spi是原生java的组件,通过META-INF/services目录进行注册,通过ServiceLoader进行加载,一般可以用在组件开发中,你在公用组件中封装好逻辑,将个性化的部分抽象出一个接口,接口通过spi的方式进行加载,在外部开发人员引用你的组件之后,通过实现接口来扩展个性化的功能,再通过META-INF/services对实现类进行注册。
组件端
先定义一个公开的接口
public interface SpiHello {
void printHello();
}
一个公开的组件
public static void print() {
InputStream resource = Tool.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("licence.txt");
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int bufSize = 1024;
byte[] buffer = new byte[bufSize];
int len = 0;
while (true) {
try {
if (!(-1 != (len = resource.read(buffer, 0, bufSize))))
break;
}
catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
bos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
ServiceLoader<SpiHello> spiHellos = ServiceLoader.load(SpiHello.class);
Iterator<SpiHello> iterable = spiHellos.iterator();
while (iterable.hasNext()) {
iterable.next().printHello();
}
System.out.println("value=" + bos.toString());
}
在开发人员使用时,需要注册他的实现类
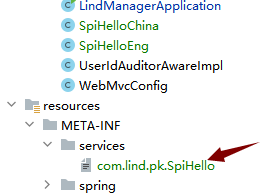
com.lind.pk.Tool.print();
结果
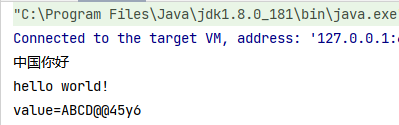
注意,在组件内部读文件时,需要采用文件流的方式,否则,在调用地将出现无法加载的问题