介绍
数据绑定是一种把用户界面元素(控件)的属性绑定到特定对象上面并使其同步的机制,使开发人员免于编写同步视图模型和视图的逻辑。
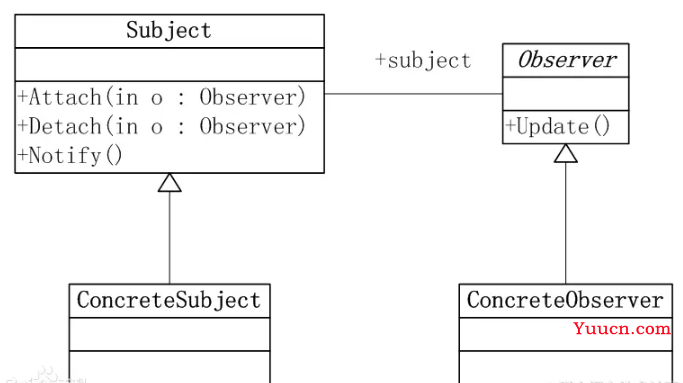
观察者模式又称为发布-订阅模式,定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当它本身的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并被自动更新。比如用户界面可以作为一个观察者,业务数据是被观察者,用户界面观察业务数据的变化,发现数据变化后,就同步显示在界面上。这样可以确保界面和数据之间划清界限,假定应用程序的需求发生变化,需要修改界面的表现,只需要重新构建一个用户界面,业务数据不需要发生变化。有以下几个角色:
- 抽象主题(Subject):提供一个接口,把所有观察者对象的引用保存到一个集合里,可以增加和删除观察者对象。
- 具体主题(Concrete Subject):将有关状态信息存入观察者对象,在本身的内部状态改变时,给所有登记过的观察者发出通知。
- 抽象观察者(Observer):为所有的具体观察者定义一个接口,在得到主题通知时更新自己。
- 具体观察者(Concrete Observer):实现更新接口。
Vue2 和 Vue3 的数据绑定都是观察者模式的实现,前者使用 Object.defineProperty,后者使用的是 Proxy。
有以下 HTML:
<div id="app">
<input type="radio" name="hello" id="hello" value="hello" v-model="title">
<label for="hello">hello</label>
<input type="radio" name="hello" id="hello2" value="hello2" v-model="title">
<label for="hello2">hello2</label>
<div v-bind="title"></div>
<input v-model="content">
<select v-model="content">
<option>world</option>
<option>world1</option>
<option>world2</option>
</select>
<div v-bind="content"></div>
<input type="checkbox" id="hobby1" value="hobby1" v-model="hobby">
<label for="hobby1">hobby1</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="hobby2" value="hobby2" v-model="hobby">
<label for="hobby2">hobby2</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="hobby3" value="hobby3" v-model="hobby">
<label for="hobby3">hobby3</label>
<br>
{{ hobby }}
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
title: 'hello',
content: 'world2',
hobby: ['hobby2'],
}
});
</script>
下面使用两种方法进行简单实现上面的双向绑定。
Object.defineProperty
语法:
Object.defineProperty(obj, prop, descriptor)
- obj:要定义属性的对象。
- prop:要定义或修改的属性的名称或 Symbol 。
- descriptor:要定义或修改的属性描述符。
- 返回值:被传递给函数的对象。
首先定义一个观察者构造函数,并实现得到主题通知时更新自己的逻辑。第一行将当前观察者绑定到函数属性上面,是为了避免全局作用域变量。
function Observer(vm, node, name, nodeType) {
// 构造函数被调用时,将当前对象绑定到函数属性上面,接下来触发 getter 时使用
Observer.target = this;
this.update = () => {
// 这里 vm[name] 读取操作会触发 getter
if (node.type === 'radio') node.checked = node.value === vm[name];
else if (node.type !== 'checkbox') node[nodeType] = vm[name];
};
this.update();
Observer.target = null; // 设置为空,避免首次触发get后重复添加
}
然后定义 Vue 构造函数,遍历 options.data 对象,为每个属性都生成一个主题(包含当前属性的观察者数组),然后使用 Object.defineProperty 劫持属性的读取和写入操作,在首次读取时添加一个对应的观察者对象,为了避免后面读取操作重复添加,在观察者构造函数里面首次更新操作完成后设置了空。
function Vue(options) {
const obj = options.data;
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => {
const subjects = [];
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
get() {
if (Observer.target) subjects.push(Observer.target);
return obj[key];
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal === obj[key]) return;
obj[key] = newVal;
// 给当前主题所有登记过的观察者发出通知
subjects.forEach(observer => observer.update());
}
});
});
}
接下来就是遍历根节点(这里只遍历一层),根据子节点的类型,传入不同的参数调用 Observer 构造函数,然后首次更新视图,并触发 getter 将观察者对象都对应放到 options.data 的每个属性主题中,然后按属性类型添加不同的事件监听。
const el = document.querySelector(options.el);
el.childNodes.forEach(node => {
if (node.nodeType === 1) {
if (node.hasAttribute('v-model')) {
const name = node.getAttribute('v-model');
if (node.type === 'checkbox') node.checked = this[name].includes(node.value);
const eventType = (node.tagName === 'INPUT' && node.type === 'text') || node.tagName == 'TEXTAREA' ? 'input' : 'change';
node.addEventListener(eventType, e => {
// 这里 this[name] 写入操作会触发 setter
if (node.type === 'checkbox') {
if (node.checked) this[name] = this[name].concat(node.value).sort();
else this[name] = this[name].filter(v => v !== node.value).sort();
} else this[name] = node.value;
});
new Observer(this, node, name, 'value');
} else if (node.hasAttribute('v-bind')) {
new Observer(this, node, node.getAttribute('v-bind'), 'textContent');
}
} else if (node.nodeType === 3 && /\{\{(.*)\}\}/.test(node.nodeValue)) {
new Observer(this, node, RegExp.$1.trim(), 'nodeValue');
}
});
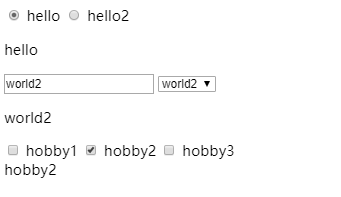
<div id="app">
<input type="radio" name="hello" id="hello" value="hello" v-model="title">
<label for="hello">hello</label>
<input type="radio" name="hello" id="hello2" value="hello2" v-model="title">
<label for="hello2">hello2</label>
<p v-bind="title"></p>
<input v-model="content">
<select v-model="content">
<option>world</option>
<option>world1</option>
<option>world2</option>
</select>
<p v-bind="content"></p>
<input type="checkbox" id="hobby1" value="hobby1" v-model="hobby">
<label for="hobby1">hobby1</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="hobby2" value="hobby2" v-model="hobby">
<label for="hobby2">hobby2</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="hobby3" value="hobby3" v-model="hobby">
<label for="hobby3">hobby3</label>
<br>
{{ hobby }}
</div>
运行:
Proxy
语法:
new Proxy(target, handler)
- target:被代理的对象
- handler:被代理对象上的自定义行为,和 Reflect 对象的所有静态方法对应,所以可以在其中调用对应的 Reflect 方法,完成默认行为,然后再部署额外的功能。
第一步定义观察者构造函数,和 Object.defineProperty 方式相同。
第二步也是定义 Vue 构造函数,不同的是使用 Proxy 劫持属性的读取和写入操作,不需要为 options.data 对象每个属性都添加主题了。其他和 Object.defineProperty 方式相同。
function Vue(options) {
const subjects = [];
this.proxy = new Proxy(options.data, {
get(obj, key, receiver) {
if (Observer.target) subjects.push(Observer.target);
const value = Reflect.get(...arguments);
return value;
},
set(obj, key, value, receiver) {
if (value === obj[key]) return;
const result = Reflect.set(...arguments);
subjects.forEach(observer => observer.update());
return result;
}
});
}
第三步遍历根节点,触发 getter 将观察者对象都放到主题的数组中,然后添加事件监听时,要触发 Proxy 的写入操作,而不是原对象。
const el = document.querySelector(options.el);
el.childNodes.forEach(node => {
if (node.nodeType === 1) {
if (node.hasAttribute('v-model')) {
const name = node.getAttribute('v-model');
if (node.type === 'checkbox') node.checked = this.proxy[name].includes(node.value);
const eventType = (node.tagName === 'INPUT' && node.type === 'text') || node.tagName == 'TEXTAREA' ? 'input' : 'change';
node.addEventListener(eventType, e => {
// 这里 this.proxy[name] 写入操作会触发 setter
if (node.type === 'checkbox') {
let value = this.proxy[name];
if (node.checked) {
this.proxy[name] = value.concat(node.value).sort();
} else this.proxy[name] = value.filter(v => v !== node.value).sort();
} else this.proxy[name] = node.value;
});
new Observer(this.proxy, node, name, 'value');
} else if (node.hasAttribute('v-bind')) {
new Observer(this.proxy, node, node.getAttribute('v-bind'), 'textContent');
}
} else if (node.nodeType === 3 && /\{\{(.*)\}\}/.test(node.nodeValue)) {
new Observer(this.proxy, node, RegExp.$1.trim(), 'nodeValue');
}
});
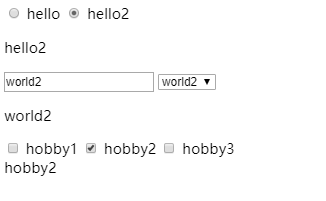
<div id="app">
<input type="radio" name="hello" id="hello" value="hello" v-model="title">
<label for="hello">hello</label>
<input type="radio" name="hello" id="hello2" value="hello2" v-model="title">
<label for="hello2">hello2</label>
<p v-bind="title"></p>
<input v-model="content">
<select v-model="content">
<option>world</option>
<option>world1</option>
<option>world2</option>
</select>
<p v-bind="content"></p>
<input type="checkbox" id="hobby1" value="hobby1" v-model="hobby">
<label for="hobby1">hobby1</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="hobby2" value="hobby2" v-model="hobby">
<label for="hobby2">hobby2</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="hobby3" value="hobby3" v-model="hobby">
<label for="hobby3">hobby3</label>
<br>
{{ hobby }}
</div>
运行:
到此这篇关于Vue2 与 Vue3 的数据绑定原理及实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Vue数据绑定内容请搜索本站以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持本站!