存储的类必须重写
equals() 和 hashCode()方法。不然无法处理 Key 的不可重复特点 。。但是其中的 value 值是可以存储重复的数据的。而 value 值则是被 Collection 接口集合存储的。 -
Map 接口与 Collection 并列存在的,用于保存具有映射关系的数据:key-value 被称为 键值对 。一个key-value 构成一个
Map.Entry。所有的 Map.Entry 构成的集合是 Set 无序的,不可重复的。 - 理解 HashMap 中的 put() 添加键值对元素数据的原理,以及扩容,和树化的机制。区别 JDK7 / JDK8 的机制不同点
-
TreeMap 的 排序是对 Key 的内容进行排序的,其中的 Key 值内部是由 Set 集合存储的,无序,不可重复性,所存储类必须重写 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法。因为会自动排序,所以还需要实现排序:两种方式一种是:
-
自然排序: TreeMap 的所有的 Key 必须实现(实现
java.lang.Comparable的接口,而且所有 的 Key 应该是同一个类的对象(因为不是同一类型无法比较判断),否则将会抛出ClasssCastException自然排序,重写其中的compareTo()抽象方法) 。在Java当中所有的包装类和String都实现了该java.lang.Comparable接口。所以一般要实现该接口的都是自定的类。 - 定制排序: 创建 TreeMap 时,传入一个 Comparator 对象,该对象负责对 TreeMap 中的所有 key 进行排序。此时不需要 Map 的 Key 实现 Comparable 接口
-
自然排序: TreeMap 的所有的 Key 必须实现(实现
11. 最后:
限于自身水平,其中存在的错误,希望大家给予指教,韩信点兵——多多益善,谢谢大家,后会有期,江湖再见!!!