"Good code is its own best documentation." - Steve McConnell
“好代码本身就是最好的文档。” —— 史蒂夫·麦克康奈尔
0x00 大纲
- 0x00 大纲
-
0x01 前言
- 数据与结构的解耦
- offsetof
- container_of
- 通用链表
- 0x02 链表节点
- 0x03 创建链表
-
0x04 插入节点
- 任意位置的插入
- 插入到最前
- 插入到最后
- 0x05 删除节点
- 0x06 替换节点
-
0x07 遍历和获取节点数据
- 遍历链表
- 获取节点数据
- 0x08 小结
0x01 前言
数据与结构的解耦
在上篇文章,我们通过将链表的节点放在具体数据类型的结构体内,这样,抽象(链表结构)不再依赖于细节(数据类型),细节(数据类型)依赖于抽象(链表结构),利用依赖倒置的思想,完成了数据与结构的解耦,进而实现了通用的链表。
offsetof
offsetof 是定义在C标准库头文件<stddef.h>中的一个宏,它会生成一个类型为size_t的无符号整型,代表一个结构成员相对于结构体起始的字节偏移量(offset)。
container_of
cotainer_of返回的是结构体成员所在结构体的起始地址(指针),它的原理是用成员变量的起始地址减去成员变量在结构体内的偏移量(用offsetof求得)。
通用链表
有了上面三个理论基础,我们就具备了创建通用链表的条件。下面将通过具体的代码来演示如何构造和使用这样的链表结构,全程图解,包你学会。
0x02 链表节点
我们的通用链表是一个双向循环链表,它由一个链表头节点list_head和若干个位于结构体中的中间节点list_node(注意不包括数据域部分)构成。
我们定义了一个名为struct list_head的结构体类型作为我们的链表节点,它包含一个指向前驱节点的指针*prev和一个指向后继节点的指针*next。同时,为了方便后续的编码和增强代码的可读性,又定义了list_head和list_node两个结构体类型别名,它们是同一种数据类型的不同名称。
typedef struct list_head
{
struct list_head *next, *prev;
} list_head, list_node;
下面的代码简单说明了这种方法给我们带来的语义上的便利,后面的代码示例将延续这样的风格。
list_head head;// 等价于 struct list_head head;
list_node node;// 等价于 struct list_head node;
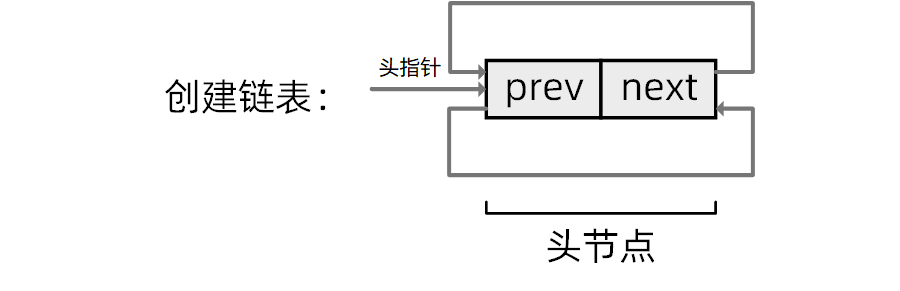
0x03 创建链表
/**
* 初始化一个链表(头)节点,它的前驱和后继指针都指向自己
* @param list: 需要初始化的节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_init(list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
0x04 插入节点
任意位置的插入
/**
* 将节点entry插入到prev和next之间
* @param entry: 新节点的指针
* @param prev: 指向插入位置前驱节点的指针
* @param next: 指向插入位置后继节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void __list_add(list_node *entry,
list_node *prev,
list_node *next)
{
next->prev = entry;
entry->next = next;
entry->prev = prev;
prev->next = entry;
}
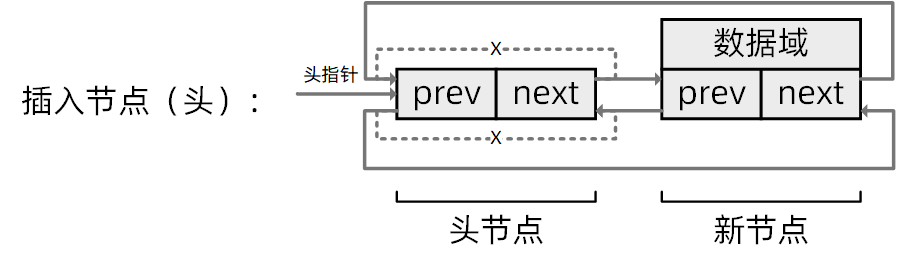
插入到最前
/**
* 将节点entry插入到头节点之后
* 头插,新节点成为第一个节点
* @param entry: 指向新节点的指针
* @param head: 指向头节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_add_head(list_node *entry,
list_head *head)
{
__list_add(entry, head, head->next);
}
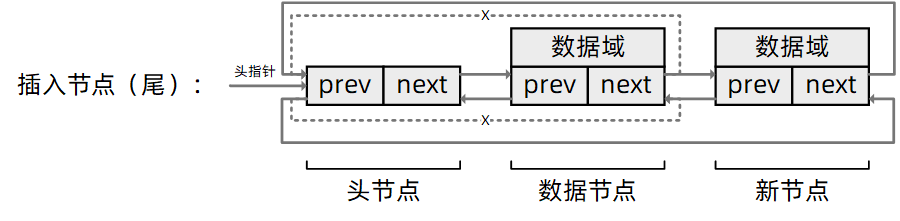
插入到最后
/**
* 将节点entry插入到头节点之前
* 尾插,新节点成为最后一个节点
* @param entry: 指向新节点的指针
* @param head: 指向头节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_add_tail(list_node *entry,
list_head *head)
{
__list_add(entry, head->prev, head);
}
0x05 删除节点
/**
* 删除节点
* @param prev: 被删除节点的前驱指针
* @param head: 被删除节点的后继指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void __list_del(list_node * prev,
list_node * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
/**
* 删除节点,并将其前驱指针和后继指针指向NULL
* @param prev: 指向被删除节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_del(list_node *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->prev = entry->next = NULL;
}
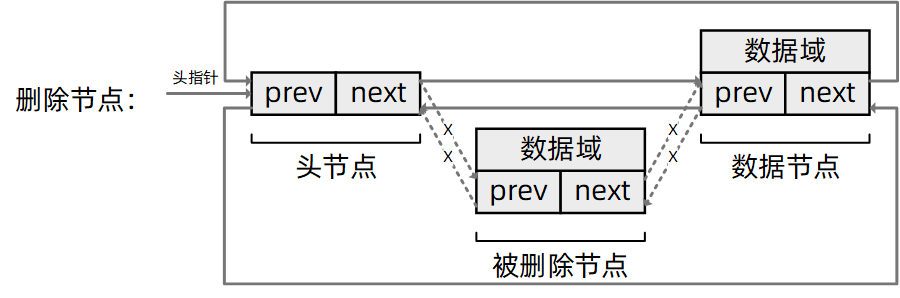
可以看到,由于节点本身并不存储数据,所以,在删除链表节点的时候,也就不用考虑对数据域进行内存释放的操作。
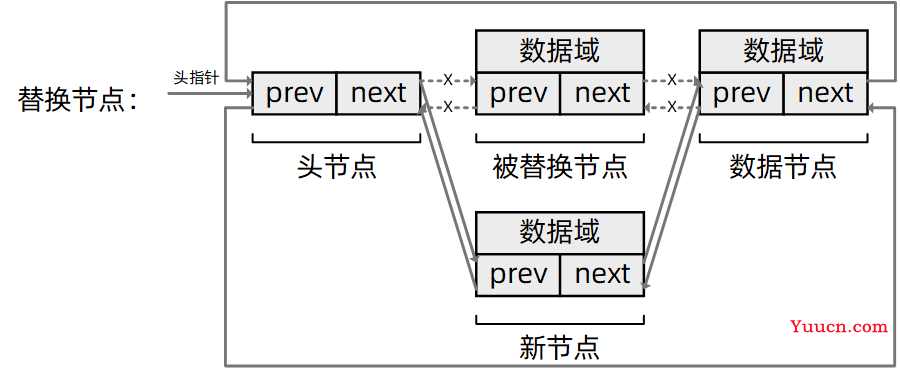
0x06 替换节点
/**
* 替换节点
* @param old: 指向被替换节点的指针
* @param entry: 指向新节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_replace(list_node *old,
list_node *entry)
{
entry->next = old->next;
entry->next->prev = entry;
entry->prev = old->prev;
entry->prev->next = entry;
}
0x07 遍历和获取节点数据
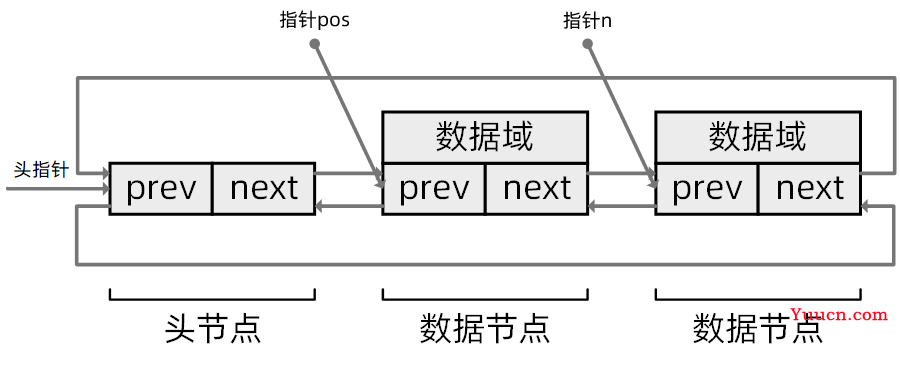
遍历链表
/**
* 快速遍历链表(不可进行删除操作)
* @param pos: 指向当前节点位置的指针
* @param head: 指向头节点的指针
* @return void
**/
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
/**
* 遍历链表(可进行删除操作)
* @param pos: 指向当前节点位置的指针
* @param n: 指向下一节点位置的指针
* @param head: 指向头节点的指针
* @return void
**/
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \
pos = n, n = pos->next)
获取节点数据
/**
* 获得节点所在数据结构体的起始地址(指针)
* @param ptr: 指向节点的指针
* @param type: 数据结构体类型
* @param member: 节点在数据结构体中被定义的变量名称
* @return void
**/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
0x08 小结
将上述的所有基本操作汇总后,得到我们的通用链表定义文件list.h(你可以在Linux内核的源码中找到它,这里的代码稍微作了一点修改):
#ifndef LIST_H
#define LIST_H
#include <stddef.h>
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) \
((type *)((char *)(ptr)-offsetof(type,member)))
typedef struct list_head
{
struct list_head *next, *prev;
} list_head, list_node;
/**
* 初始化一个链表(头)节点,它的前驱和后继指针都指向自己
* @param list: 需要初始化的节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_init(list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
/**
* 将节点entry插入到prev和next之间
* @param entry: 新节点的指针
* @param prev: 指向插入位置前驱节点的指针
* @param next: 指向插入位置后继节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void __list_add(list_node *entry,
list_node *prev,
list_node *next)
{
next->prev = entry;
entry->next = next;
entry->prev = prev;
prev->next = entry;
}
/**
* 将节点entry插入到头节点之后
* 头插,新节点成为第一个节点
* @param entry: 指向新节点的指针
* @param head: 指向头节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_add_head(list_node *entry,
list_head *head)
{
__list_add(entry, head, head->next);
}
/**
* 将节点entry插入到头节点之前
* 尾插,新节点成为最后一个节点
* @param entry: 指向新节点的指针
* @param head: 指向头节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_add_tail(list_node *entry,
list_head *head)
{
__list_add(entry, head->prev, head);
}
/**
* 删除节点
* @param prev: 被删除节点的前驱指针
* @param head: 被删除节点的后继指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void __list_del(list_node * prev,
list_node * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
/**
* 删除节点,并将其前驱指针和后继指针指向NULL
* @param prev: 指向被删除节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_del(list_node *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->prev = entry->next = NULL;
}
/**
* 替换节点
* @param old: 指向被替换节点的指针
* @param entry: 指向新节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline void list_replace(list_node *old,
list_node *entry)
{
entry->next = old->next;
entry->next->prev = entry;
entry->prev = old->prev;
entry->prev->next = entry;
}
/**
* 判断循环双链表是否为空(只有头节点)
* @param head: 指向头节点的指针
* @return void
**/
static inline int list_empty(const list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
/**
* 快速遍历链表(不可进行删除操作)
* @param pos: 指向当前节点位置的指针
* @param head: 指向头节点的指针
* @return void
**/
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
/**
* 遍历链表(可进行删除操作)
* @param pos: 指向当前节点位置的指针
* @param n: 指向下一节点位置的指针
* @param head: 指向头节点的指针
* @return void
**/
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \
pos = n, n = pos->next)
/**
* 获得节点所在数据结构体的起始地址(指针)
* @param ptr: 指向节点的指针
* @param type: 数据结构体类型
* @param member: 节点在数据结构体中被定义的变量名称
* @return void
**/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
#endif // LIST_H