1. 凯撒加密算法
1.1 算法逻辑
根据一个固定偏移值(offset), 将字母向一个方向偏移, 进行加密.
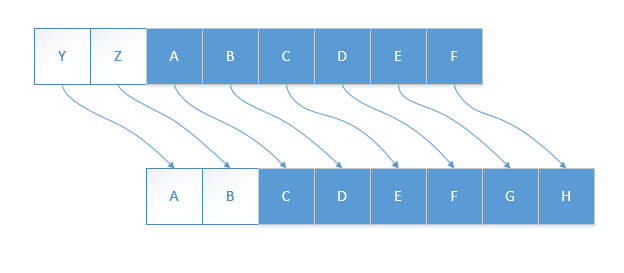
1.2 初步思路
- 获取明文(
plaintext) - 获取明文字符串的单独字符
- 进行字符值偏移
- 当偏移超出字母范围时, 回到第一个字母处继续偏移.
- 得到密文(
ciphertext)
1.3 初步编程
/*
凯撒密码:
偏移量
A(65)~Z(90)
a(97)~z(122)
方法1: 但偏移量超过范围时, 返回到最初循环
方法二:进行数组偏移(加密)
方法三:进行数组回位(解密)
*/
public class Task01_Caesar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输入明文
String plaintext = "I told it was a lie. ";
// 明文加密
String password = leadingPlaintext(plaintext, 10);
System.out.println(password);
// 密文解密
String plaintext1 = leadingPassword(password, 10);
System.out.println(plaintext1);
}
// 凯撒密码加密
public static String leadingPlaintext(String plaintext, int leadingNum) {
String password = "";
// 将明文转化成字符数组
char[] charPassword = plaintext.toCharArray();
// 进行加密操作
int[] intPassword = new int[charPassword.length];
for (int i = 0; i < charPassword.length; i++) {
// 将字符数组转化成字符码数组
intPassword[i] = (int)charPassword[i];
// 字符码数组偏移&范围限定
intPassword[i] = limitLetter(intPassword[i], intPassword[i]+leadingNum);
// 偏移字符码数组重新输出为字符数组
charPassword[i] = (char)intPassword[i];
// 将字符数组转化成字符串
password = String.valueOf(charPassword);
}
return password;
}
// 凯撒密码解密
public static String leadingPassword(String password, int leadingNum) {
String plaintext = "";
// 将密码转化成字符数组
char[] charPassword = password.toCharArray();
// 进行解密操作
int[] intPassword = new int[charPassword.length];
for (int i = 0; i < charPassword.length; i++) {
// 将字符数组转化成字符码数组
intPassword[i] = (int)charPassword[i];
// 字符码数组偏移&范围限定
intPassword[i] = limitLetter(intPassword[i], intPassword[i]-leadingNum);
// 偏移字符码数组重新输出为字符数组
charPassword[i] = (char)intPassword[i];
// 将字符数组转化成字符串
plaintext = String.valueOf(charPassword);
}
return plaintext;
}
// 进行范围限定
public static int limitArea(int num, int min, int max) {
int area = 26; // 限定范围区间
while (num < min || num > max) {
if (num < min) {
num += area;
} else if (num > max) {
num -= area;
}
}
return num;
}
// 进行字母范围限定
public static int limitLetter(int originNum, int leadingNum) {
if (originNum >=65 && originNum <= 90) {
leadingNum = limitArea(leadingNum, 65, 90);
} else if (originNum >= 97 && originNum <= 122) {
leadingNum = limitArea(leadingNum, 97, 122);
}
return leadingNum;
}
}
我的思路是:
- 首先将字符串转化为字符数组
- 字符数组可以转化为整型数组
- 对数组进行偏移
- 对偏移的数组进行校正
- 将数组重新返回为字符串
然后我使用了4个方法, 第一个方法(leadingPlaintext)和第二个方法(leadingPassword)进行数组偏移, 其中调用了第三, 四个方法进行偏移数组校正.
1.4 查询算法
public class Task02_Caesar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String plaintext = "I'm a robot. ";
String pwd = caesar(plaintext, 5);
String str = caesar(pwd, -5);
System.out.println(pwd);
System.out.println(str);
}
public static String caesar(String text, int offset) {
String cipher = "";
for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); i++) {
// 迭代字符
char c = text.charAt(i);
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') { // 若当前选中字符为大写字母
c += (offset % 26);
if (c < 'A') {
c += 26;
} else if (c > 'Z') {
c -= 26;
}
} else if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') { // 若当前选中字符为小写字母
c += (offset % 26);
if (c < 'a') {
c += 26;
} else if (c > 'z') {
c -= 26;
}
}
cipher += c;
}
return cipher;
}
}
1.5 思路重置
- 不需要将字符串转化为字符数组, 可以通过
String.charAt()方法在for循环里直接获取单独的字符. 不需要使用String.toCharArray()方法将字符串转化为字符数组. - 因为字符char本质其实是数字, 所以可以直接使用char进行逻辑判断, 不需要将其转换为数字码点再判断.
-
当需要框定一个数的范围, 进行A-B循环时, 可以通过取余操作进行限定.
b = (b % 26)+1(限定范围1~26的数字)
1.6 A-B循环
/*
* description: 1~26循环数输出
*/
public class Task03_ABLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
System.out.print(i%26+1+" ");
if (i%26+1 == 26) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}