1. 路由概念
路由的本质就是一种对应关系,根据不同的URL请求,返回对应不同的资源。那么url地址和真实的资源之间就有一种对应的关系,就是路由。
SPA(Single Page Application)单页面应用程序,基于前端路由而起:整个网站只有一个页面,通过监听地址栏中的变化事件,来通过Ajax局部更新内容信息显示、同时支持浏览器地址栏的前进和后退操作。
前端路由有两种模式:hash 模式和 history 模式。
2. hash模式
概述:
hash 路由模式是这样的:http://xxx.abc.com/#/xx。 有带#号,后面就是 hash 值的变化。改变后面的 hash 值,它不会向服务器发出请求,因此也就不会刷新页面。并且每次 hash 值发生改变的时候,会触发 hashchange 事件。因此我们可以通过监听该事件,来知道 hash 值发生了哪些变化。
window.addEventListener('hashchange', ()=>{
// 通过 location.hash 获取到最新的 hash 值
console.log(location.hash);
});
使用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>hash路由</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>
<!-- 通过标签导航 声明式导航 -->
<a href="#/home" rel="external nofollow" >首页</a>
<!-- location.href='#/home' js方式进行导航切换 编程式导航 -->
</li>
<li>
<a href="#/about" rel="external nofollow" >关于</a>
</li>
</ul>
<div id="routerView"></div>
<script>
const routerRender = () => {
// 每次都置空hash
let html = ''
// 根据地址栏hash值的不同返回对应的资源
try {
// 如果hash值为空就给一个home
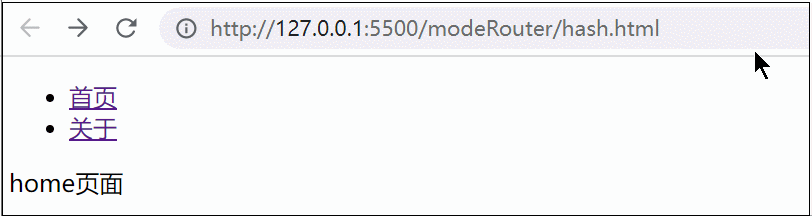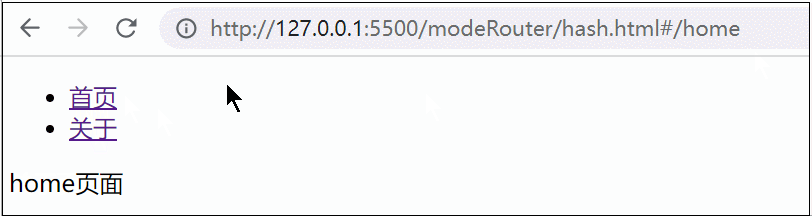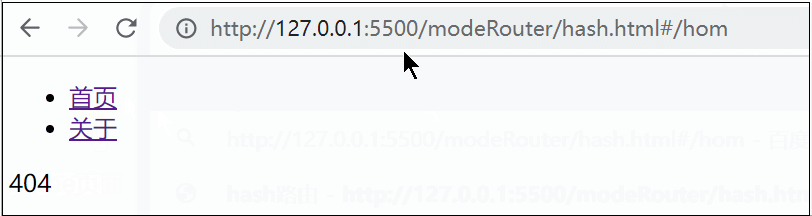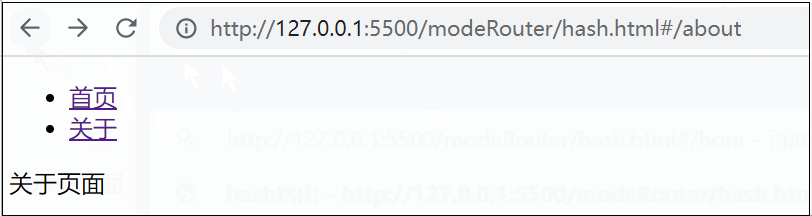
let hash = location.hash || '#/home'
html = component[hash.slice(2)]()
} catch (error) {
html = `<div>404</div>`
}
// 渲染到页面上
document.getElementById('routerView').innerHTML = html
}
const component = {
home() {
return `<div>home页面</div>`
},
about() {
return '<div>关于页面</div>'
}
}
window.onload = function () {
routerRender()
}
// 事件,监听地址栏中的hash值变化,实现回退
window.addEventListener('hashchange', routerRender)
</script>
</body>
</html>
注意:hash 模式既可以通过声明式导航,也可以通过编程式导航,上面的案例展示的是声明式导航。而下面将要讲到的 history 模式只能通过编程式导航实现,因为 history 是 js 对象。
优缺点:
优点:hash模式兼容性很强,刷新浏览器,页面还会存在
缺点:地址栏不优雅,有#存在,不利于seo,记忆困难
3. history路由模式
概述:
HTML5的History API为浏览器的全局history对象增加了该扩展方法。它是一个浏览器(bom)的一个接口,在window对象中提供了onpopstate事件来监听历史栈的改变,只要历史栈有信息发生改变的话,就会触发该事件。
history.pushState({},title,url); // 向历史记录中追加一条记录
history.replaceState({},title,url); // 替换当前页在历史记录中的信息。
window.addEventListener('popstate', function(event) {
console.log(event)
})
使用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>history模式</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="https://www.jb51.net/home" rel="external nofollow" >首页</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="https://www.jb51.net/about" rel="external nofollow" >关于</a>
</li>
</ul>
<div id="routerView"></div>
<script>
const component = {
home() {
return `<div>home页面</div>`
},
about() {
return '<div>关于页面</div>'
}
}
const routerRender = pathname => {
let html = ''
try {
html = component[pathname]()
} catch (error) {
html = `<div>404</div>`
}
document.getElementById('routerView').innerHTML = html
}
// history模式,它的路由导航,只能通过js来完成 , history它是js对象
// 给链接添加点击事件
document.querySelectorAll('a').forEach(node => {
node.addEventListener('click', function (evt) {
// 阻止a标签的默认跳转行为
evt.preventDefault()
// 跳转到指定的地址,能回退
// history.pushState
// 跳转到指定持址,不能回退
// history.replaceState
history.pushState({}, null, this.href)
// 渲染
routerRender(this.href.match(/\/(\w+)$/)[1])
})
})
// 在网页加载完毕后立刻执行的操作,即当 HTML 文档加载完毕后,立刻渲染 home 中的标签
window.onload = () => {
routerRender('home')
}
// 回退
window.addEventListener('popstate', function () {
routerRender(location.pathname.slice(1))
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
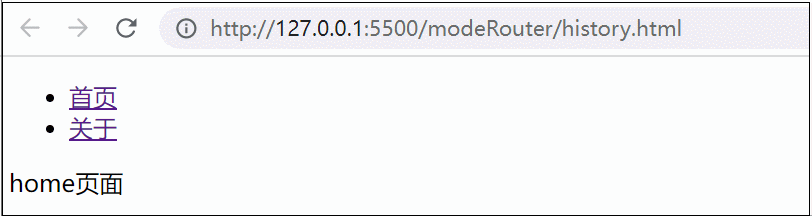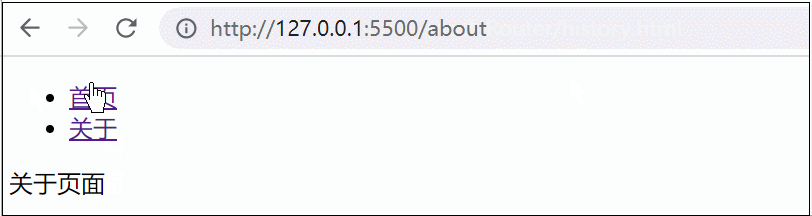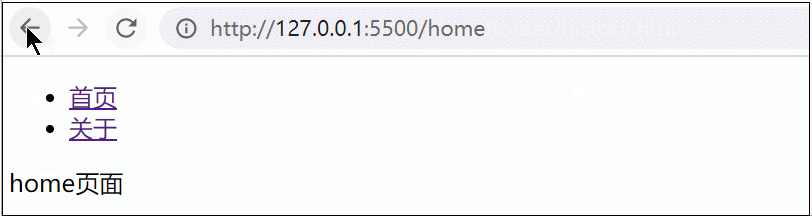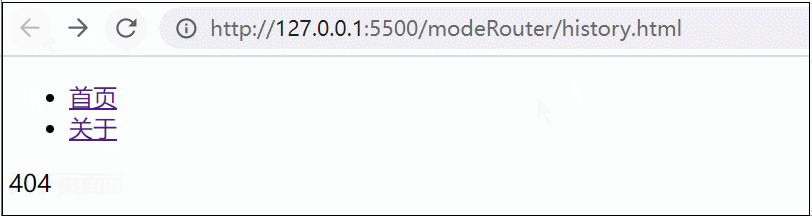
优缺点:
缺点:history模式,兼容性较差,刷新页面,页面会404,需要服务器端配置支持
优点:地址栏更优雅,方便记忆,有利于有seo
到此这篇关于Vue路由模式中的hash和history模式详细介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Vue路由模式 内容请搜索本站以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持本站!