参见generalized focal loss paper
其中包含有Quality Focal Loss 和 Distribution Focal Loss。
目录
-
- Quality Focal Loss
- Distribute Focal Loss
Quality Focal Loss
先来说一下Quality Focal Loss,
在这之前,先要了解一下Focal Loss, 在这篇文章里有写过。
它主要是解决class imbalance,同时降低容易分类的weight,使训练更集中到难分类的上面
我们从cross entropy入手:
cross entropy的公式如下:
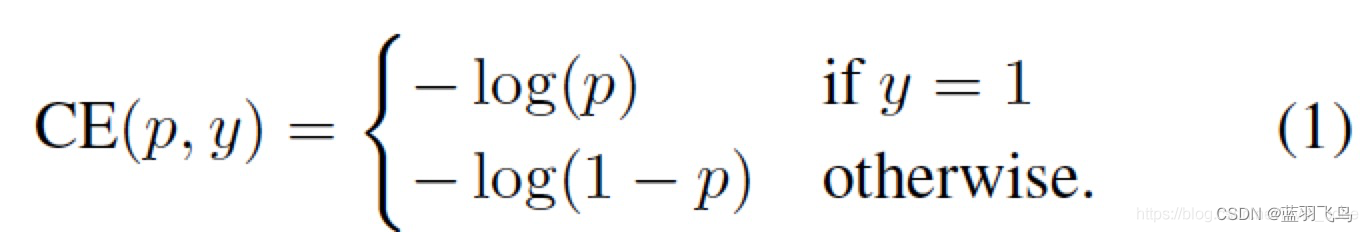
把其中的y=1时为p, y=0时1-p 写成一个
p
t
p_{t}
pt
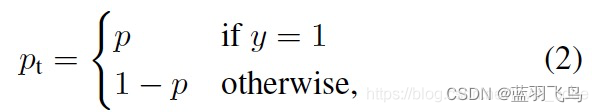
那么,cross entropy可以简化为:
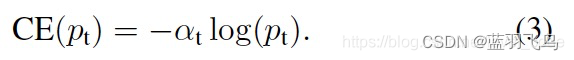
降低容易分类的weight, 比如
p
t
=
0.9
p_{t}=0.9
pt=0.9时,很容易分类,降低它的weight, 同时结合
α
t
\alpha_{t}
αt解决class imbalance的问题。
这个就是Focal Loss的公式。
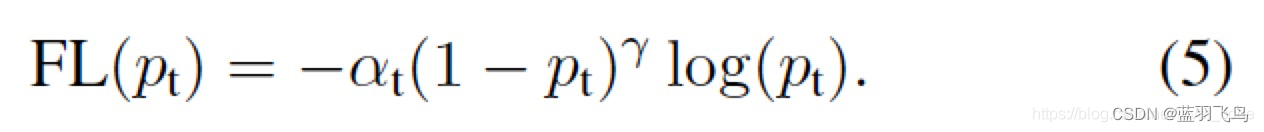
现在有一个问题,就是(1)训练集和测试集的用途是不同的,训练集单独用来训练,却和测试集一起在现实中做推理。而且supervision只用于positive sample, 但是有时negative sample会有更高的score

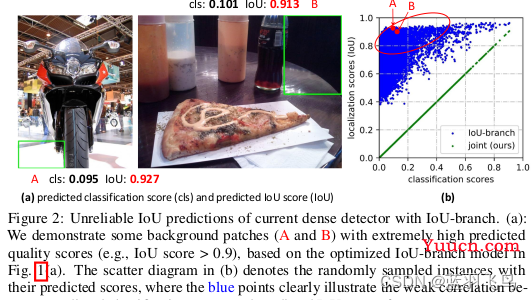
背景的IOU可能比positive sample还要大,所以作者把IOU和分类的score结合起来,
而且把one-hot label给soft化,具体就是把label的1 乘以 IOU,
这里的IOU是指预测出的bounding box和与之匹配的ground truth box的IOU。范围在0~1之间。
理论上来说一个预测box会匹配一个gt_box, 当匹配多个时,取cost最小的那个。
至于如何匹配,就是计算一张图片中有效的(自己定义)预测box和这张图片所有的ground truth box的IOU,
再取IOU>阈值的box作为最终预测的box。
每个box还会有一个class score.
class score经过sigmoid运算后就是公式中的
σ
\sigma
σ
公式中的
y
y
y是label乘以对应的IOU。
为了解决class imbalance的问题,还需要结合Focal Loss,
但是Focal Loss的label是0,1,而这里的soft label是小数,
所以把Focal Loss中的两项做一下扩展:
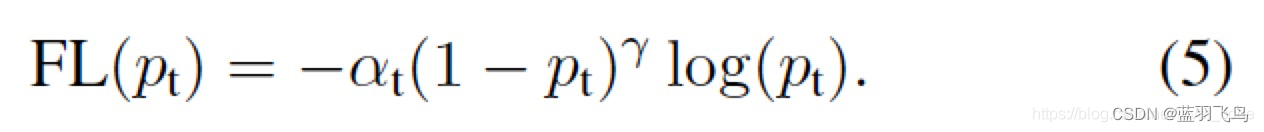

因此得到最后的QFL公式:
![]()
具体看下代码:
def quality_focal_loss(pred, target, beta=2.0):
r"""Quality Focal Loss (QFL) is from `Generalized Focal Loss: Learning
Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection
<https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.04388>`_.
Args:
pred (torch.Tensor): Predicted joint representation of classification
and quality (IoU) estimation with shape (N, C), C is the number of
classes.
target (tuple([torch.Tensor])): Target category label with shape (N,)
and target quality label with shape (N,).
beta (float): The beta parameter for calculating the modulating factor.
Defaults to 2.0.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Loss tensor with shape (N,).
"""
assert (
len(target) == 2
), """target for QFL must be a tuple of two elements,
including category label and quality label, respectively"""
# label denotes the category id, score denotes the quality score
label, score = target #label:gt label,score:gt score(IOU),
# negatives are supervised by 0 quality score
#pred:预测的class score
pred_sigmoid = pred.sigmoid() #sigmoid:1/(1+e^-x)
scale_factor = pred_sigmoid
zerolabel = scale_factor.new_zeros(pred.shape) #全0
#label全为0时的qfl loss,即先把背景的loss填上
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits( #等价于sigmoid+binary entropy, 更稳定
pred, zerolabel, reduction="none"
) * scale_factor.pow(beta)
# FG cat_id: [0, num_classes -1], BG cat_id: num_classes
bg_class_ind = pred.size(1) #背景的下标
#label是前景的下标,注意这是gt label
pos = torch.nonzero((label >= 0) & (label < bg_class_ind), as_tuple=False).squeeze(
1
)
pos_label = label[pos].long() #取出下标对应的前景gt label
# positives are supervised by bbox quality (IoU) score
scale_factor = score[pos] - pred_sigmoid[pos, pos_label] #公式中的(y-sigma)
#在有前景的对应位置填上gfl的前景loss
loss[pos, pos_label] = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(
pred[pos, pos_label], score[pos], reduction="none"
) * scale_factor.abs().pow(beta) #公式中的QFL(sigma)不要负号
loss = loss.sum(dim=1, keepdim=False)
return loss
Distribute Focal Loss
再来说Distribution focal loss
一般来说,预测值x 和真实标签y 之间,是假设的Dirac delta分布,即
![]()
这表示预测值x 总有一个标签y与之对应。
那么将它与x相乘就能复原标签y.
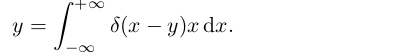
如果已经给出了y的范围,就能限制住积分的上下限。
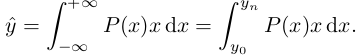
连续变离散(比如每间隔1取一次值)。

P(x)是网络输出经过softmax处理后的结果,但是P(x)可以有不同的分布,
公式(5) 中可以看到能得到y 的不同组合很多,例如下图
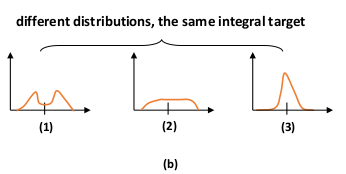
直观上来看,分布(3)得到标签y的准确性更高,
因此就推出 要把预测的P(x) 尽可能地在 y 处有较大的概率。
因此就取靠近y 的两个label,
y
i
y_{i}
yi 和
y
i
+
1
y_{i+1}
yi+1,
类似GFL公式,同时不需要考虑class imbalance, 所以只需取cross entropy的那一项:

看下它的代码
def distribution_focal_loss(pred, label):
r"""Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) is from `Generalized Focal Loss: Learning
Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection
<https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.04388>`_.
Args:
pred (torch.Tensor): Predicted general distribution of bounding boxes
(before softmax) with shape (N, n+1), n is the max value of the
integral set `{0, ..., n}` in paper.
label (torch.Tensor): Target distance label for bounding boxes with
shape (N,).
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Loss tensor with shape (N,).
"""
dis_left = label.long()
dis_right = dis_left + 1
weight_left = dis_right.float() - label
weight_right = label - dis_left.float()
loss = (
F.cross_entropy(pred, dis_left, reduction="none") * weight_left
+ F.cross_entropy(pred, dis_right, reduction="none") * weight_right
)
return loss